The document discusses several topics related to integrating information and communication technologies (ICT) into the South African education system including:
1) The benefits of using ICT to provide access to knowledge and improve education for all.
2) Principles for using ICT in education such as improving access to resources, communication, and opportunities to excel.
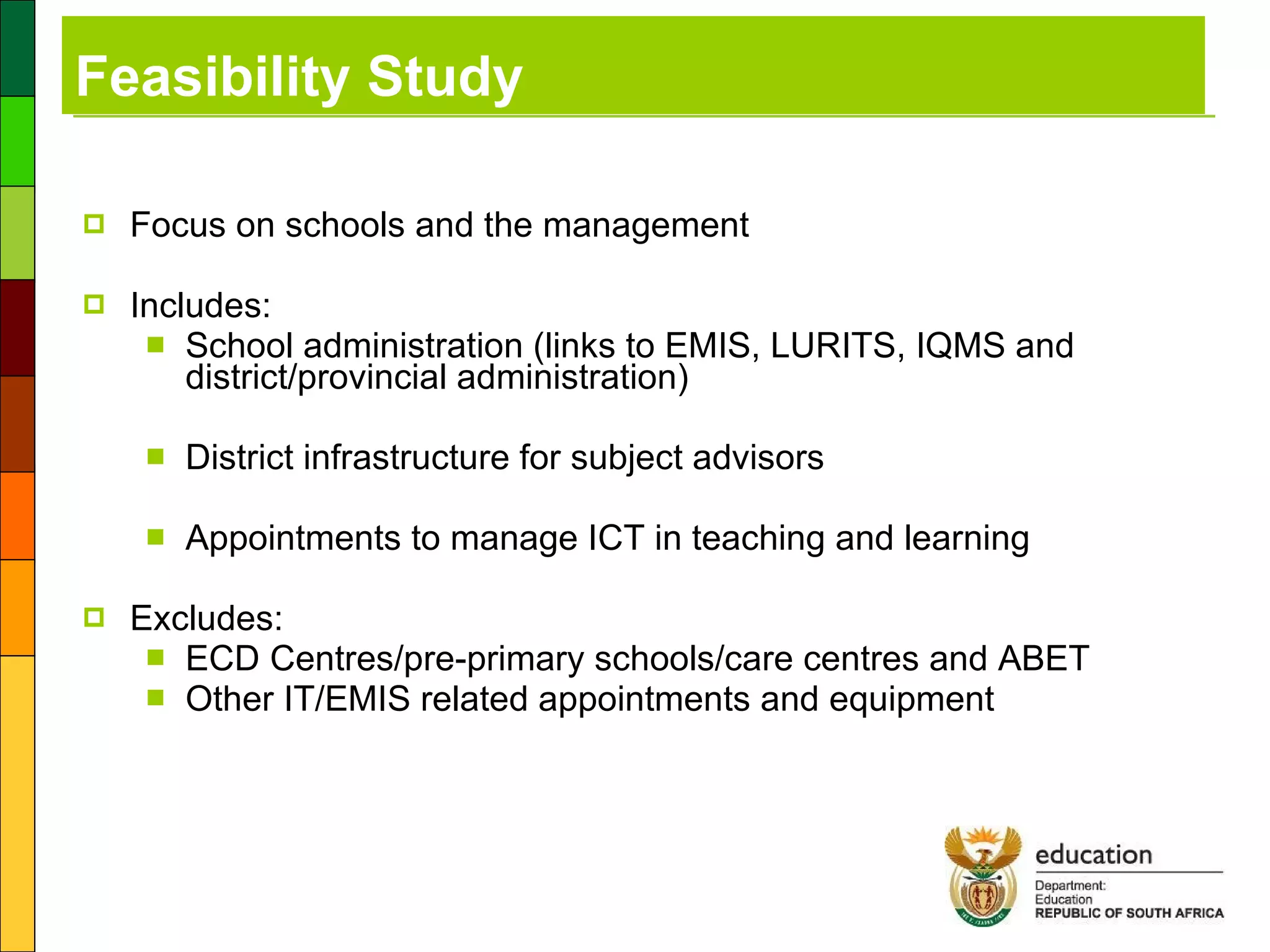
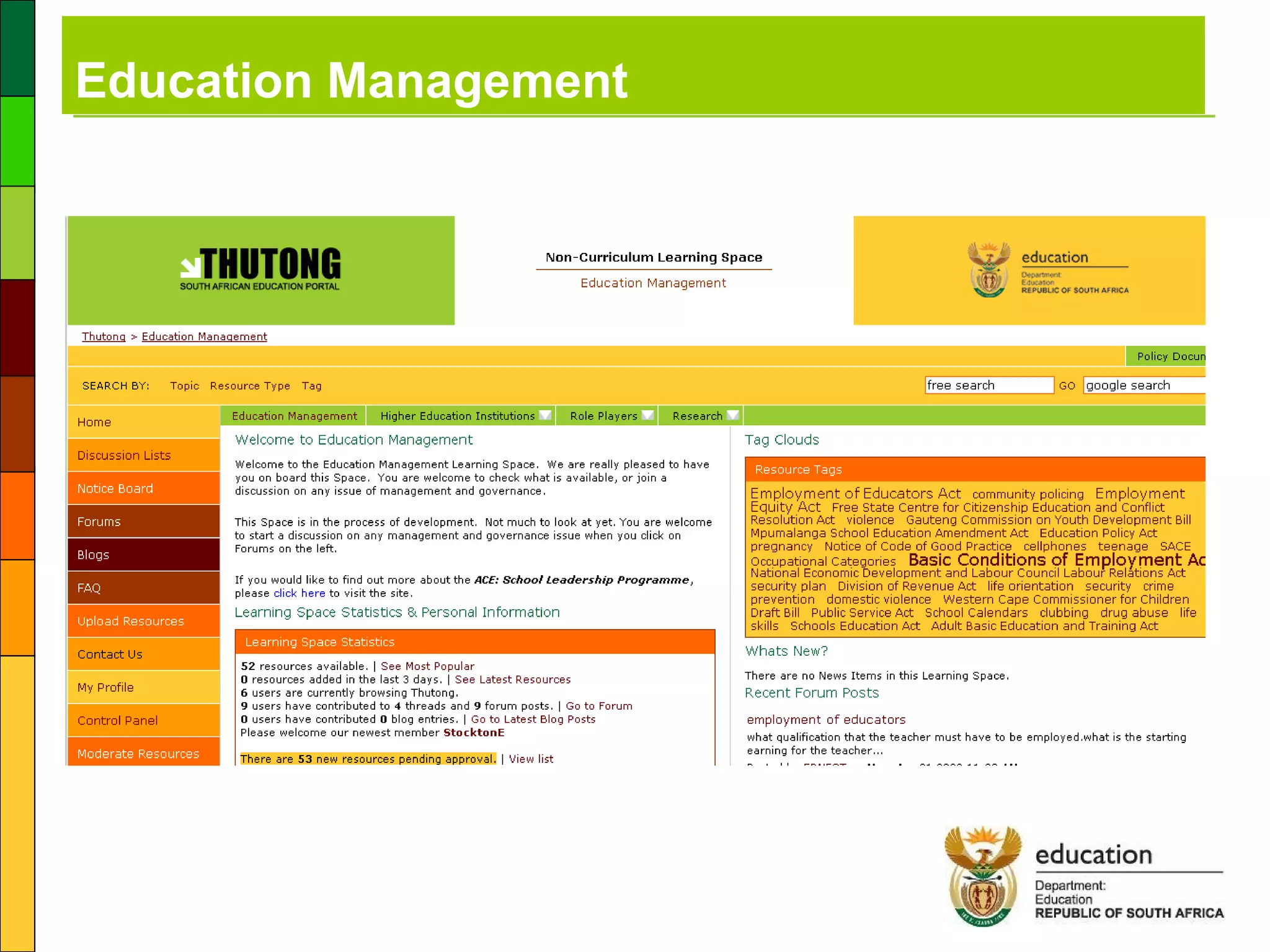
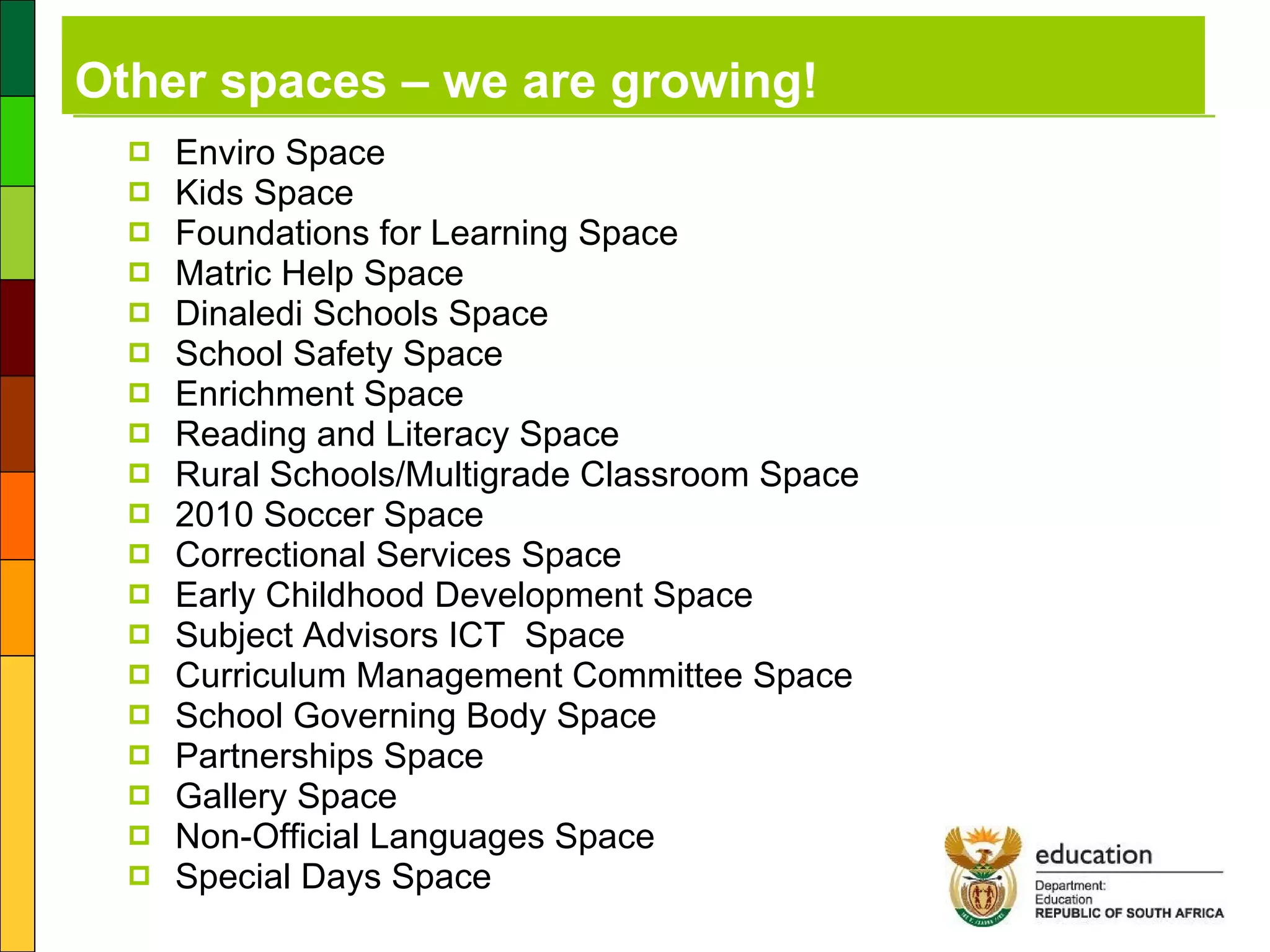
3) A feasibility study conducted by the Department of Education to outline a plan to provide ICT infrastructure, connectivity, training and support to schools.























![Thank you… Joy Rosario Department of Education [email_address] http://www.thutong.doe.gov.za](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090602libraryconference-090604050946-phpapp02/75/Library-Conference-DoE-talk-30-2048.jpg)