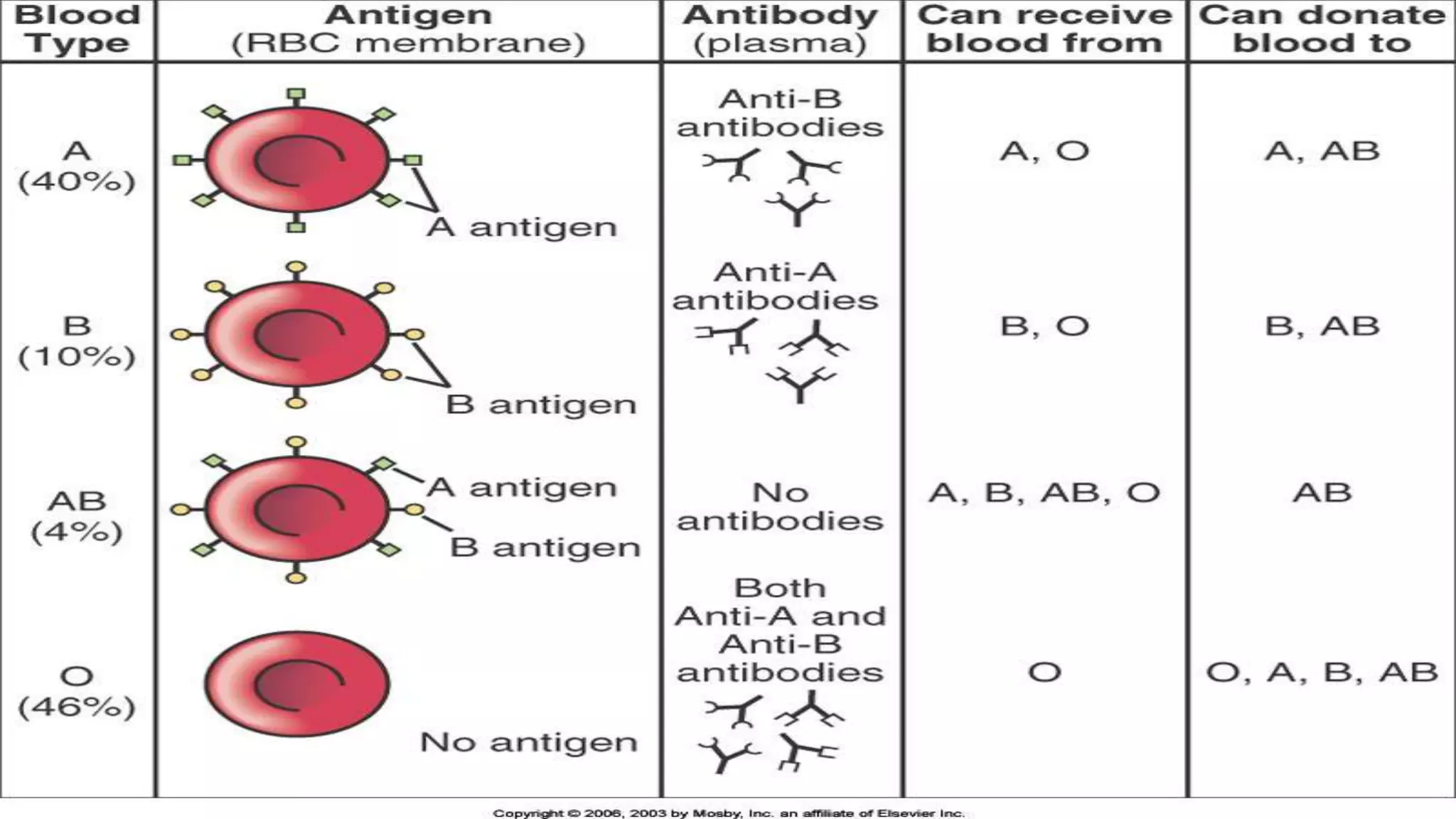
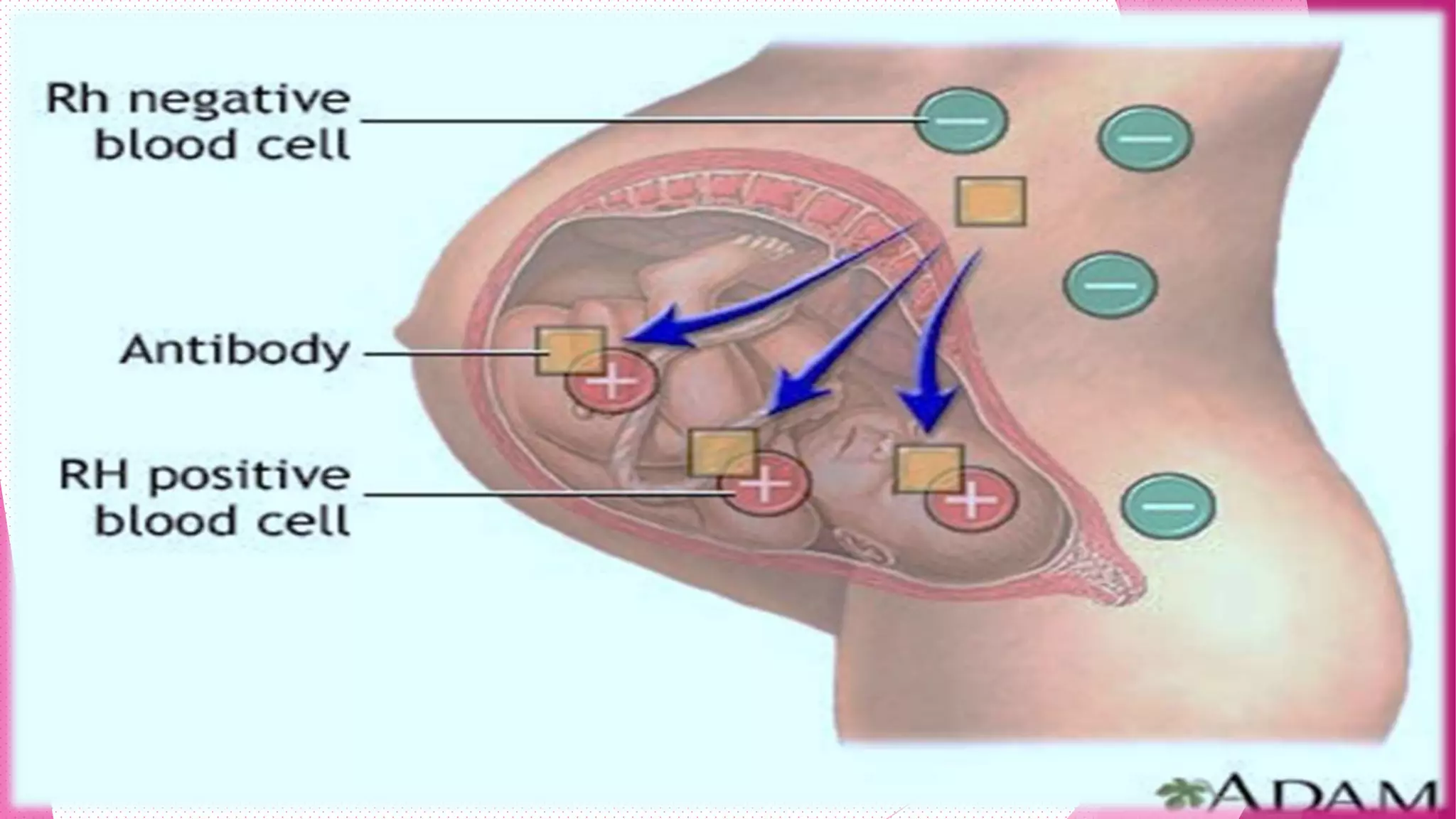
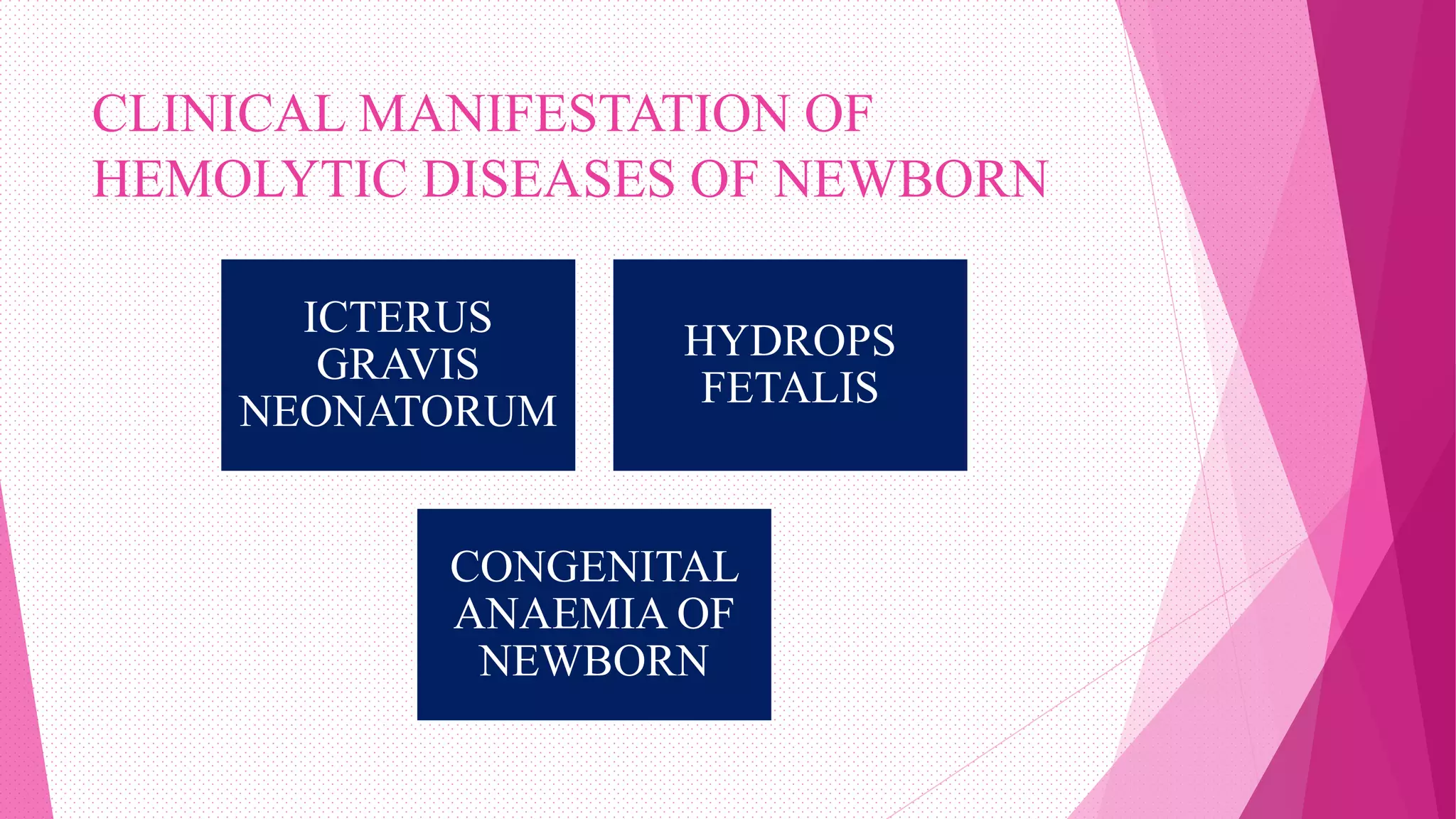
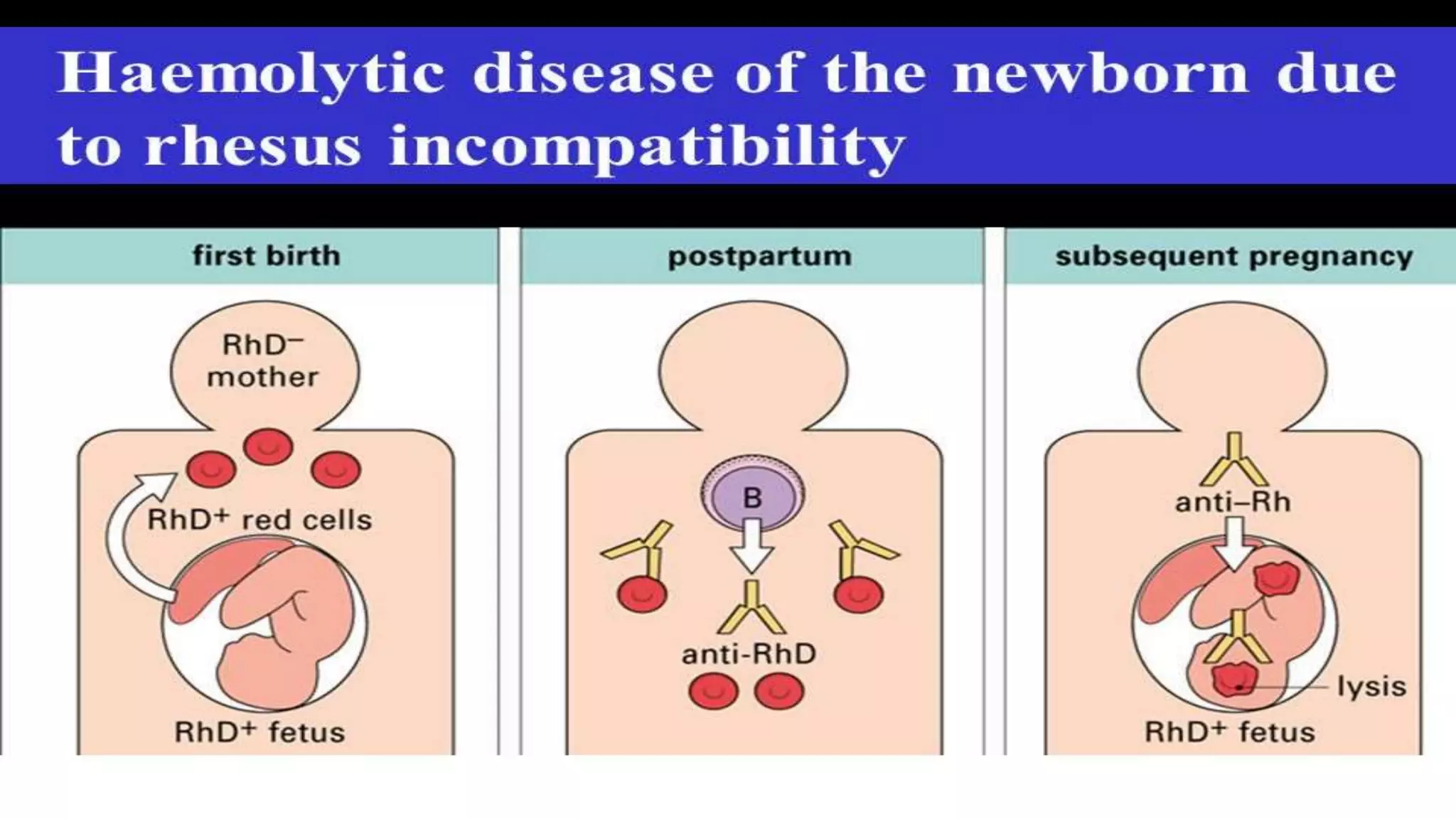
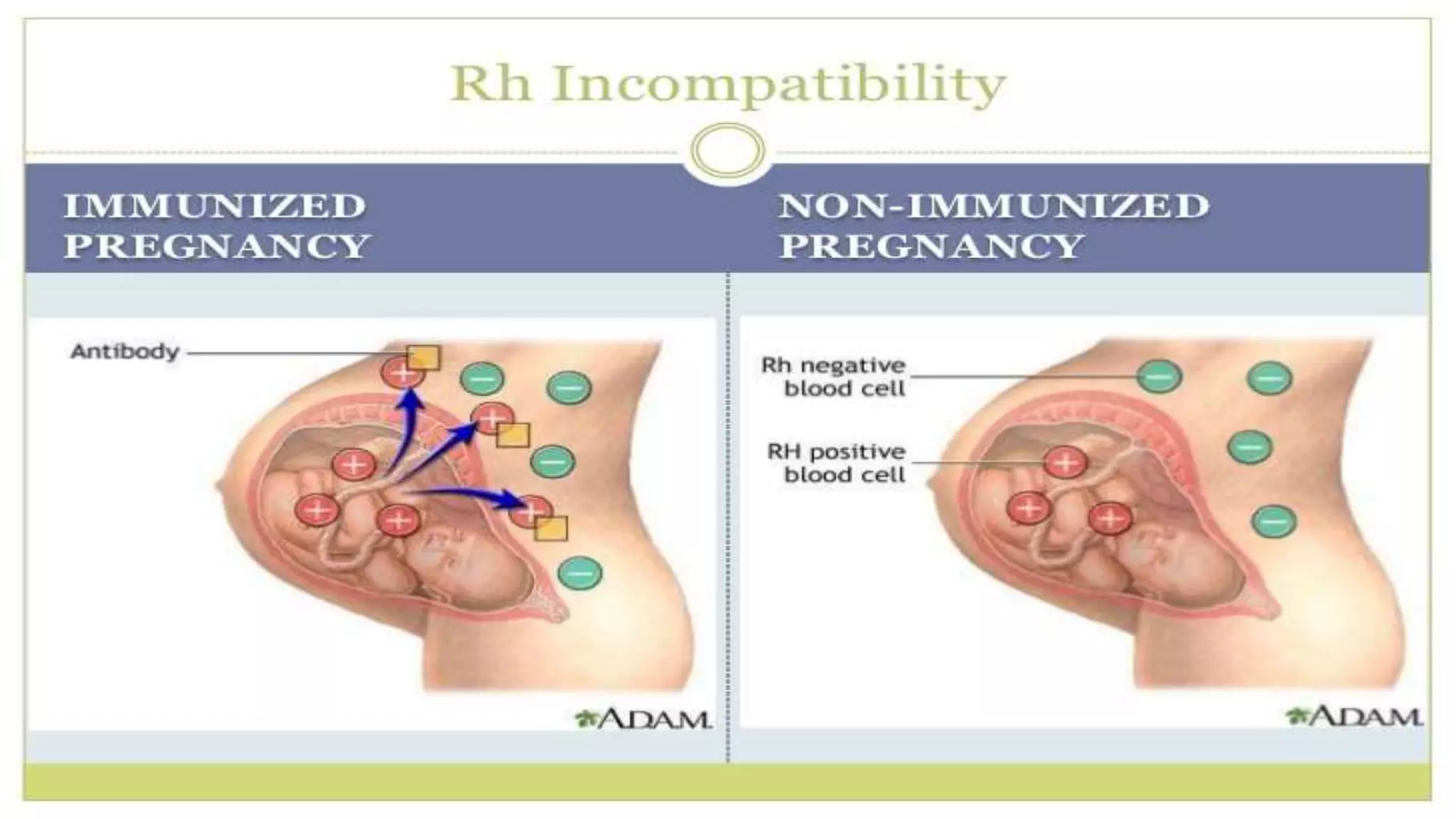
Rh incompatibility occurs when a pregnant woman with Rh negative blood is carrying a baby with Rh positive blood. During pregnancy or delivery, the baby's Rh positive blood can enter the mother's bloodstream and trigger an immune response. This response produces antibodies that can destroy the baby's red blood cells if the mother has a subsequent Rh positive baby. Rh incompatibility can cause jaundice, anemia and in severe cases hydrops fetalis in the baby. Diagnosis involves blood tests to check the mother's Rh status and antibody levels. Treatment may include Rh immunoglobulin injections during pregnancy to prevent sensitization.