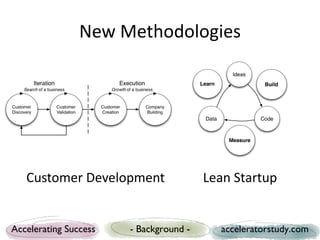
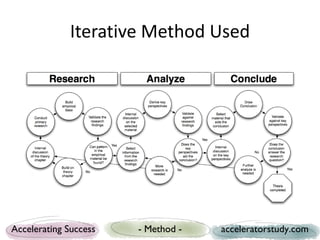
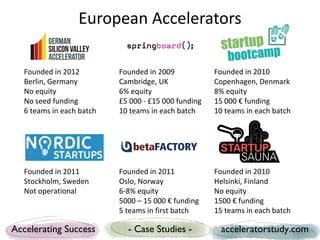
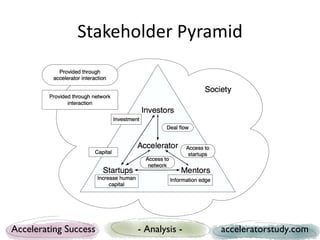
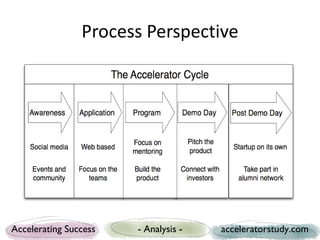
The document presents a study on seed accelerators, including their defining characteristics and operational models. It emphasizes the role of accelerators in supporting startups through mentorship, funding, and structured programs while analyzing various accelerators from the US and Europe. Key findings reveal the importance of connecting stakeholders, such as mentors, investors, and startups, through a defined process that fosters innovation and job creation.