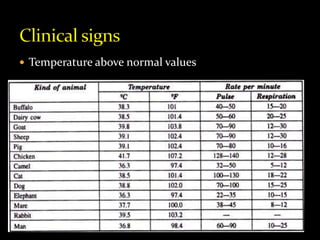
This document discusses heat stroke and hypothermia. Heat stroke is caused by a high body temperature from excessive heat production, environmental heat absorption, or deficient heat loss. It is characterized by a temperature above normal, increased heart rate and breathing, lack of sweating, and thirst. Left untreated it can cause organ dysfunction, convulsions, and death. Treatment involves cooling the body with ice water and fluids, along with medications. Hypothermia is caused by insufficient heat production and excessive heat loss, leading to subnormal body temperature and symptoms like cold skin and lethargy. Treatment focuses on warming the body with heated rooms and fluids along with medications in severe cases.