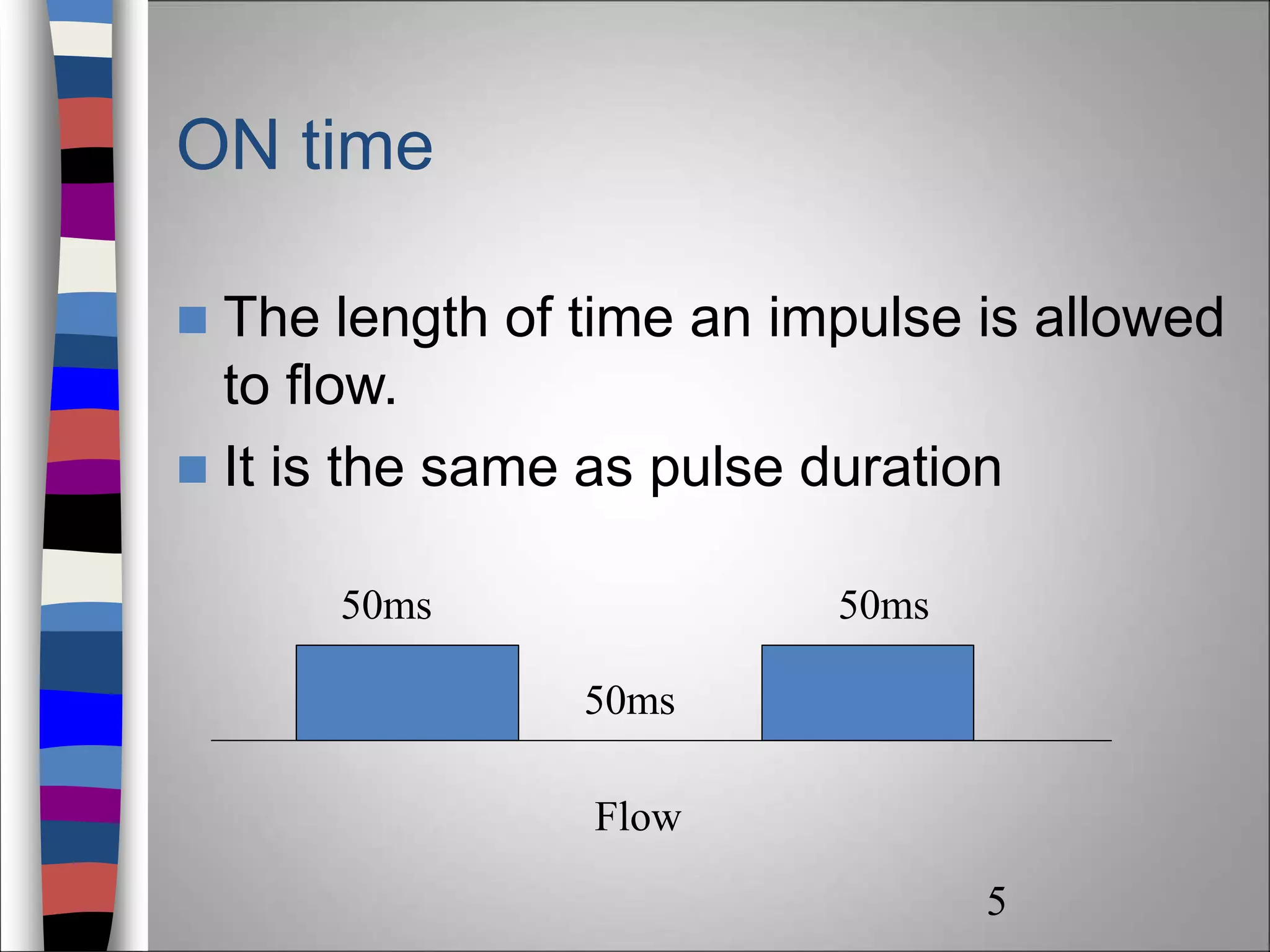
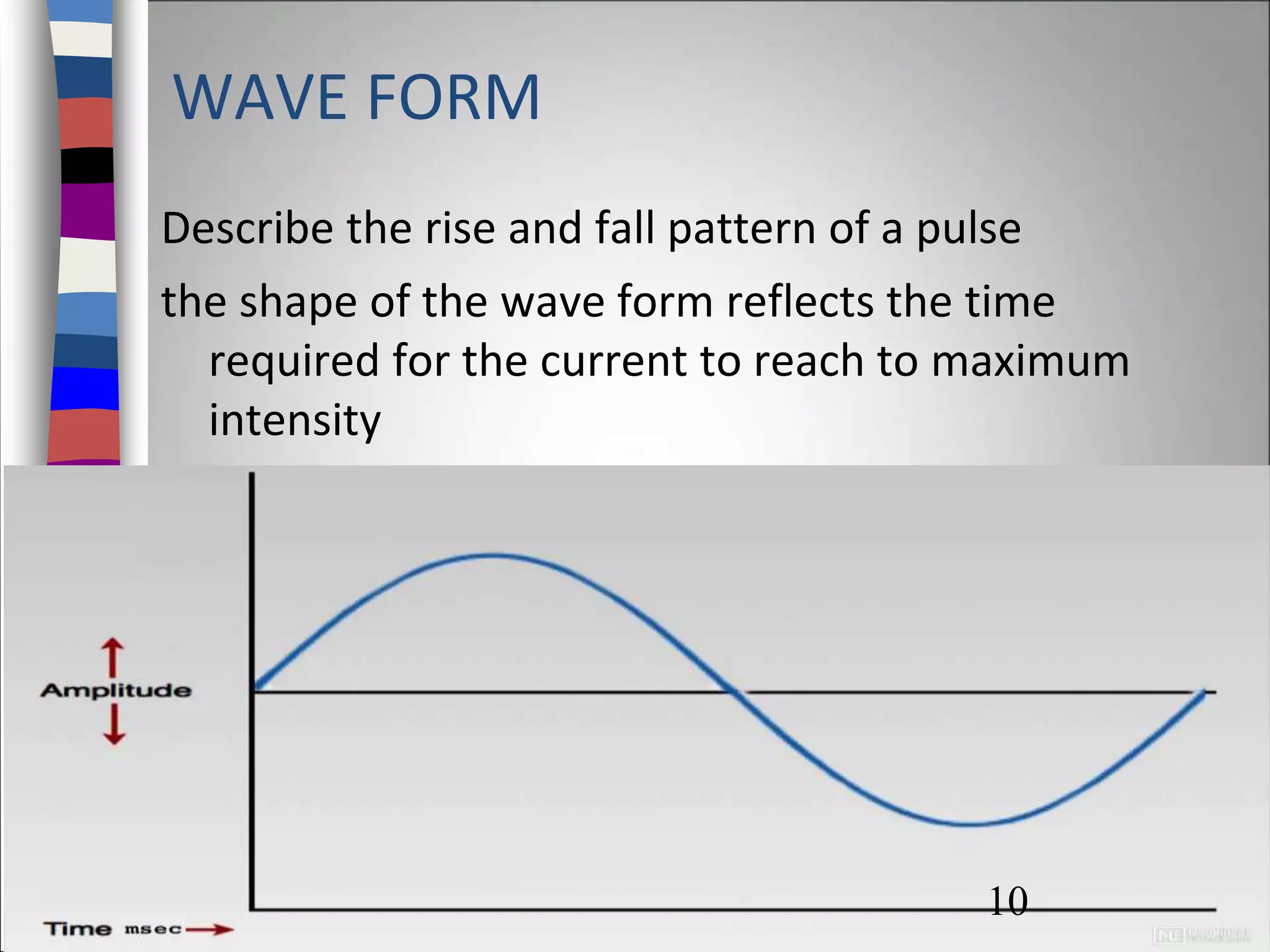
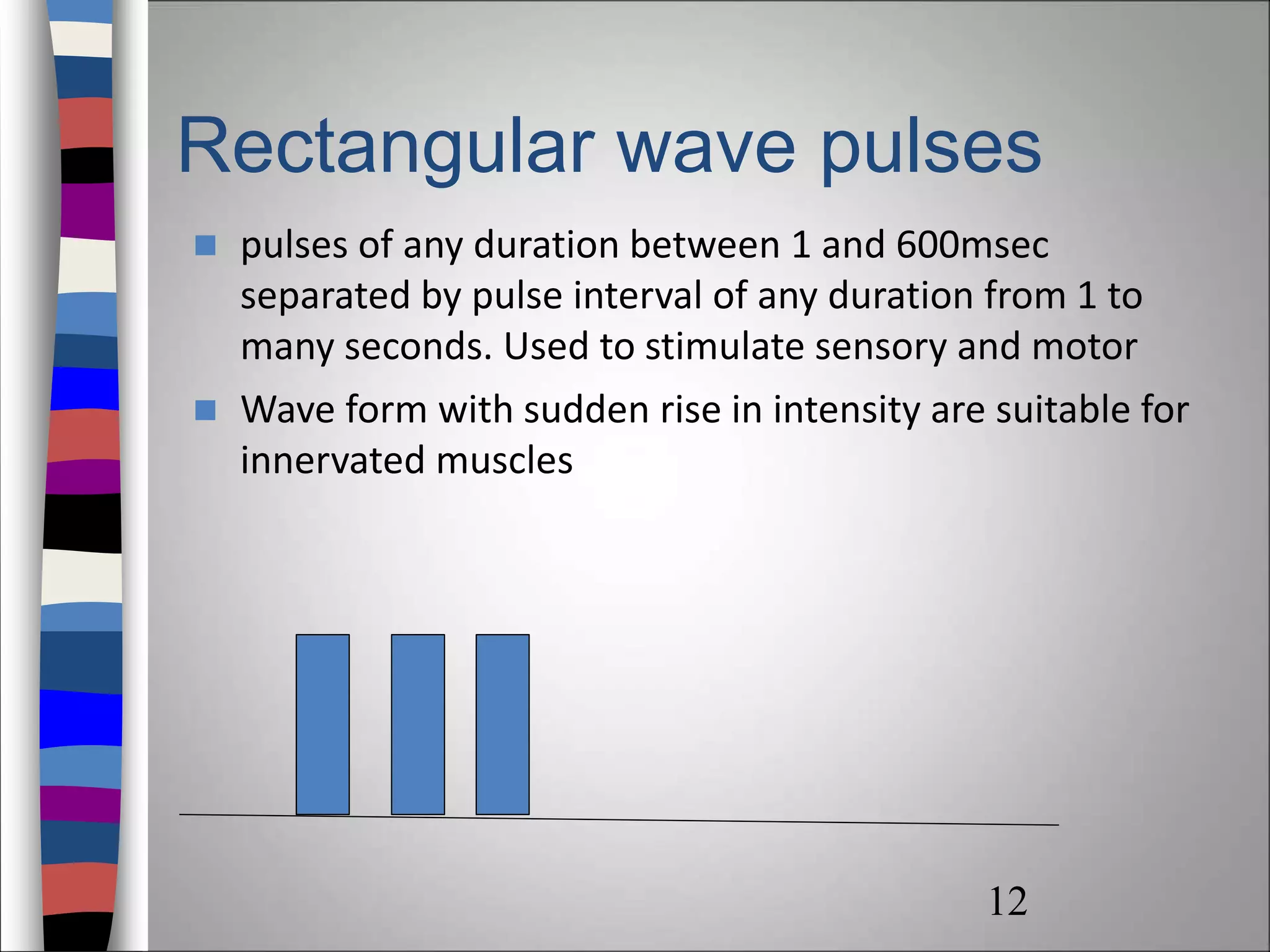
Interrupted direct current (IDC) is a pulsing current used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes, characterized by varying pulse durations, waveforms, and electrical properties. IDC can stimulate sensory and motor nerves, producing different physiological effects, including muscle contractions and skin responses. Proper application techniques and consideration of contraindications are essential to ensure safe and effective treatment.