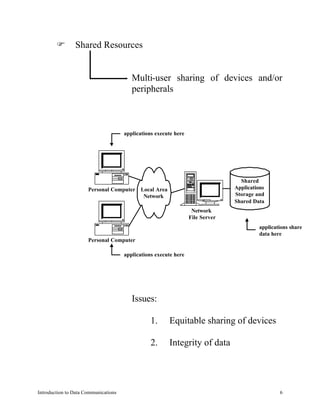
This document introduces data communications and computer networks. It defines data communication as relaying binary messages between two points, and computer networks as interconnected autonomous computers. The goals of networks are resource sharing, high reliability through replication, cost savings, and powerful communication. Networks can enable access to remote information, email, banking, libraries, bulletin boards, and online shopping. Networks are classified by the distance between communicating processors, from circuit boards to planets. Connectivity alternatives include stand-alone computers, time-sharing, and local area networks that share resources and applications.