Embed presentation
Download as ODP, PPTX

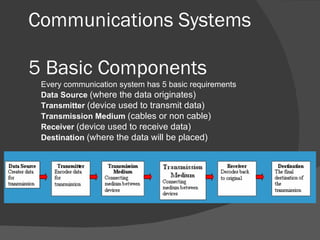
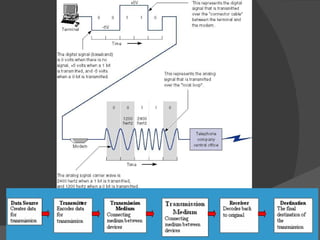
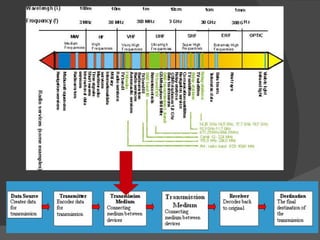
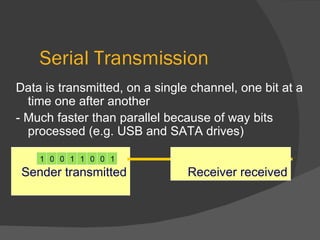
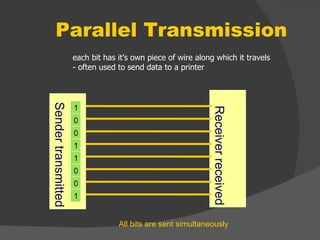

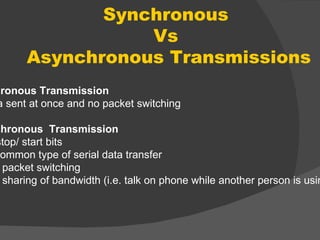
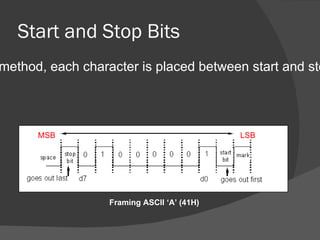
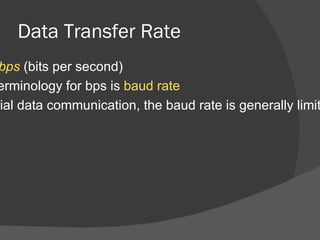




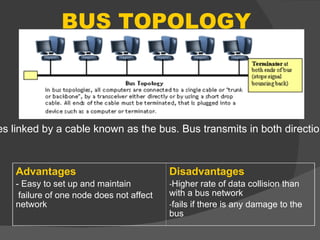
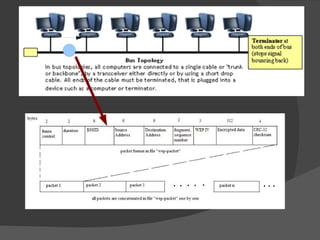

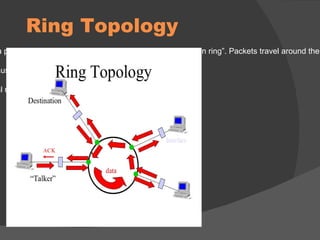
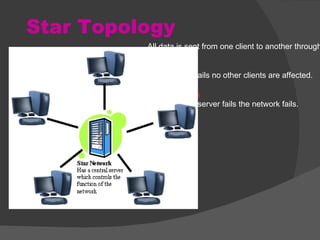

The document discusses the basic components of communication systems and data transmission methods. It explains that every communication system has 5 basic requirements: a data source, transmitter, transmission medium, receiver, and destination. It then describes serial and parallel transmission methods and how asynchronous transmission is the most common type of serial data transfer as it allows packet switching and bandwidth sharing. Finally, it discusses different network topologies like bus, ring, and star and compares their advantages and disadvantages.



















