This document discusses strategies for recruiting and developing talent both internally and externally. It covers:
1. Factors that determine the relevant labor market and sources for external recruitment, including advertisements, employee referrals, and educational institutions.
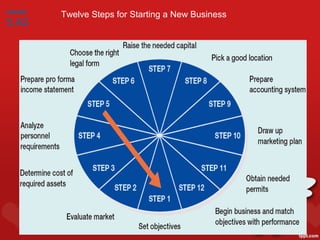
2. Principles for effective recruitment, including getting candidates who are a good fit, emphasizing compensation and workplace culture, and promoting from within to retain talent.
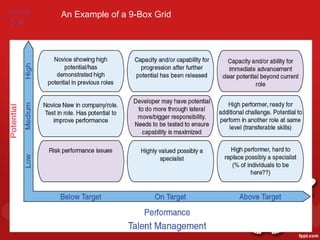
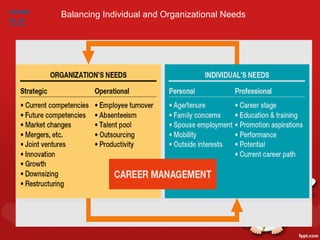
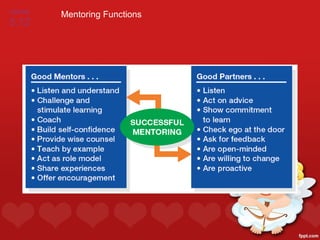
3. Methods for identifying and developing talent internally, such as performance appraisals, assessment centers, mentoring programs, and career development initiatives to match individual and organizational goals.
4. Considerations for recruiting a diverse talent pool and developing women and minorities, including overcoming barriers like the glass ceiling.