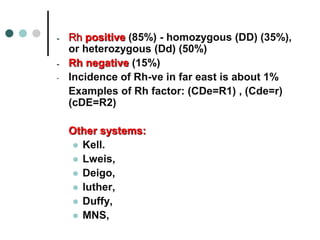
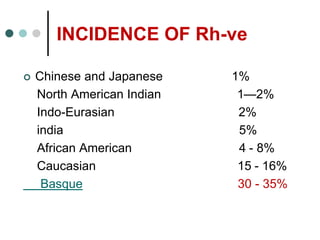
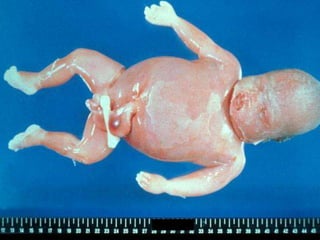
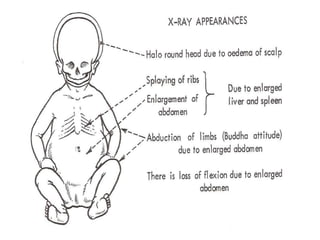
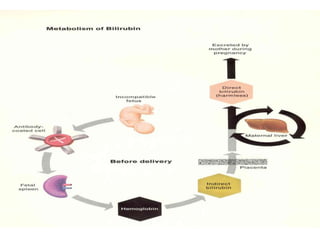
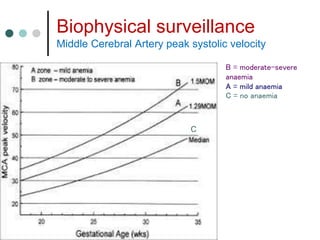
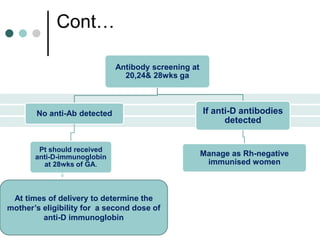
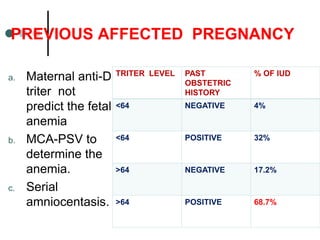
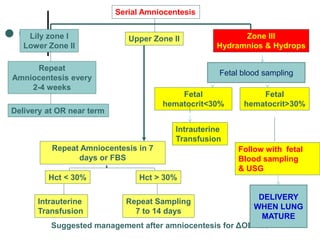
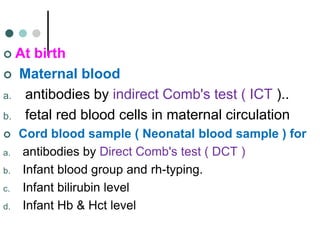
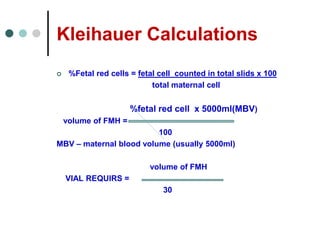
Rh-isoimmunization is a condition where an Rh-negative mother produces antibodies against an Rh-positive fetus, leading to potential hemolytic disease of the newborn. It involves a series of historical discoveries and complex immunological responses that can result from factors such as miscarriage, feto-maternal hemorrhage, and previous sensitization. Effective management includes screening, antibody monitoring, and potential interventions like intrauterine transfusions to address fetal anemia.