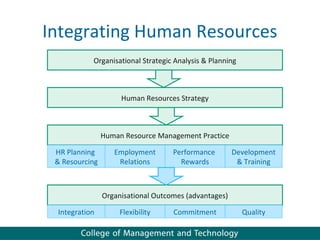
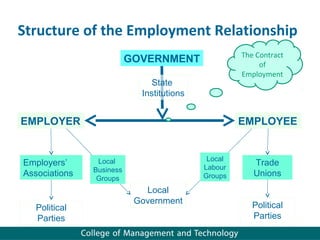
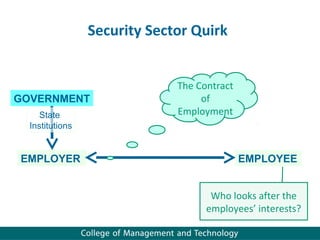
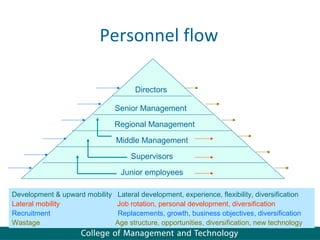
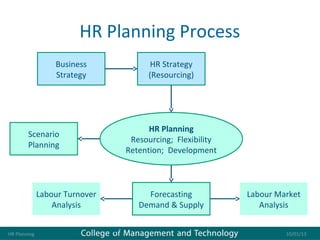
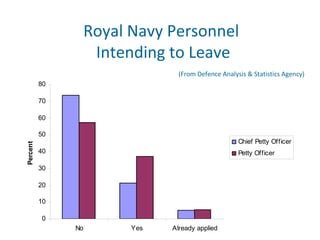
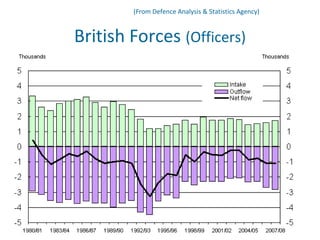
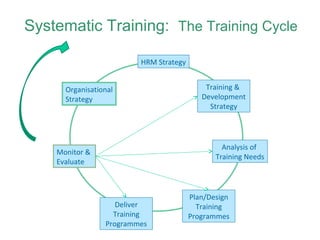
Human resource management seeks competitive advantage through strategic workforce deployment. There are two views of HRM: hard HRM focuses on using people to achieve goals through control, while soft HRM values employees and seeks commitment through cooperation. The standard HRM agenda includes employment relations, performance management, and training and development. Integrating HRM practices supports organizational goals. Managing the employment relationship depends on expectations and security. Developing potential involves training cycles and reward management motivates performance.

![Human Resource Management
• Human resource management … seeks to achieve
competitive advantage [operational effectiveness]
through the strategic deployment of a highly
committed and capable workforce, using an
integrated array of cultural, structural and personal
techniques.
• (John Storey, 1995)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanresourcemanagement1and2-130110000736-phpapp02/85/Human-resource-management-1and2-2-320.jpg)