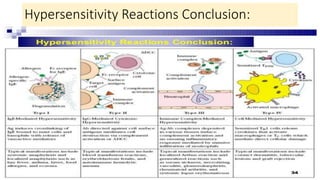
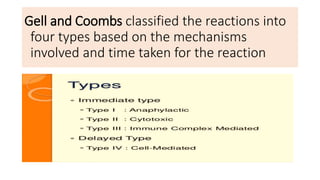
Hypersensitivity reactions are immune responses that are harmful or unpleasant for the host. There are four main types of hypersensitivity reactions classified based on the mechanisms involved:
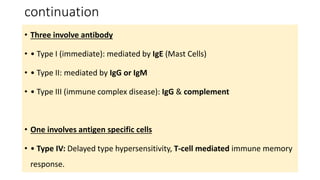
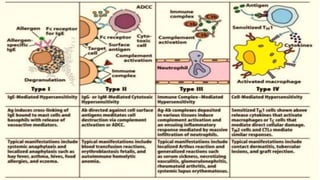
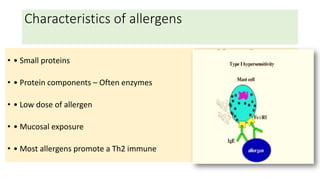
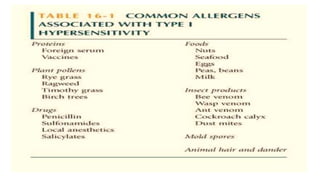
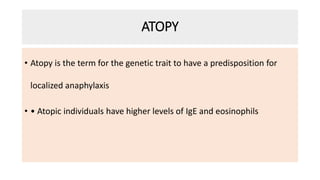
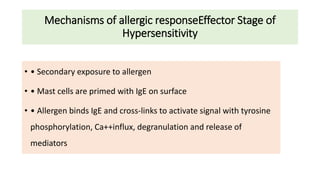
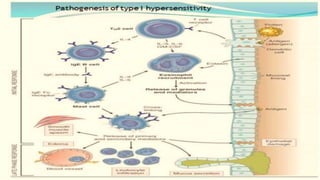
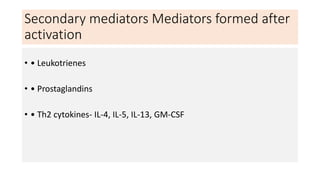
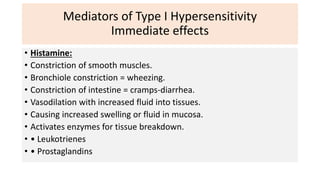
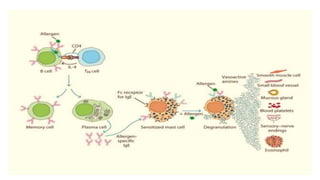
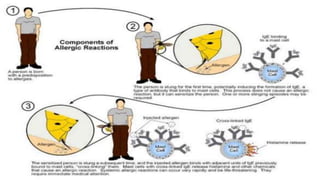
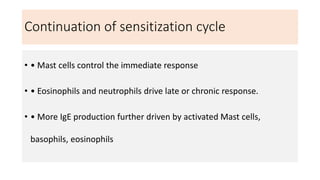
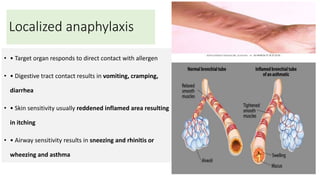
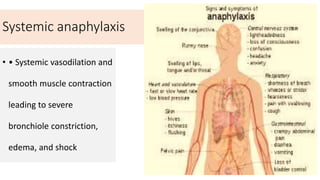
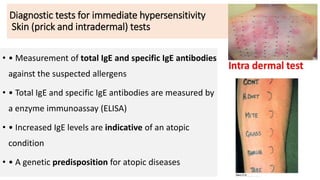
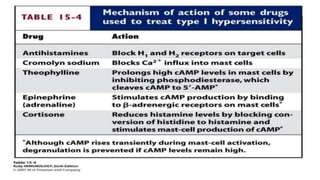
Type I reactions are immediate and mediated by IgE antibodies binding to mast cells. Common examples include allergic rhinitis and anaphylaxis.
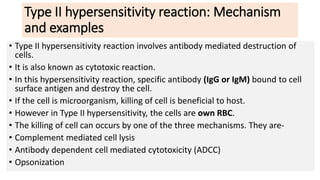
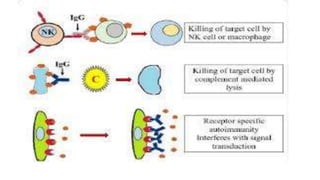
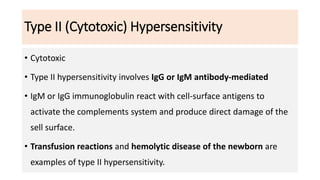
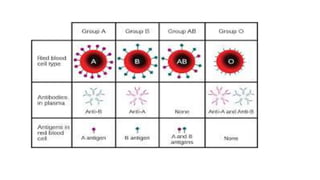
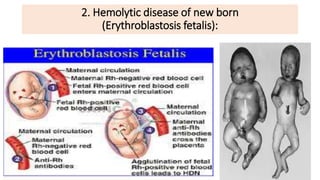
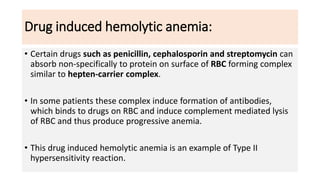
Type II reactions are cytotoxic and involve IgG or IgM binding to cell surfaces and activating the complement system. Examples include blood transfusion reactions and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
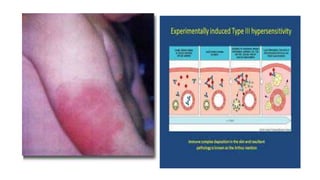
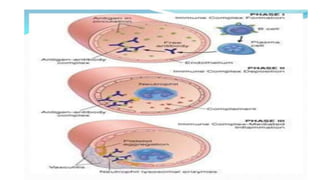
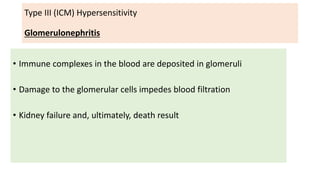
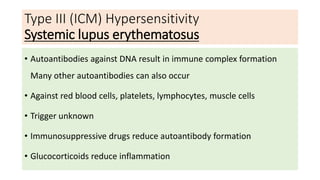
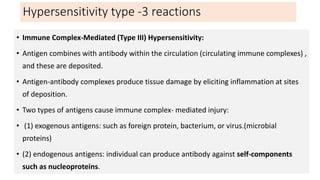
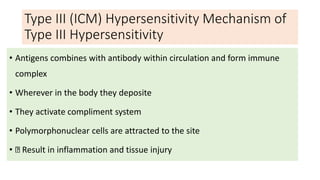
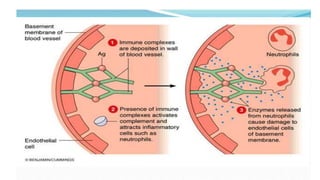
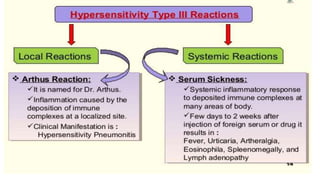
Type III reactions are immune complex-mediated where circulating immune complexes deposit in tissues, activating the complement system and causing inflammation. Examples include serum sickness and hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
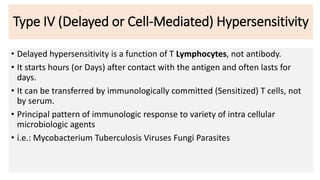
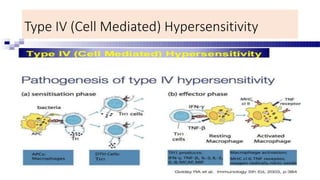
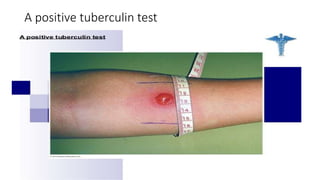
Type IV reactions are delayed and









![Examples of Immune Complex-Mediated Diseases:
[ diseases and antigens ]
• Systemic lupus erythematosus : DNA, and nucleoproteins antigens.
• Polyarteritis nodosa : Hepatitis B virus surface antigen
• Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis : Streptococcal cell wall antigen.
• Acute glomerulonephritis : Bacterial antigens (Treponema); parasite antigens
(malaria, schistosomes); and tumor antigens.
• Reactive arthritis : Bacterial antigens (Yersinia).
• Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypersensensitivityrxn2024-240218102346-98c3bbd8/85/Notes-39-320.jpg)