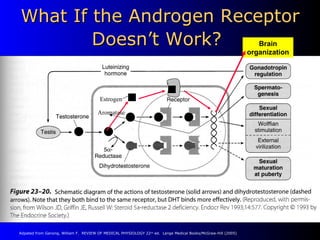
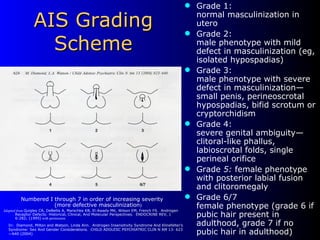
The document discusses Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS), a condition caused by mutations in the androgen receptor gene, leading to individuals with a male karyotype developing female characteristics. It highlights the differences between complete AIS and partial AIS, including how gender identity varies among affected individuals and the psychological implications of their conditions. The text argues for a broader understanding of gender beyond binary definitions, acknowledging that AIS individuals navigate complex identities influenced by biological and social factors.