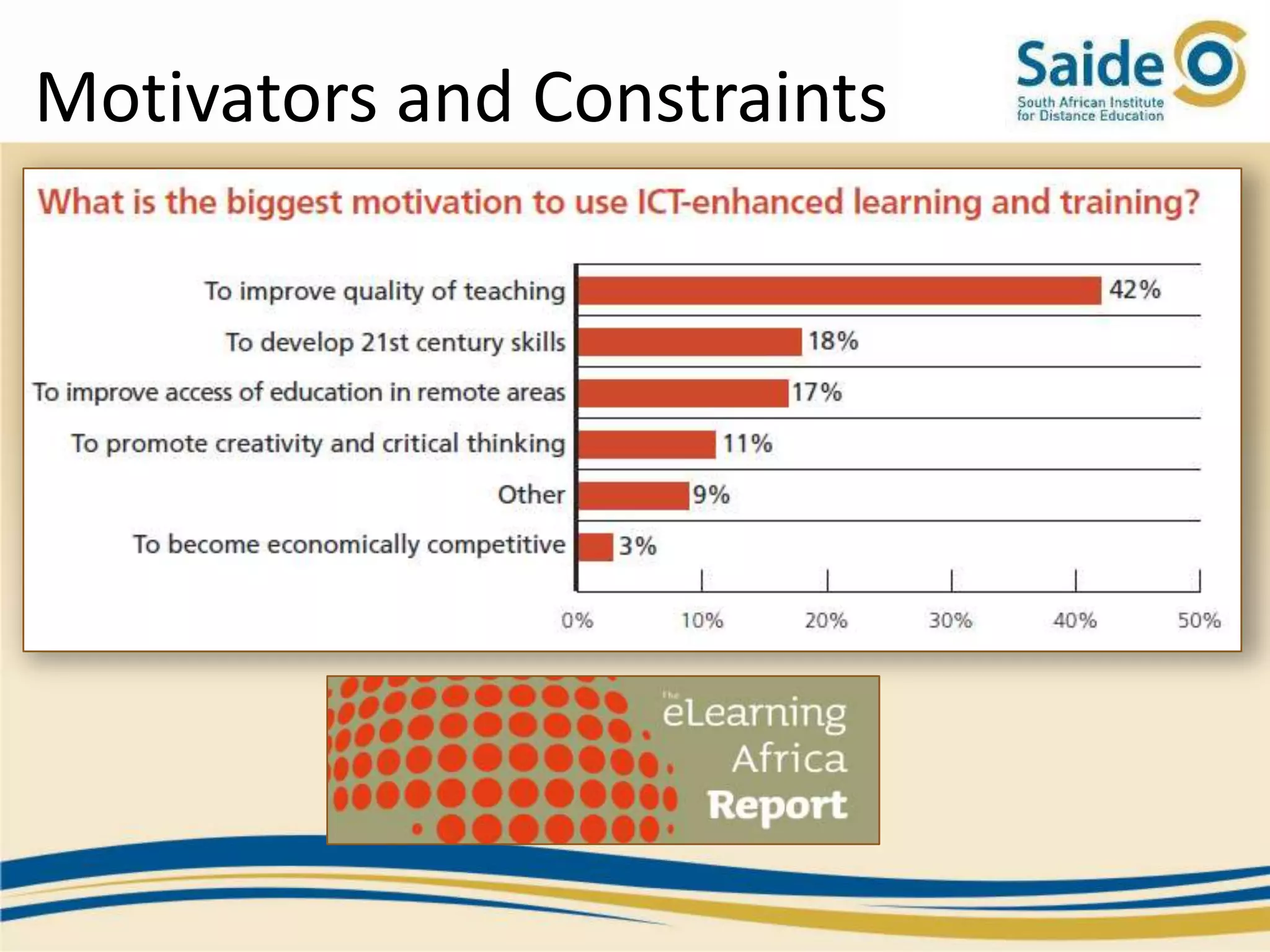
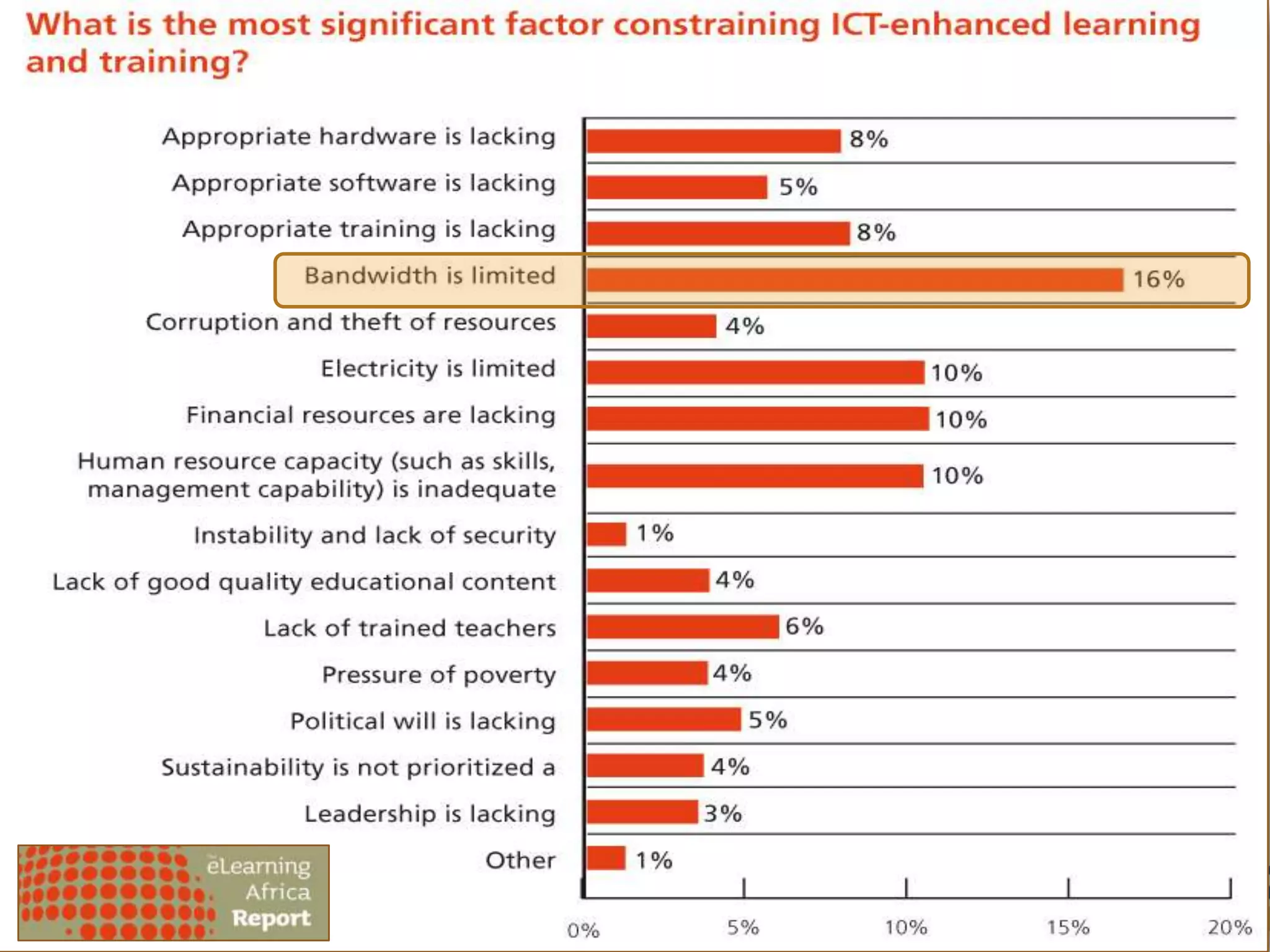
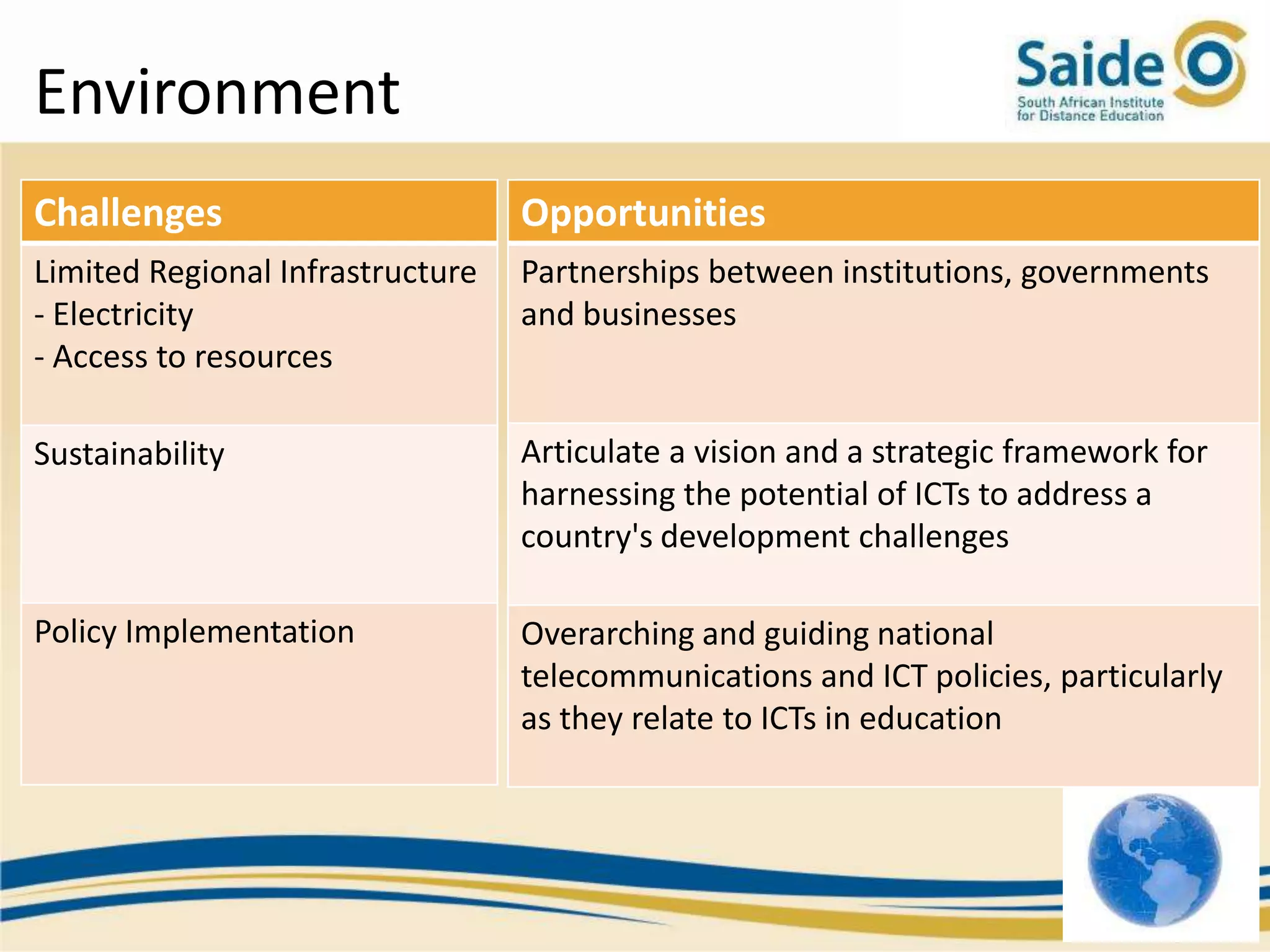
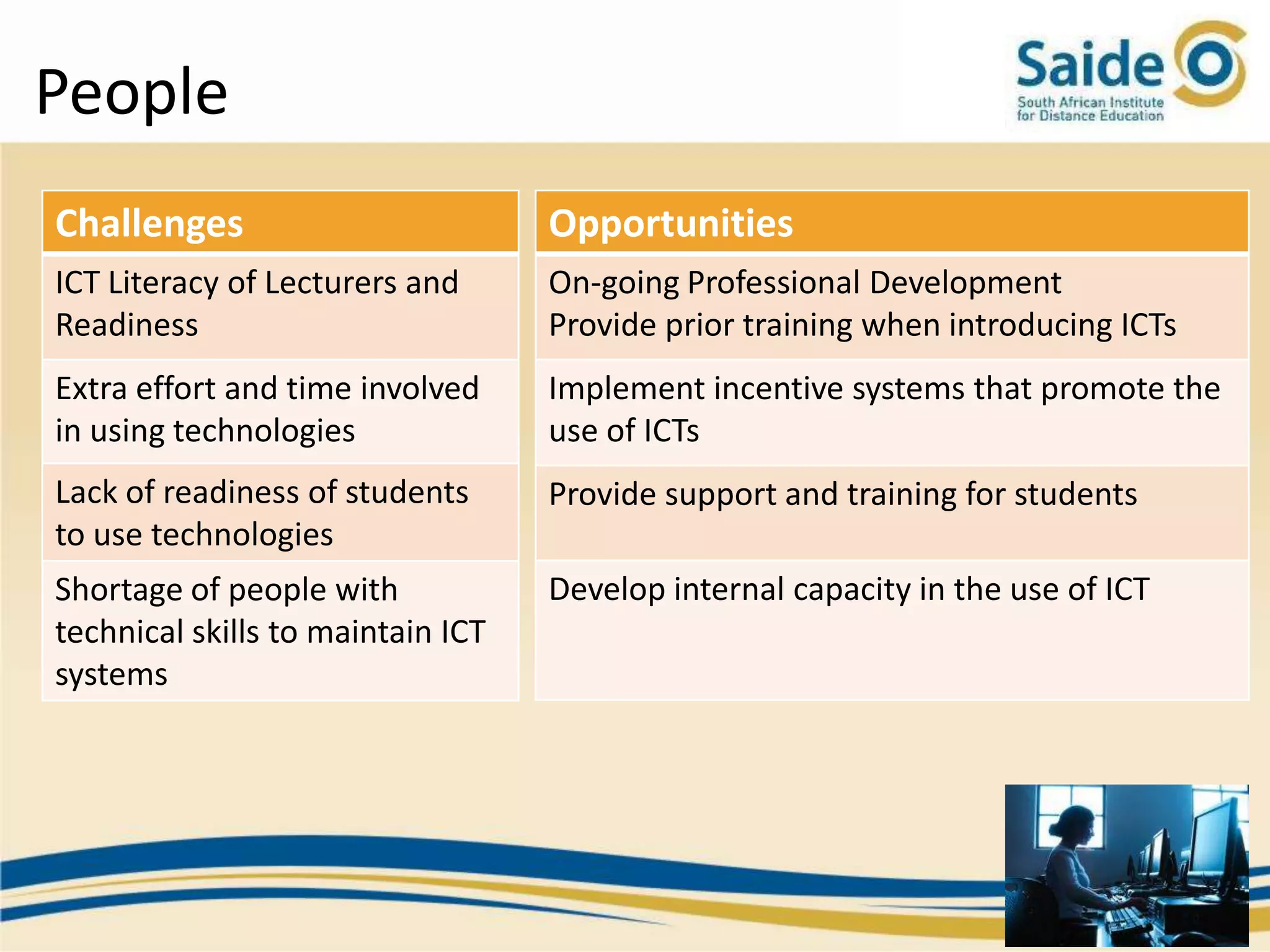
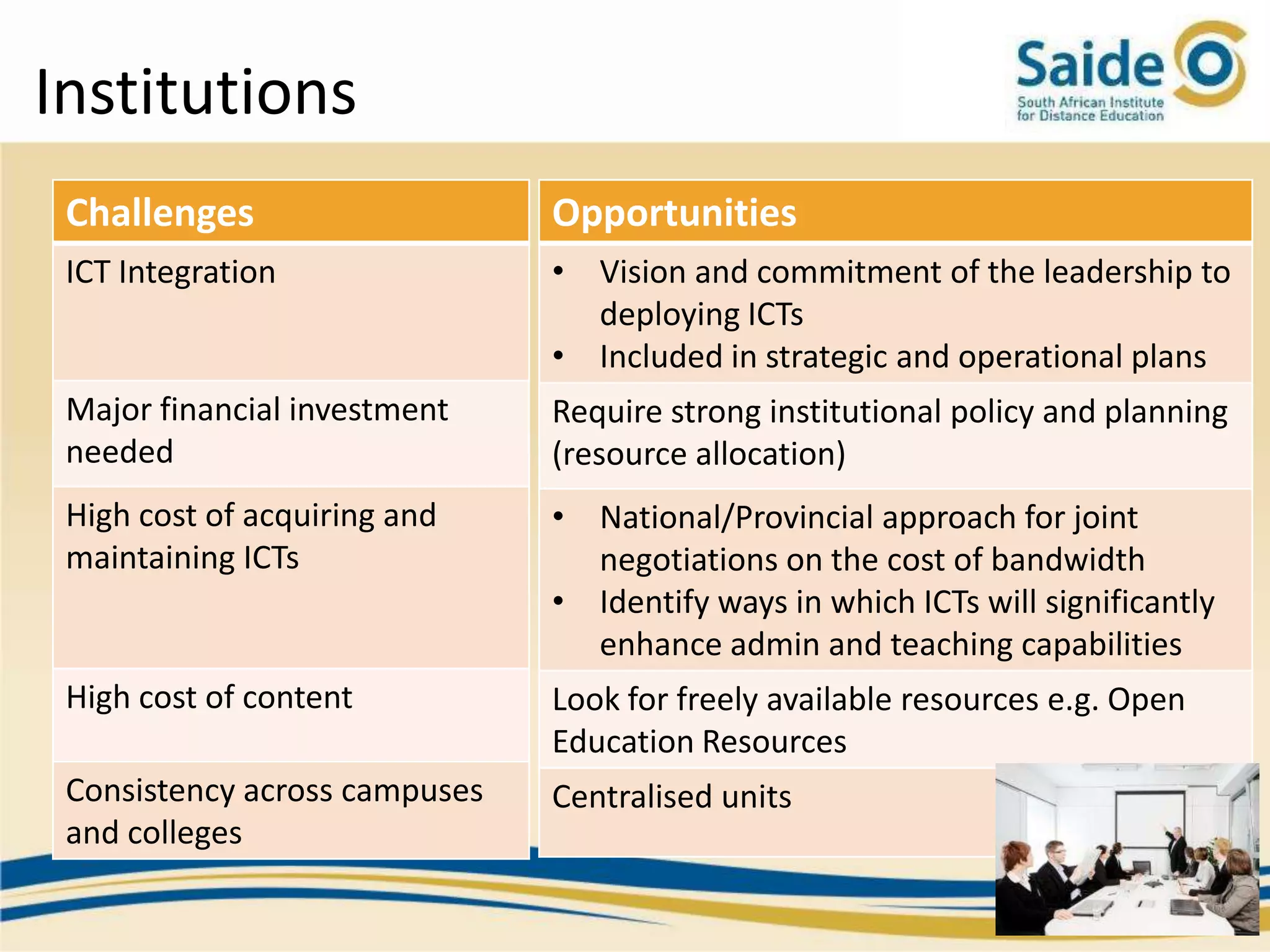
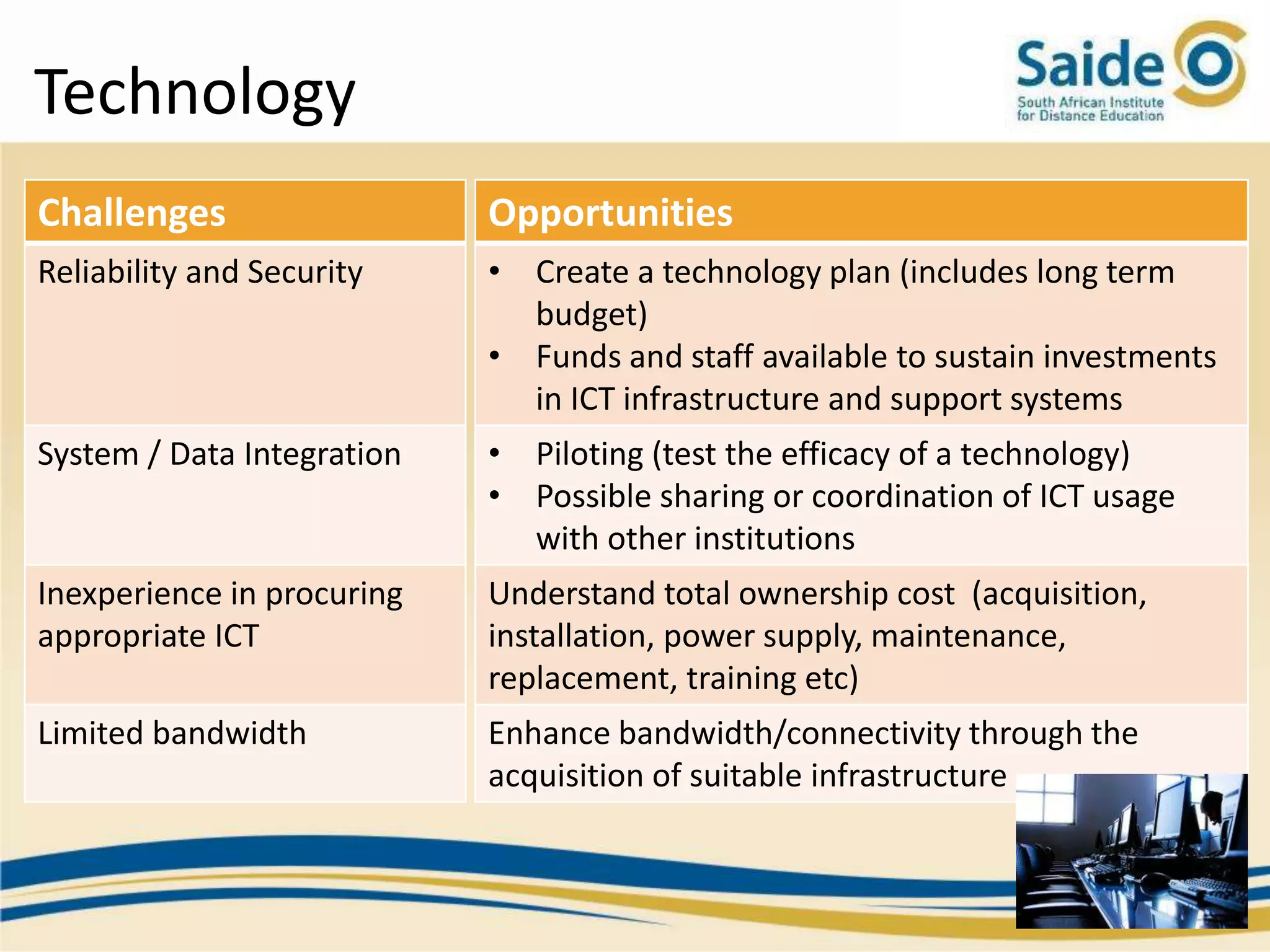
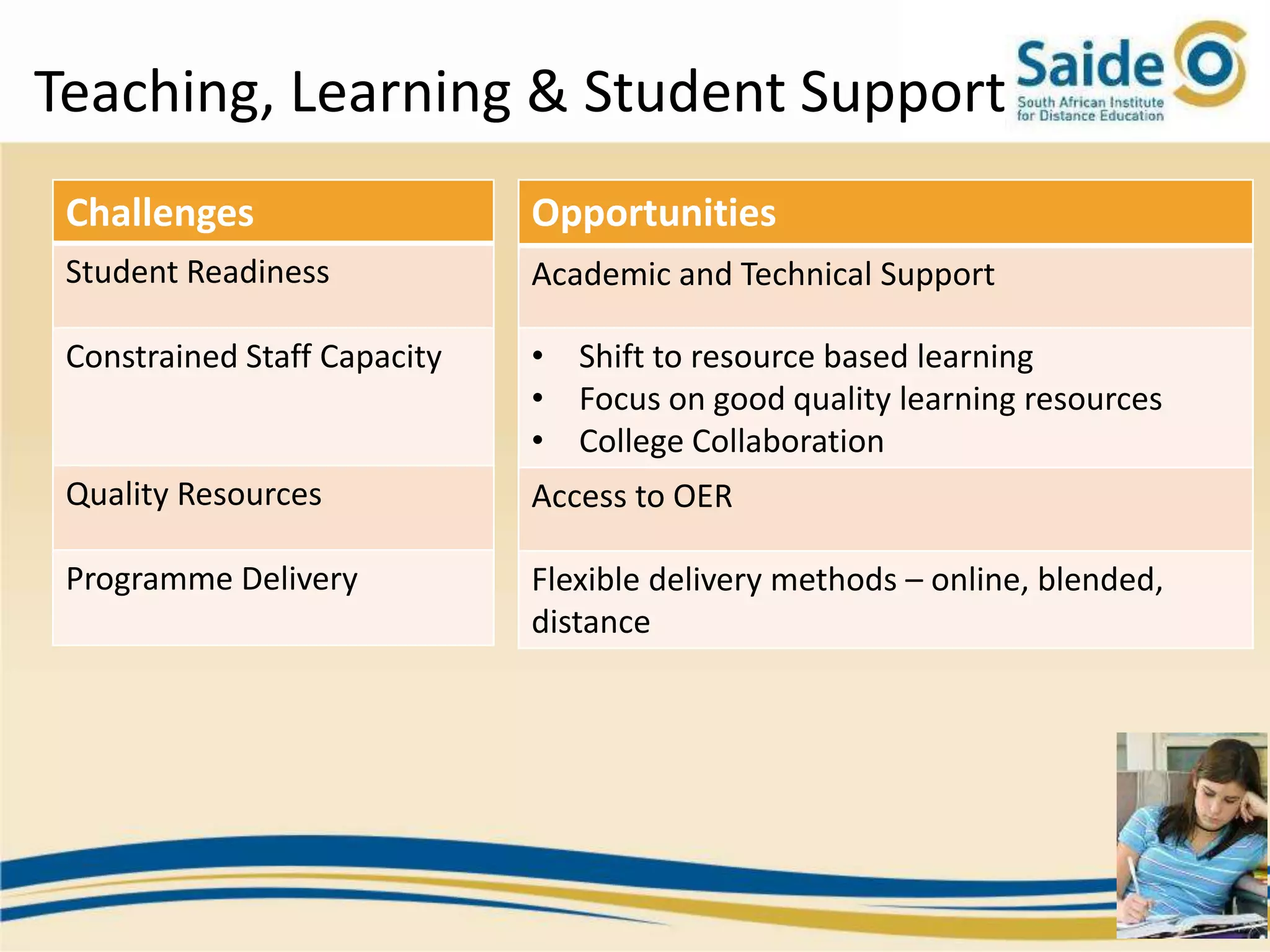
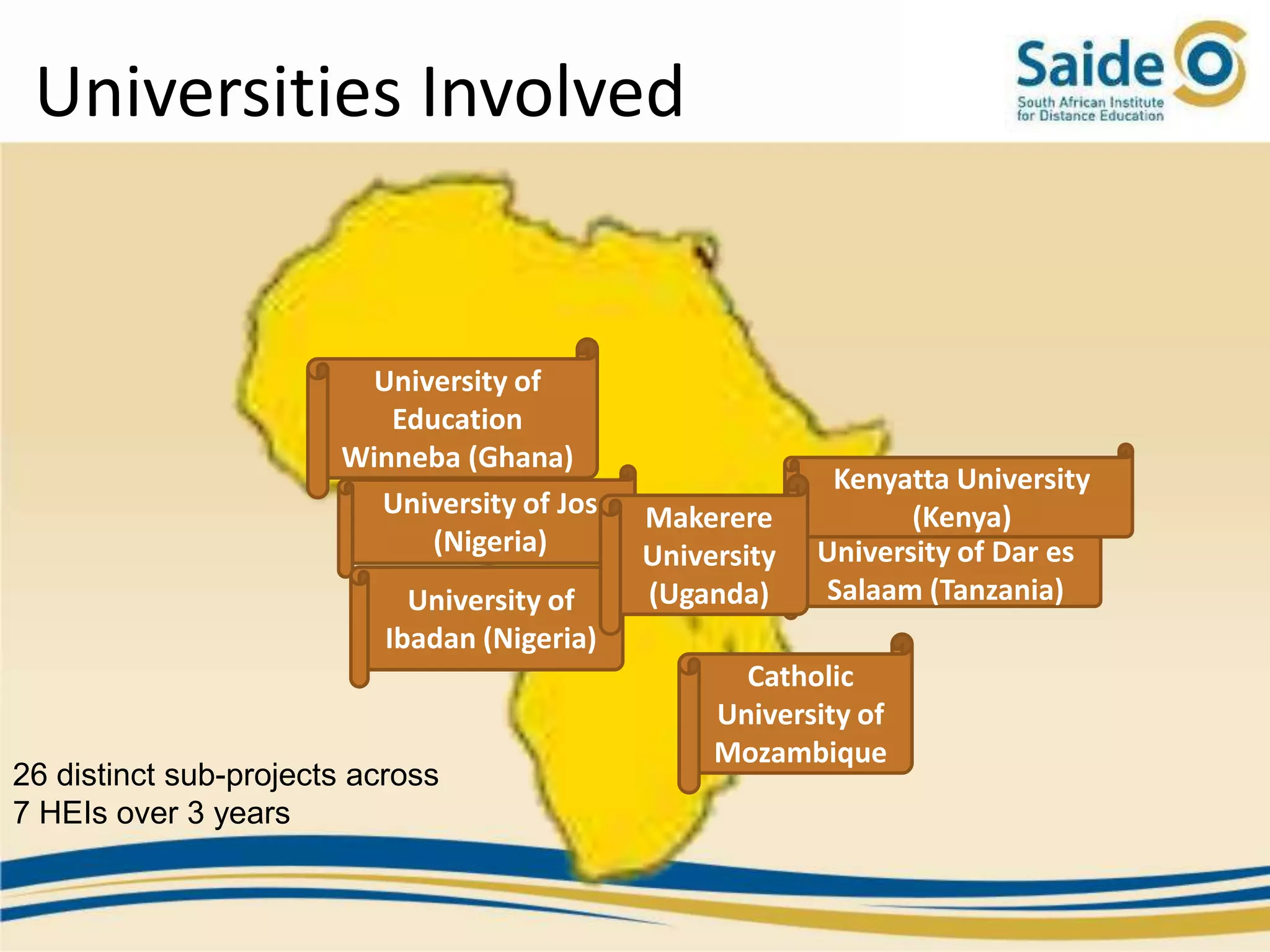
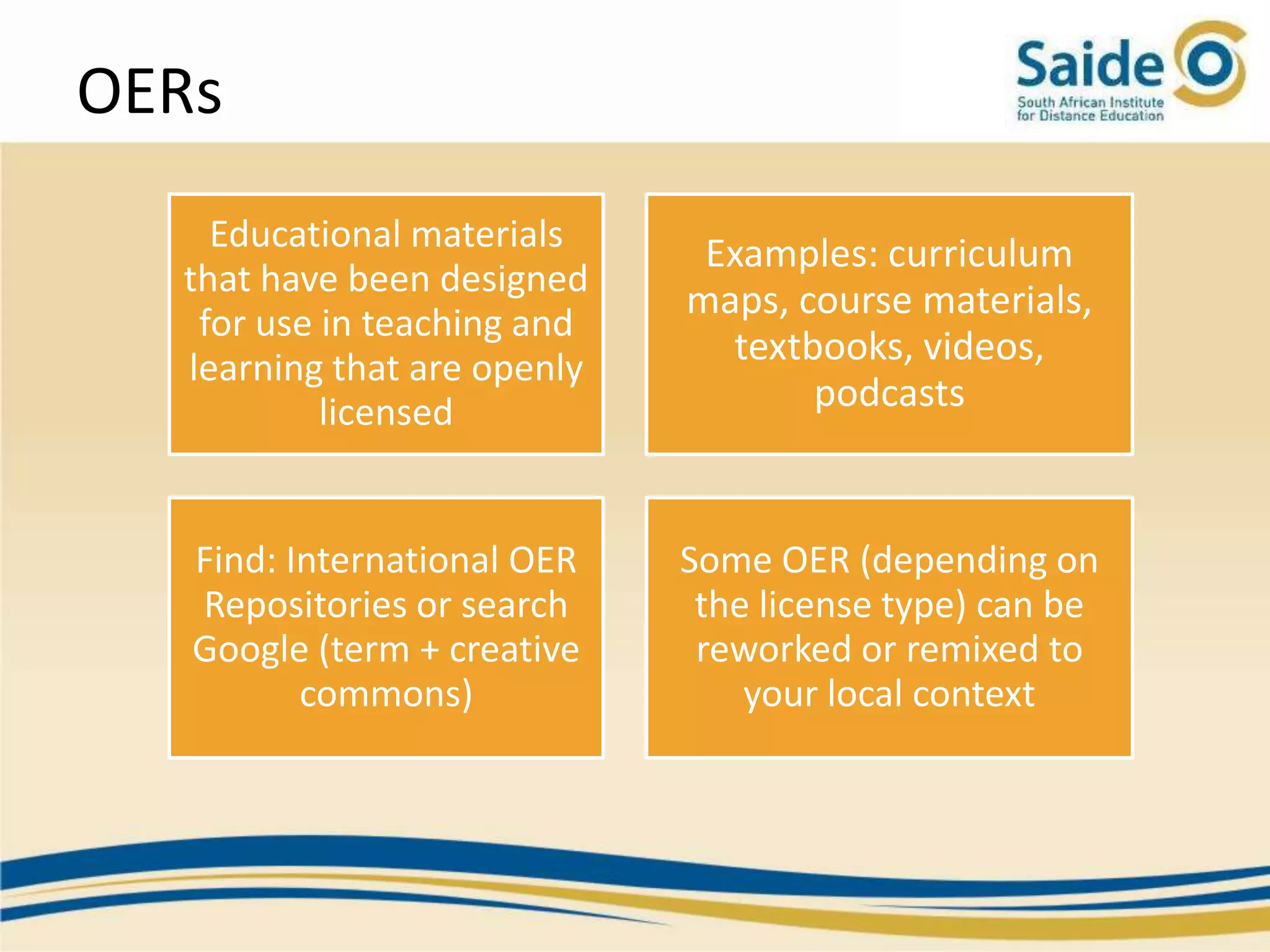
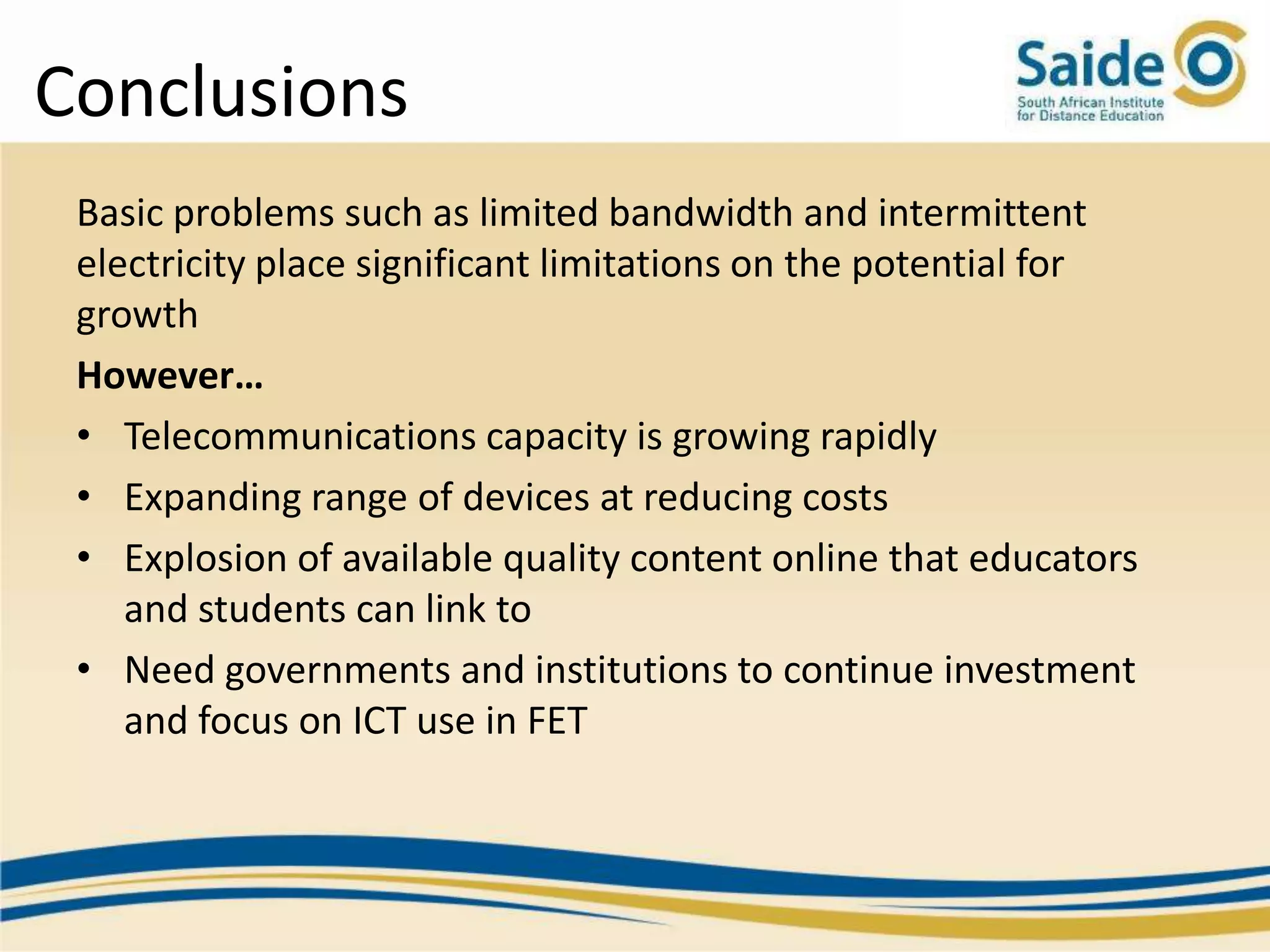
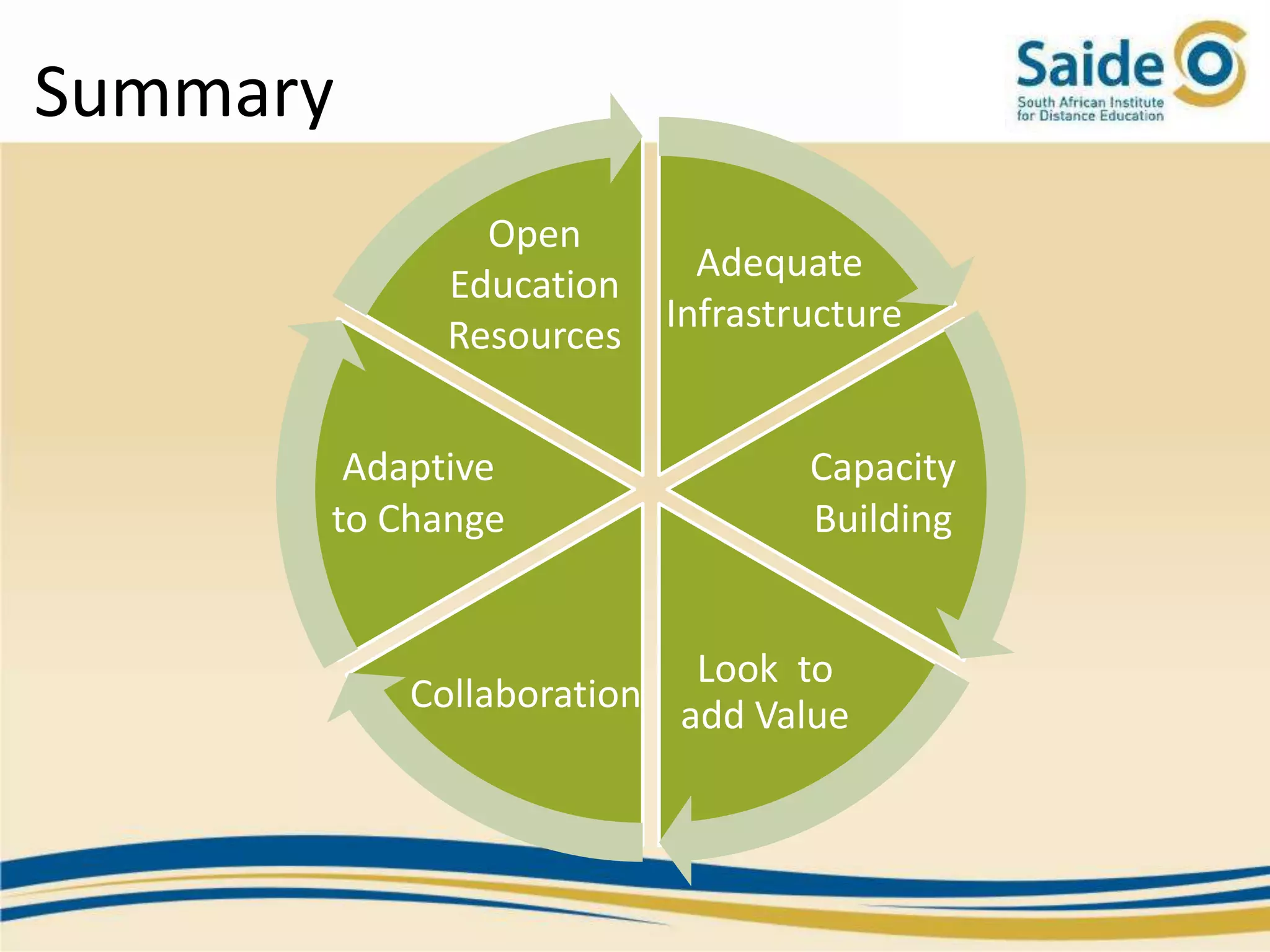
This document summarizes a presentation on integrating information and communication technologies (ICT) into teaching and learning in South African Further Education and Training (FET) colleges. It discusses the context and challenges of ICT integration, including limited infrastructure, financial constraints, and lack of digital skills. It also highlights opportunities such as partnerships, open educational resources, and collaborative projects. The presentation concludes by describing a case study of an initiative that supported several African universities in developing ICT strategies through capacity building, policy development, and resource sharing. Key lessons included the need for institutional buy-in, strategic planning, and inter-institutional collaboration to promote sustainable ICT integration.