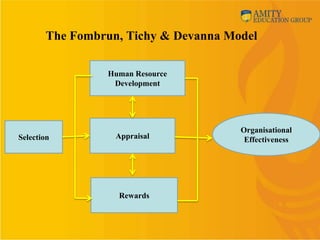
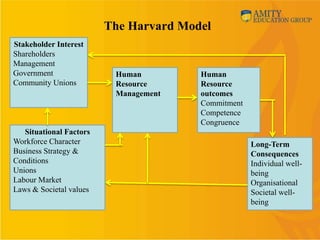
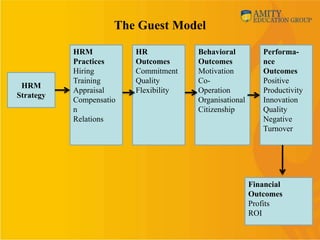
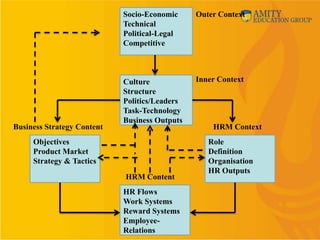
This document provides an overview of human resource management (HRM). It discusses why organizations need to study HRM as people are critical to running organizations. It defines HRM and outlines its nature, scope, and functions. The document also discusses different HRM models like the Fombrun, Tichy & Devanna model, the Harvard model, the Guest model, and the Warwick model. It compares personnel management, human resource development (HRD), and strategic HRM. Finally, it covers the internal and external environment of HRM and some changing roles and challenges for HRM.