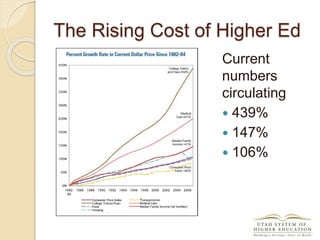
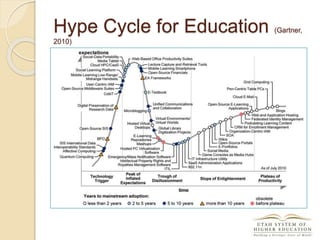
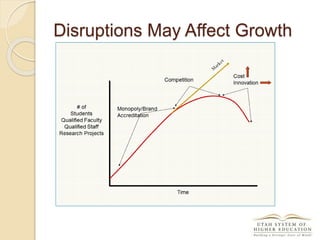
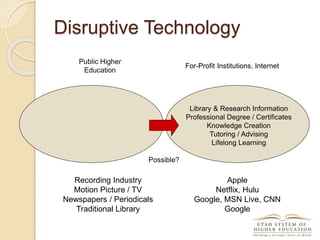
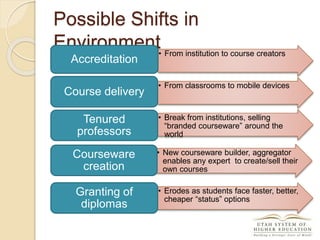
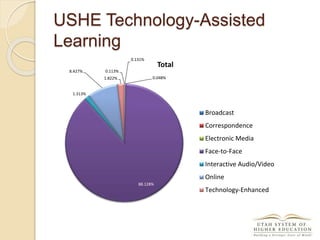
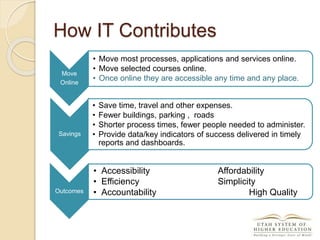
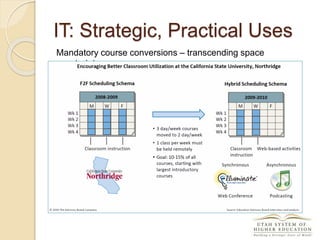
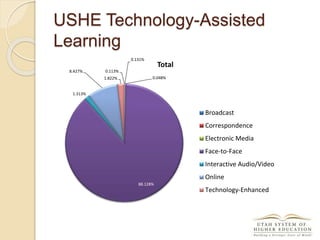
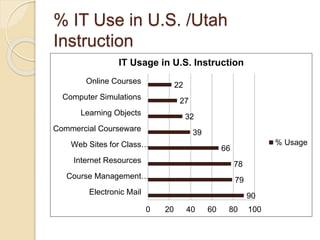
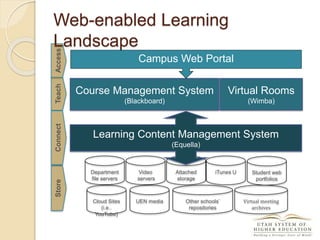
The document discusses the financial unsustainability of the current higher education model and highlights the transformative potential of technology in increasing accessibility and quality. It emphasizes the necessity for institutions to adapt to technological advancements and outlines recommendations for improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Strategies include online course offerings, investment in digital resources, and collaboration on technology-enhanced learning initiatives.