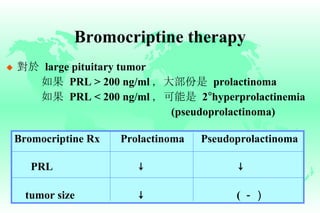
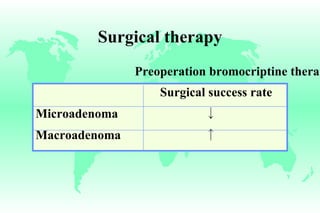
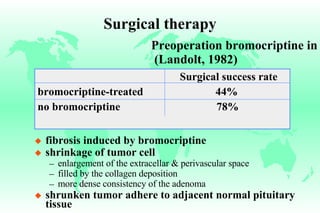
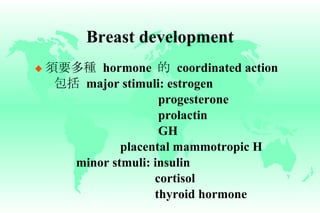
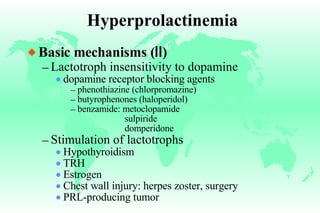
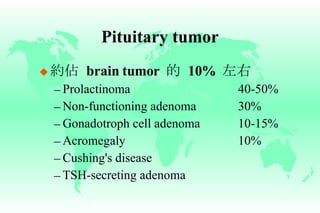
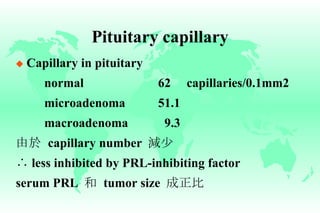
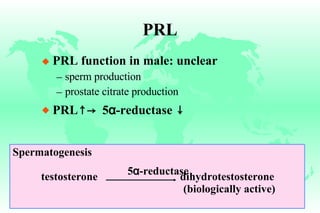
Hyperprolactinemia is caused by increased levels of the hormone prolactin, which is regulated by the hypothalamus. Elevated prolactin levels can be caused by hypothalamic or pituitary tumors, systemic diseases, or certain drugs. Common symptoms of hyperprolactinemia in females include menstrual irregularities and galactorrhea, while males commonly experience symptoms related to mass effects of pituitary tumors such as headaches and visual abnormalities. Treatment options for hyperprolactinemia depend on the size and invasiveness of any pituitary tumors, and may involve dopamine agonists such as bromocriptine or surgery.





































![Bromocriptine therapy Intolerate to oral therapy 時,可改用 vaginal administration (the same dosage) Patient 必須被告知可能 restore fertility ∴ 須事先使用 mechanical contraception ( 否則會在服藥治療期間 conception 而不自知 ) 直到 regular menstrual flow × 3 cycles Not teratogenic in human fetal loss congenital malformation Injectable form available in Europe effective for 4-6 wk : not increased ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperprolactinemia-1218072839103651-8/85/Hyperprolactinemia-43-320.jpg)