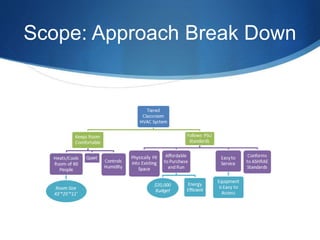
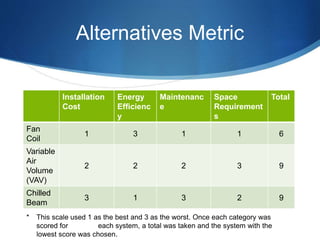
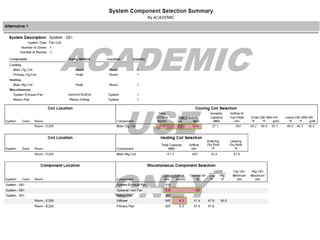
The Siemens Room Renovation project involved replacing the HVAC system in room E 219 of the Olmsted Building. An ME team analyzed the old fan coil system and considered three replacement options: a two-pipe fan coil system, variable air volume system, and chilled beam system. They determined the updated fan coil system would be the most cost effective solution. The project scope was to research systems, install and commission the new HVAC by spring 2015, and benchmark the installed system.