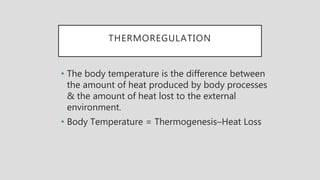
The document provides a comprehensive overview of fever, defining it as an elevation in body temperature above normal levels, often as a response to infection or other causes. It discusses the physiology of thermoregulation, factors influencing body temperature, various types of fever, and their classifications based on duration and severity. Additionally, it outlines management strategies and includes references for further reading on the topic.