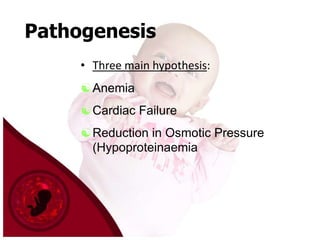
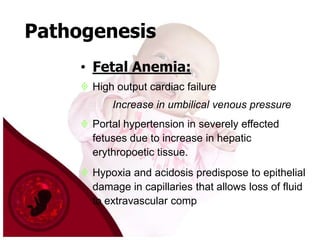
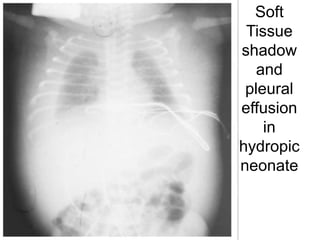
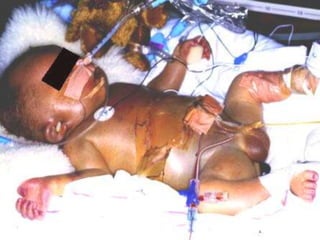
Hydrops fetalis is a severe condition where excess fluid builds up in fetal tissues. It can be caused by immune or non-immune factors. Immune hydrops is caused by fetal anemia from blood incompatibility between mother and fetus, while non-immune hydrops can result from conditions like infections, heart defects, or genetic abnormalities. Symptoms include excess amniotic fluid and swelling visible on ultrasound. After birth, symptoms are pale skin, edema, enlarged organs, and respiratory distress. Diagnosis involves ultrasounds, blood tests, and other procedures to investigate potential causes. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include help with breathing, removing excess fluid, and kidney support.