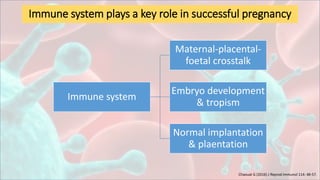
1. Despite growing evidence of the involvement of immunological alterations in recurrent implantation failure (RIF), there are no existing evidence-based guidelines focusing on immunological factors of RIF.
2. Antiphospholipid syndrome is one of the most frequent acquired risk factors for RIF. Antiphospholipid antibodies may induce a procoagulant state at the placenta through several mechanisms, leading to defective placentation and a relevant pathogenic mechanism in RIF.
3. Other immunological factors associated with RIF include the expansion of peripheral natural killer cells, deregulation of uterine natural killer cells, interactions between maternal killer immunoglobulin-like receptors and paternal HLA molecules on trophoblast cells,