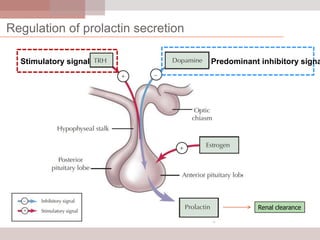
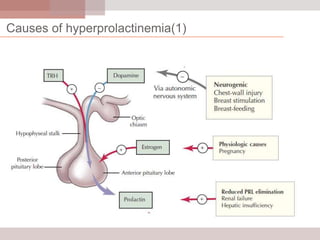
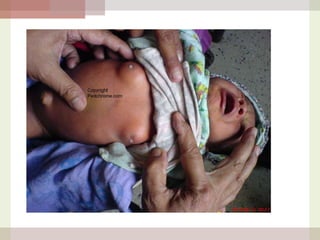
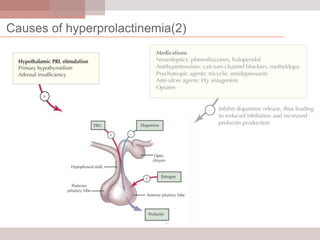
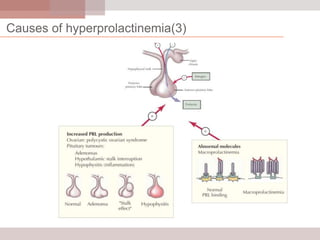
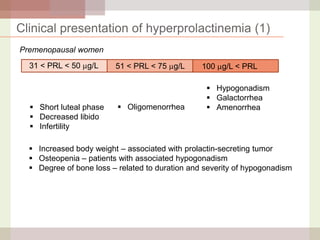
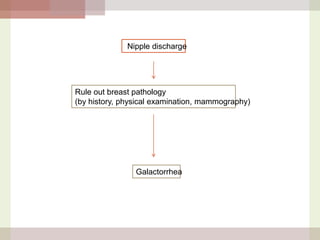
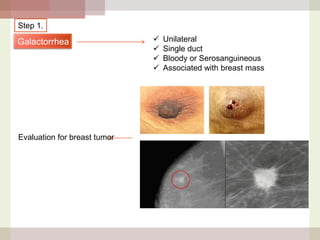
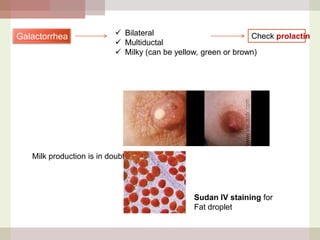
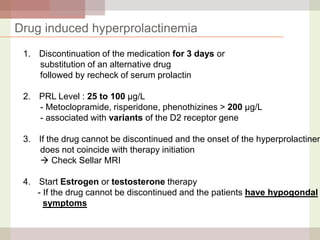
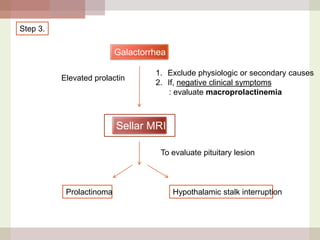
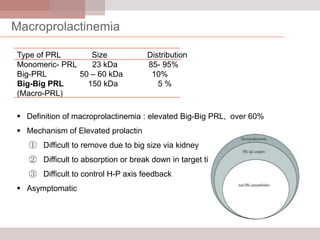
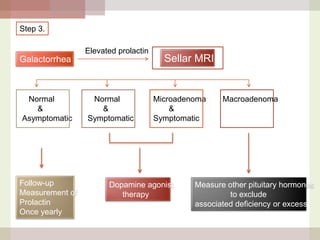
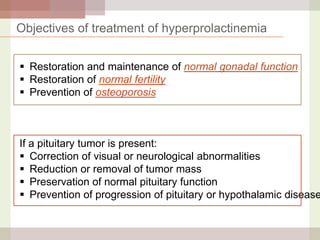
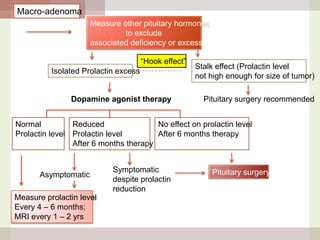
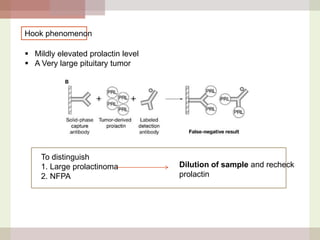
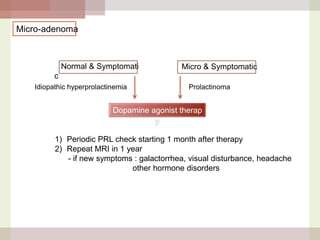
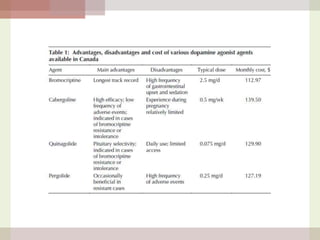
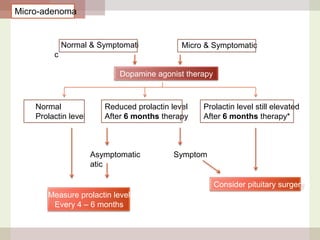
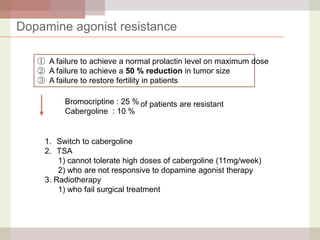
This document discusses hyperprolactinemia, including its causes, clinical presentations, evaluation, and treatment. The main causes of elevated prolactin levels are pituitary adenomas and medications. Clinical presentations vary depending on gender and prolactin level, and can include galactorrhea, amenorrhea, infertility, and decreased libido. Evaluation involves checking prolactin, excluding physiological causes, and using MRI to identify pituitary lesions. Treatment aims to restore normal hormone levels and fertility. Dopamine agonists are first-line therapy and can shrink tumors in many cases. Surgery may be considered if medications fail or for large macroadenomas.