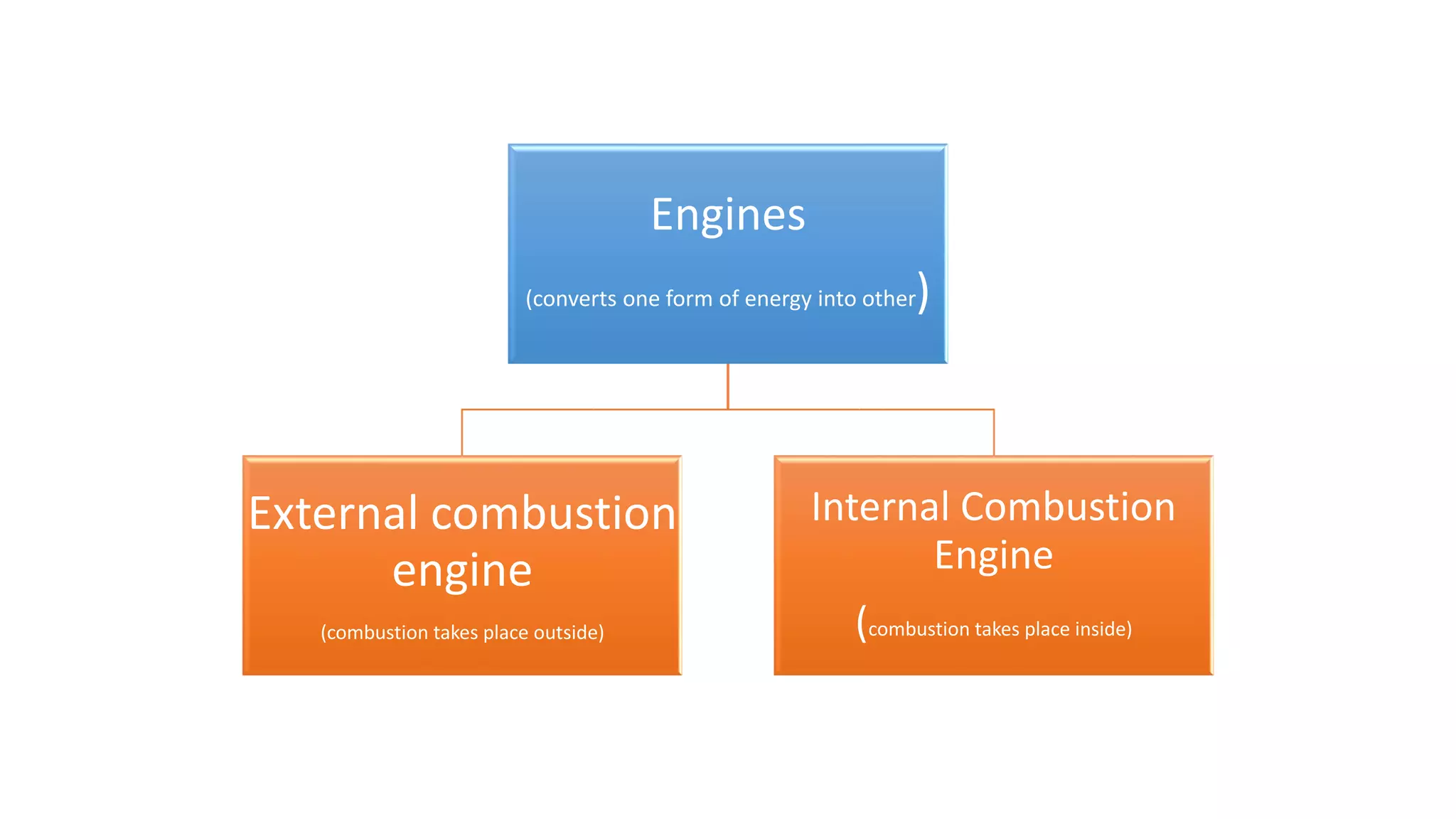
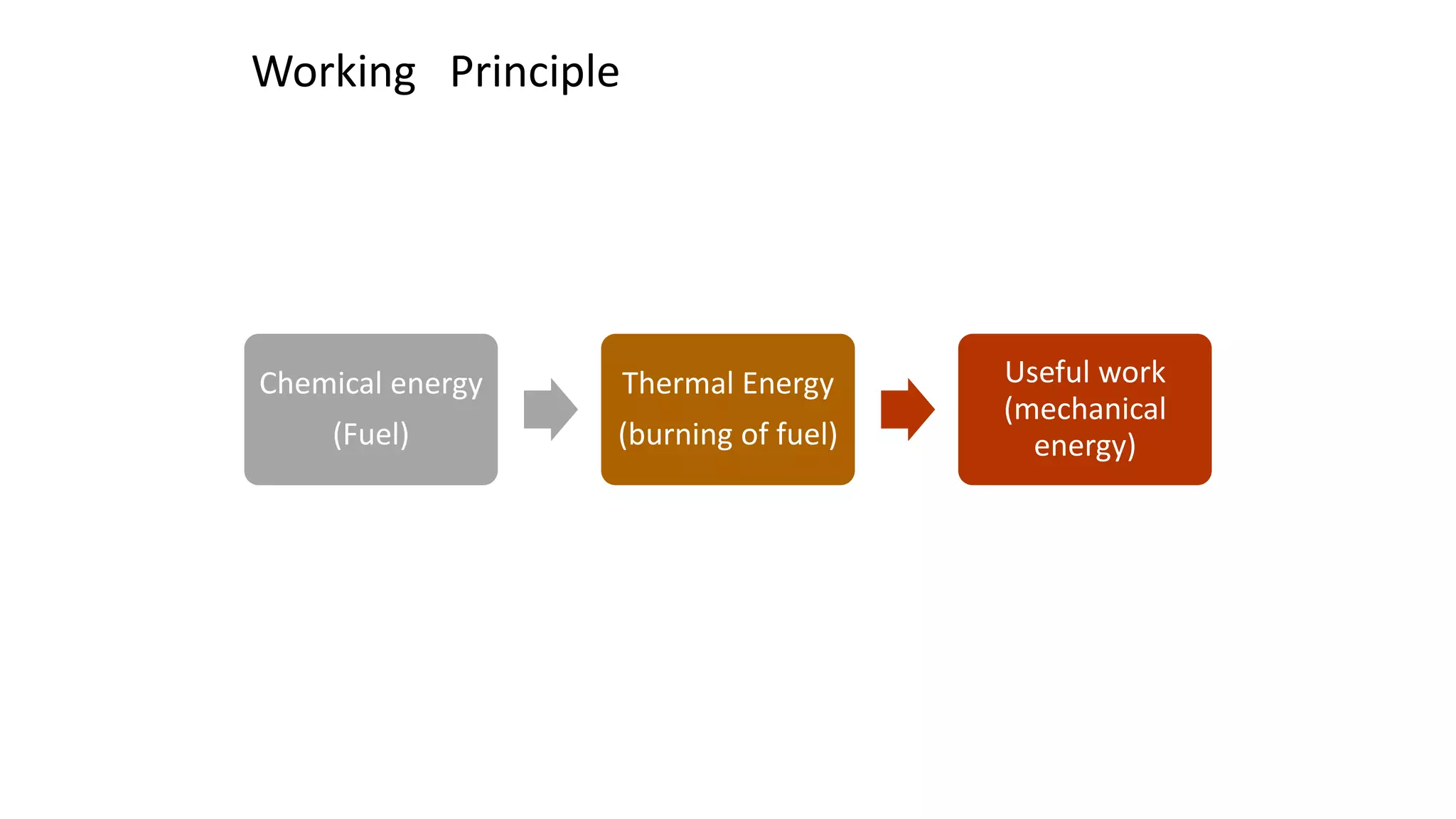
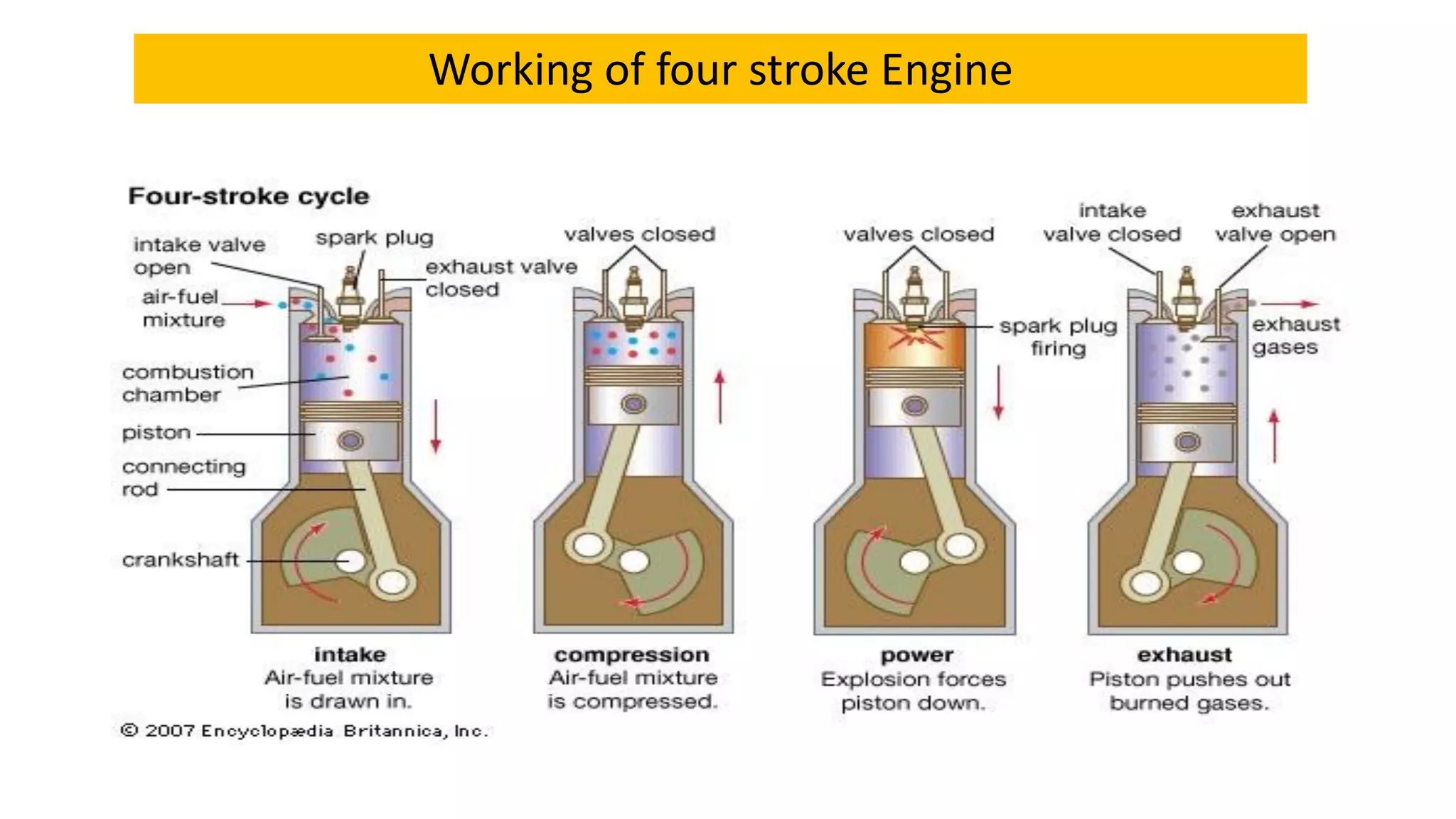
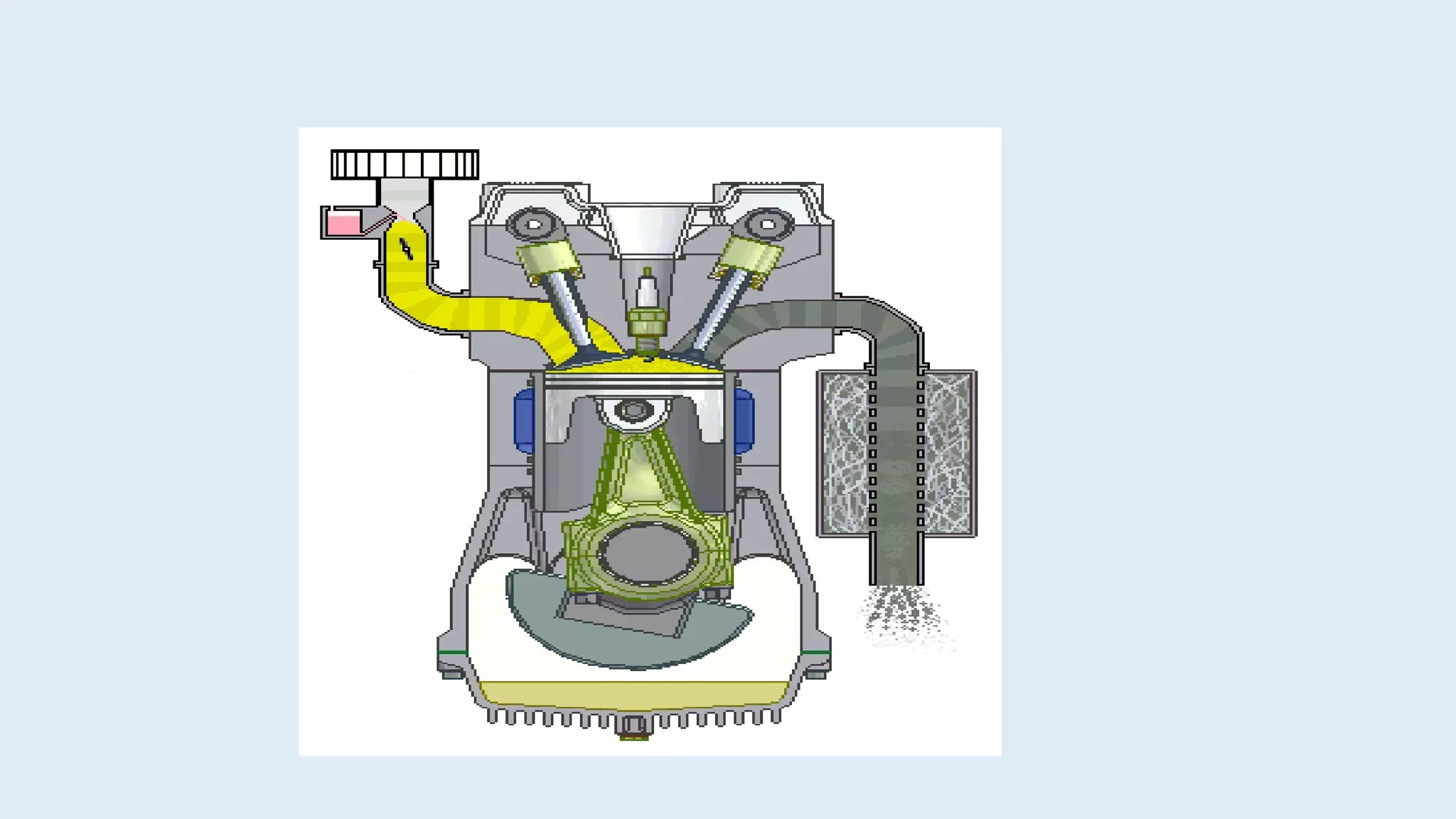
The document discusses the basics of internal combustion (IC) engines. It describes IC engines as converting chemical energy from fuel into thermal and then mechanical energy. The working principle involves combustion occurring inside the engine cylinder, where high pressure and temperature gases exert force on the piston. A four stroke engine is then explained as intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes. Key parts of a four stroke IC engine are also defined, including the piston, crankshaft, connecting rod, flywheel, valves, and spark plug. Applications mentioned are road vehicles, aircraft, and small machines.