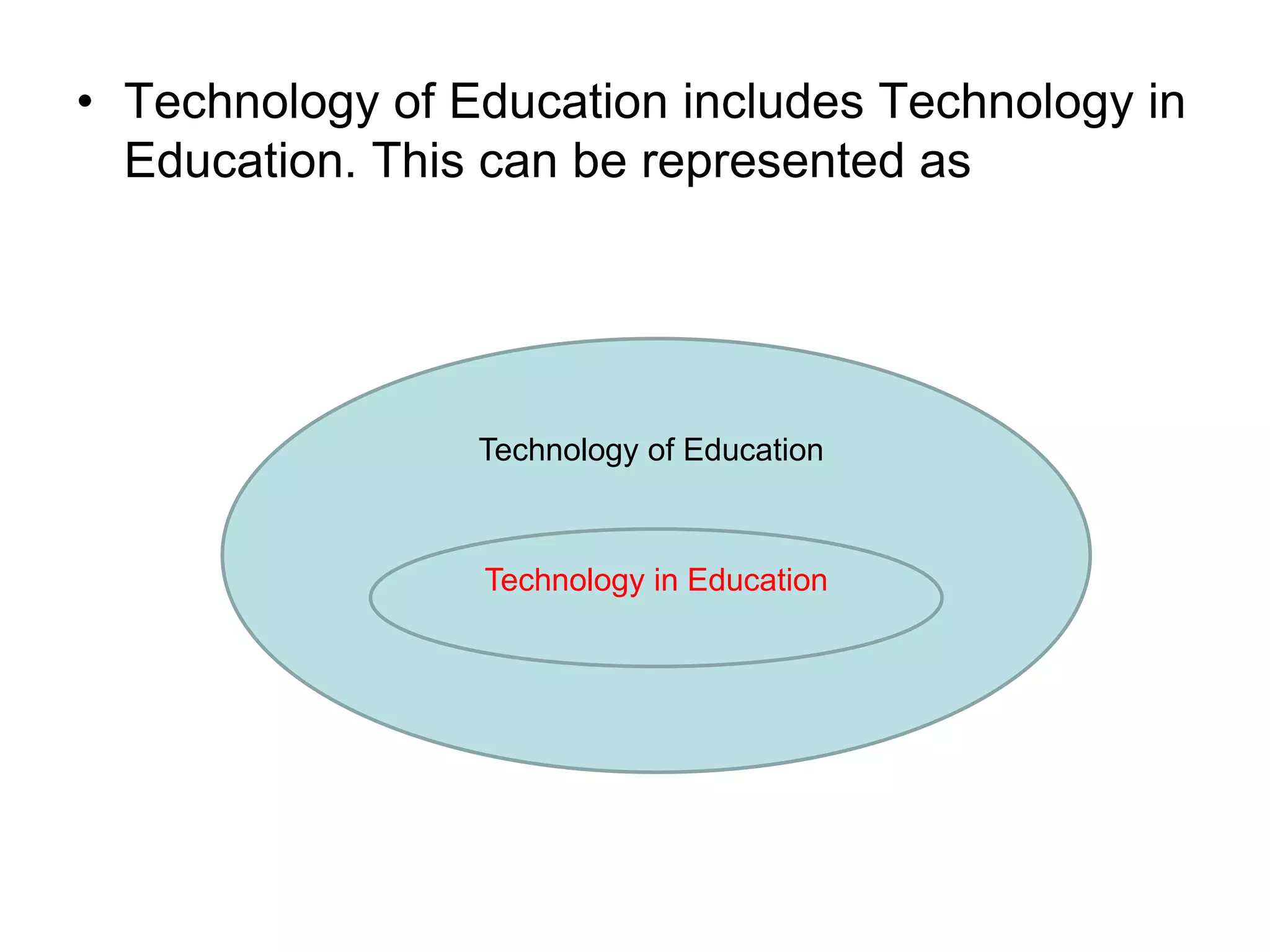
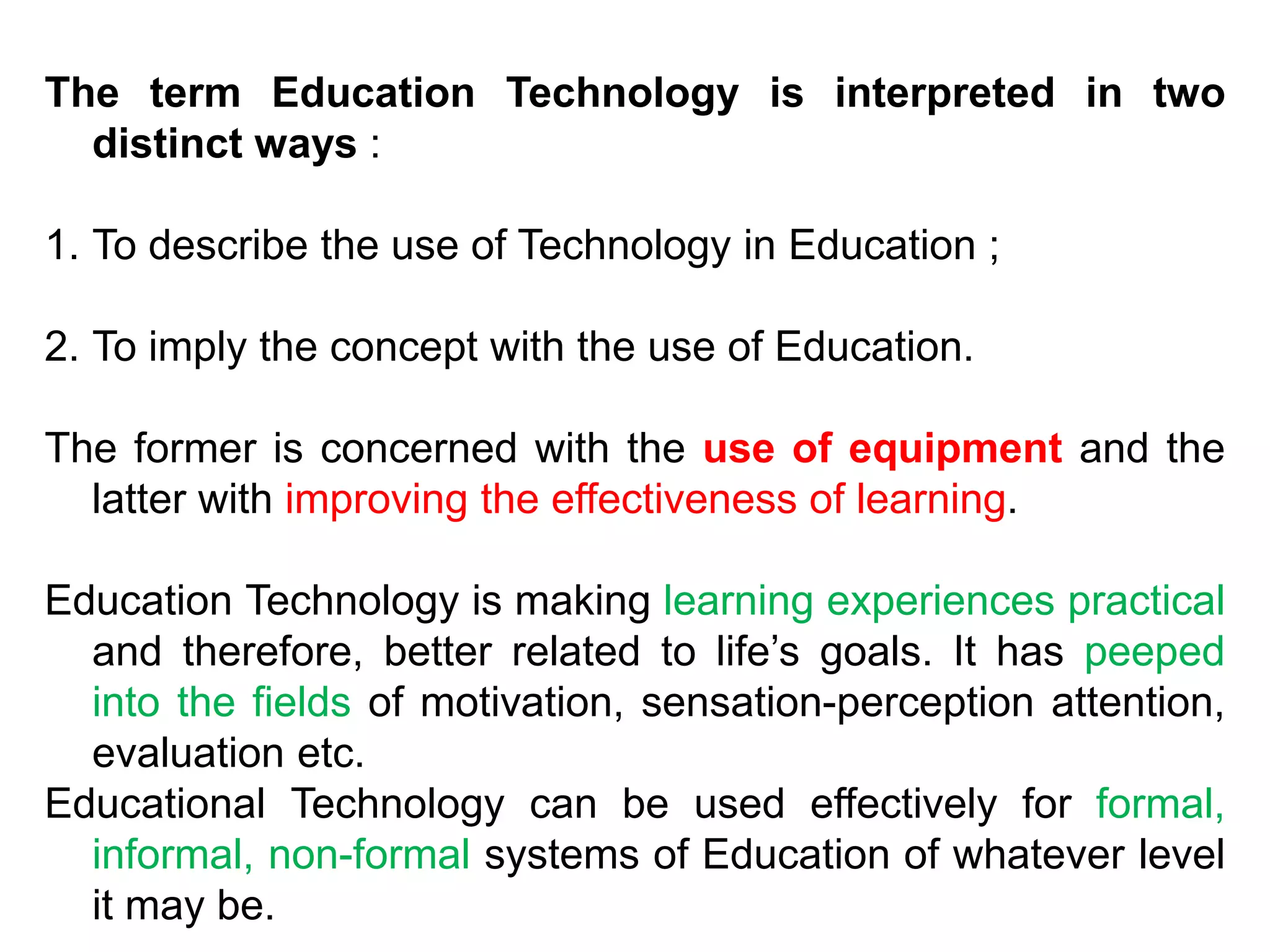
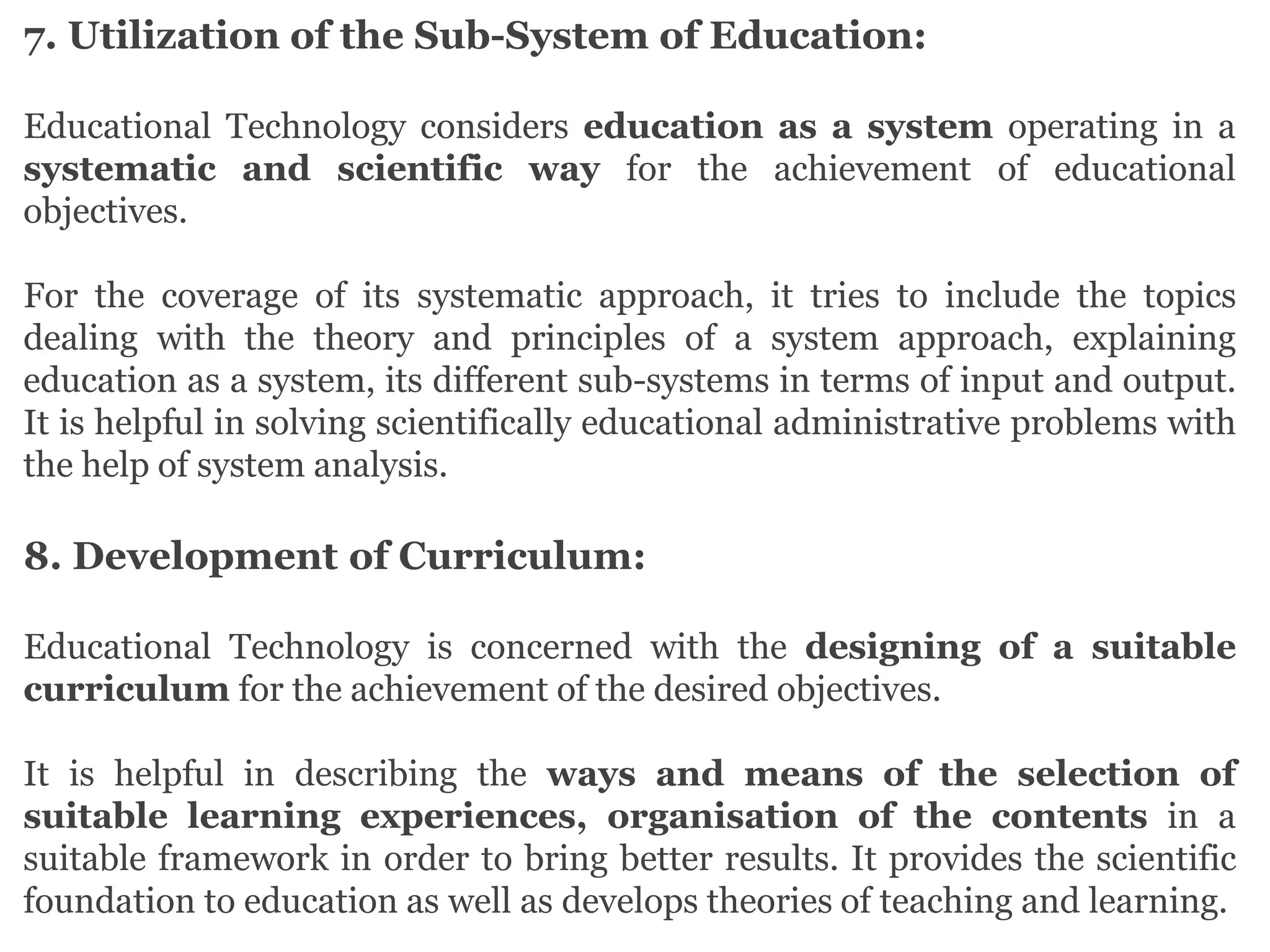
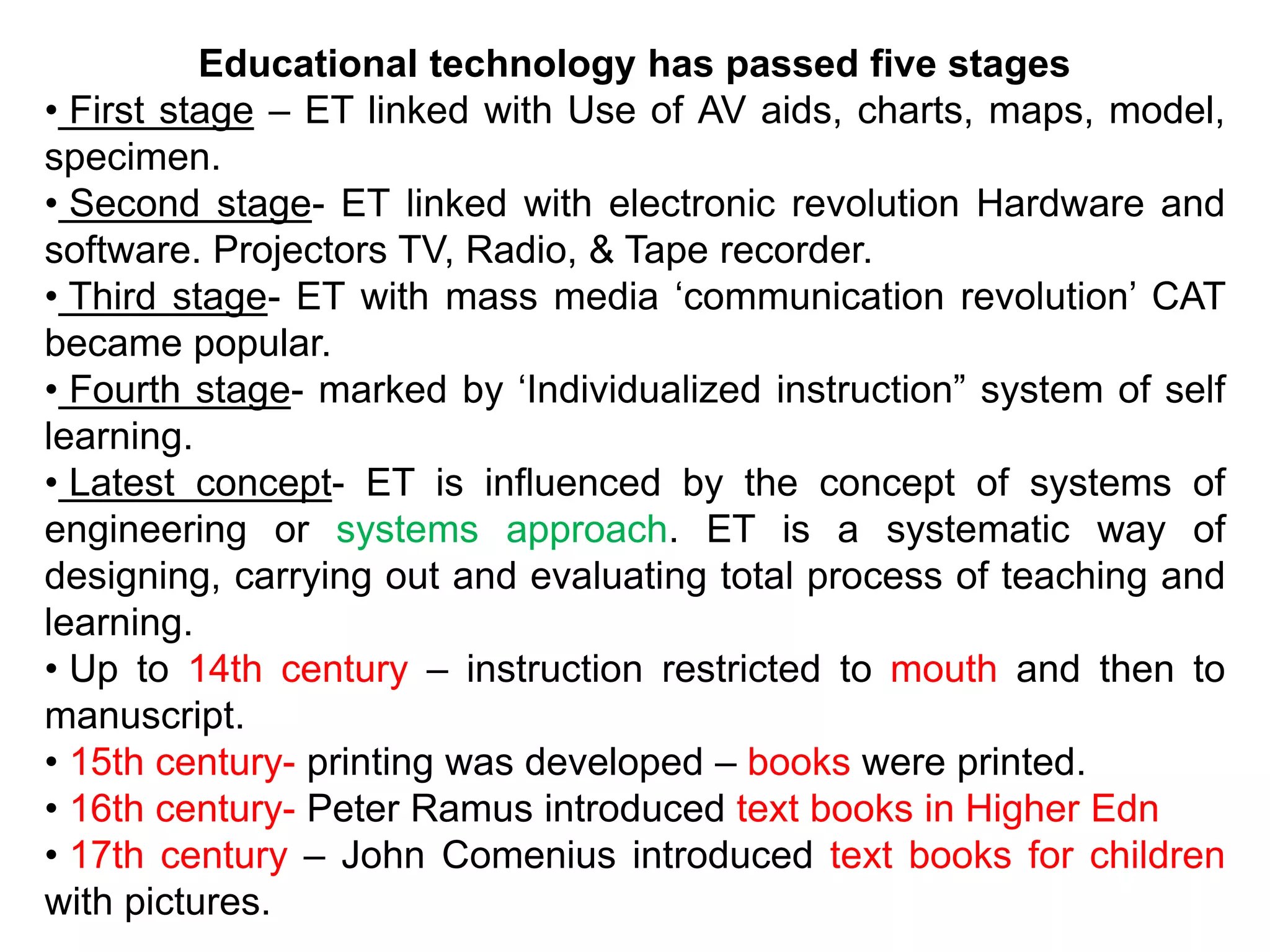
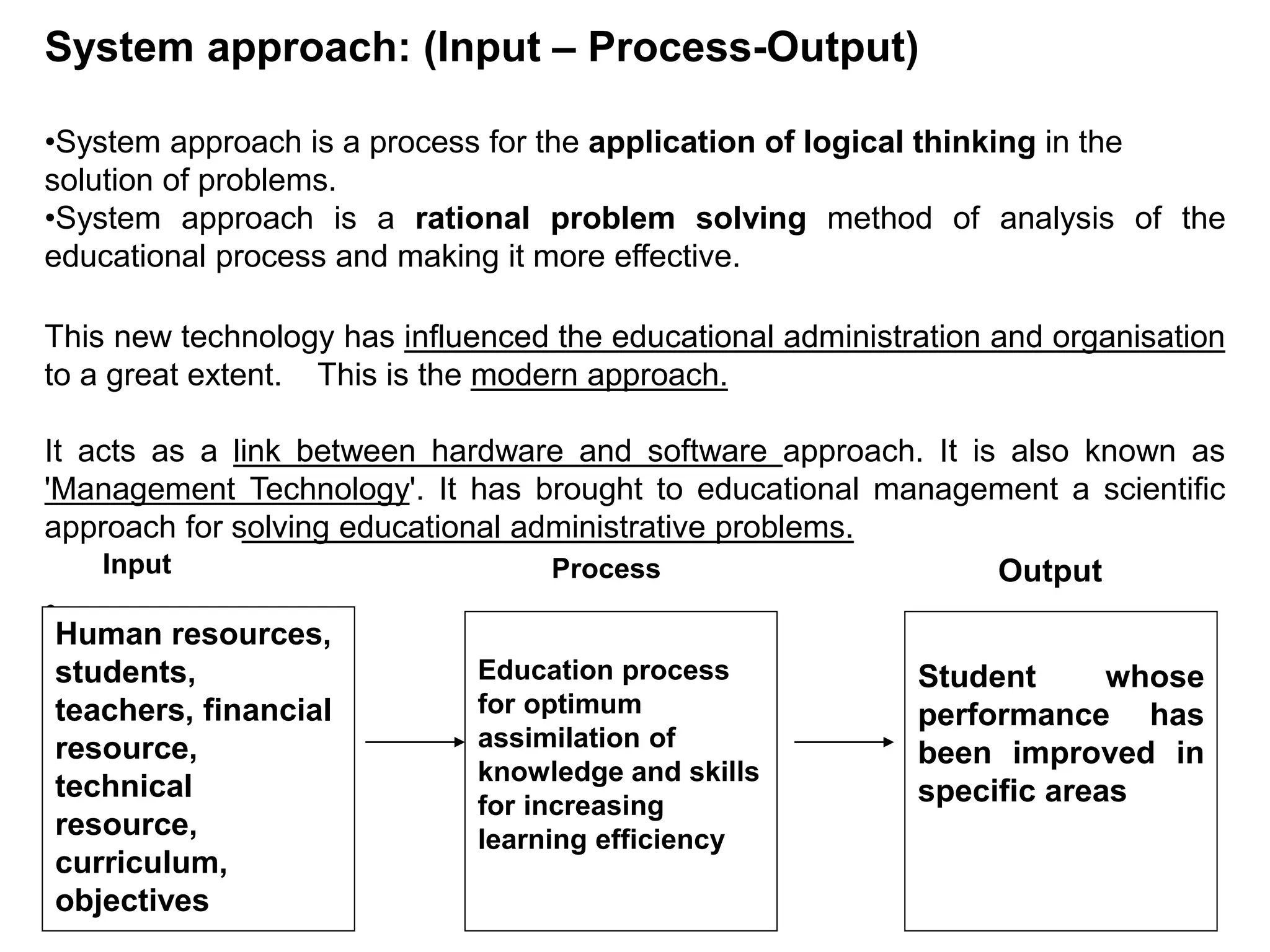
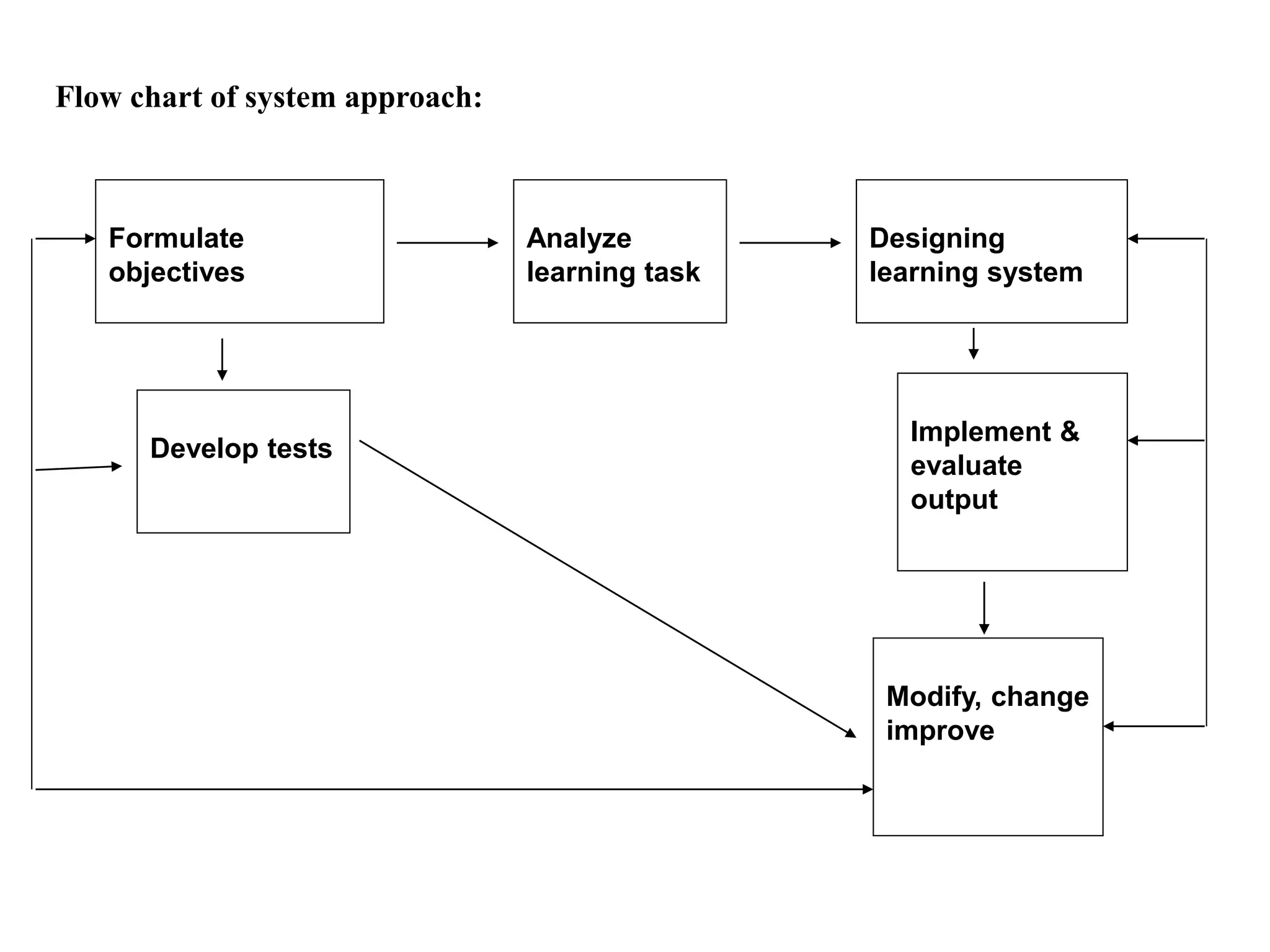
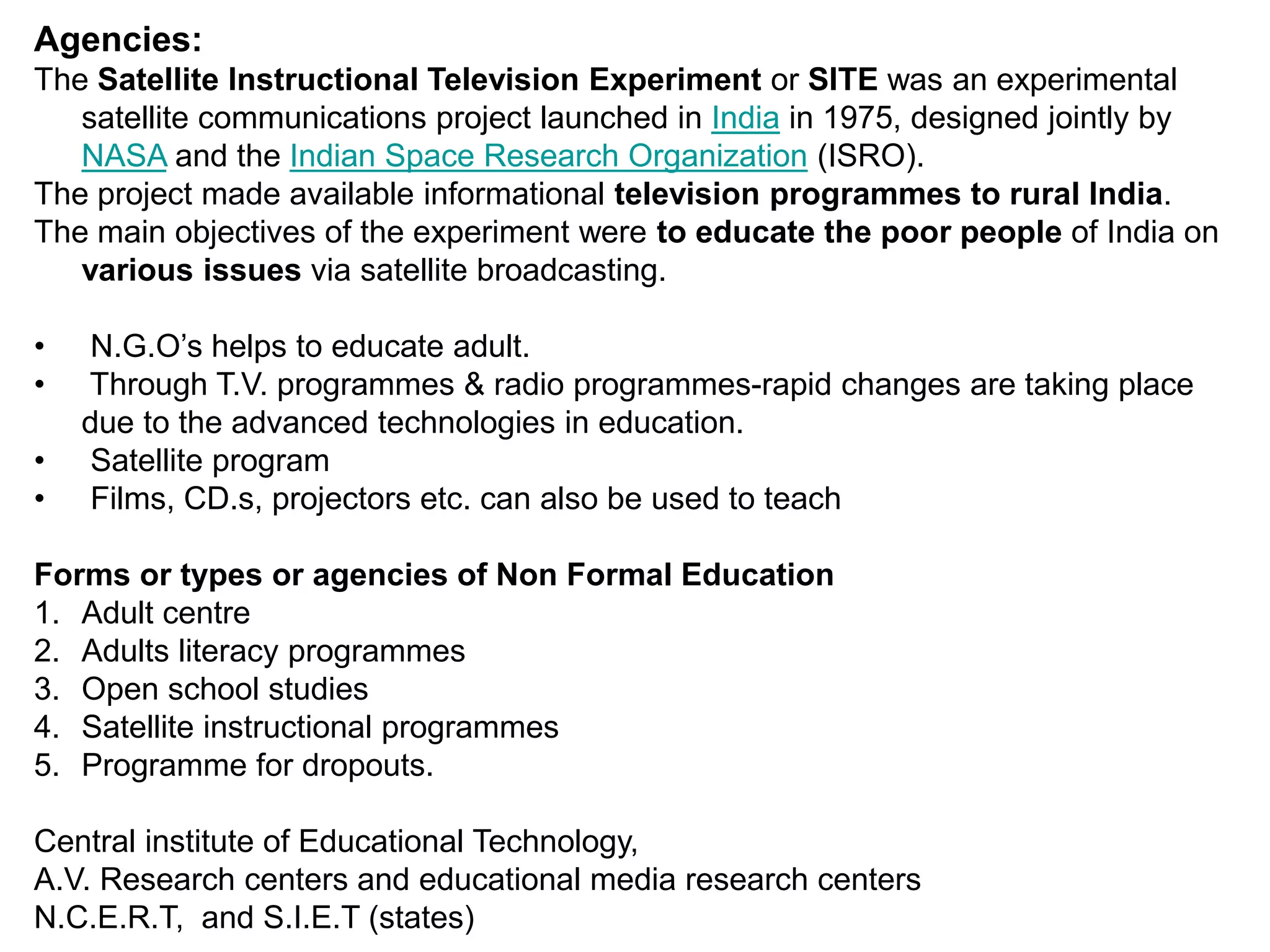
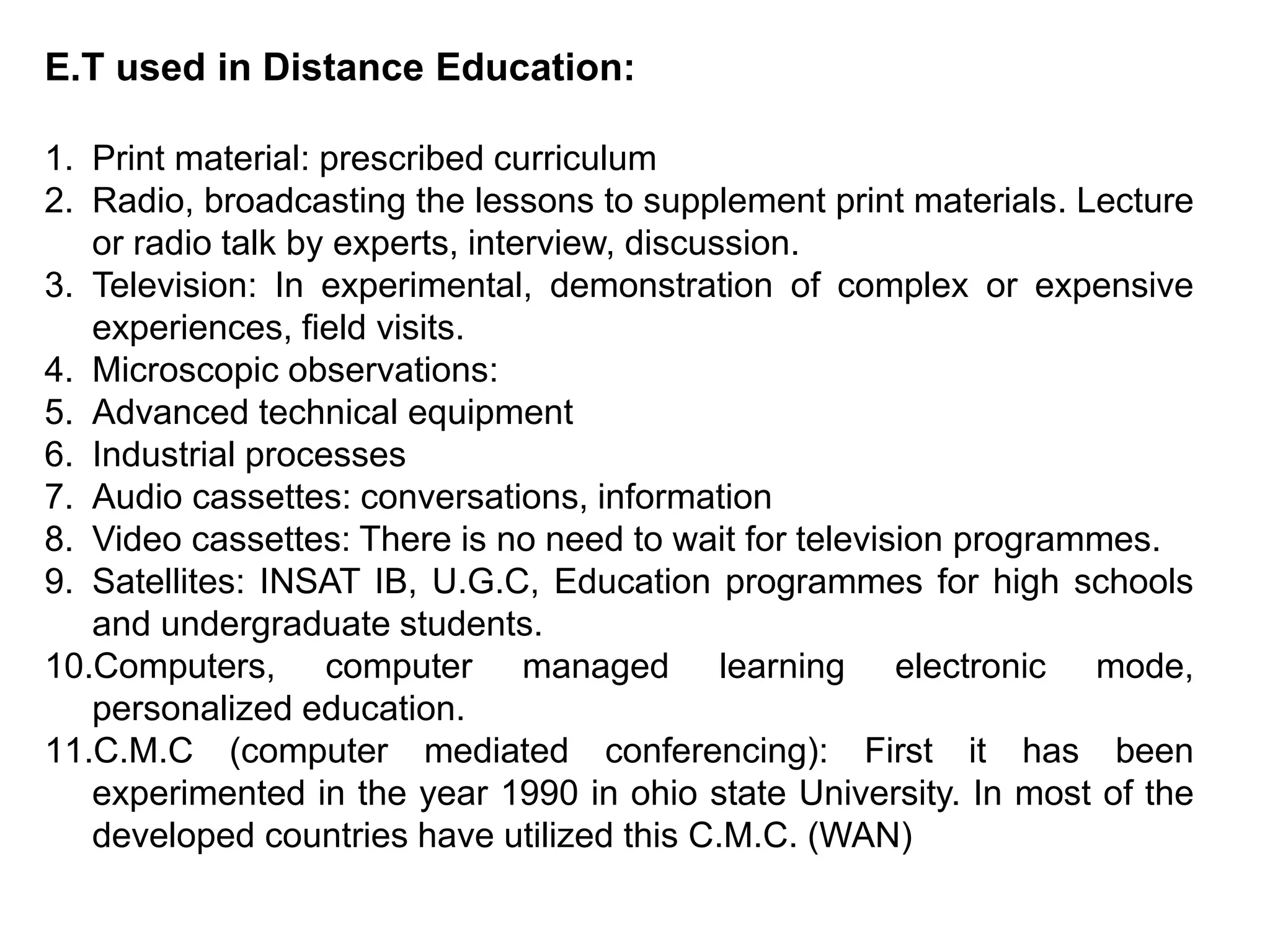
Educational technology refers to the use of scientific methods and technology to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of teaching and learning. It involves systematically designing instructional strategies, selecting appropriate content and media, and evaluating outcomes. Educational technology aims to facilitate learning by creating optimal learning environments and bringing the best instructional methods and resources. It is an interdisciplinary field that uses psychological and communication theories to develop, apply and evaluate techniques, systems and aids for improving the learning process.