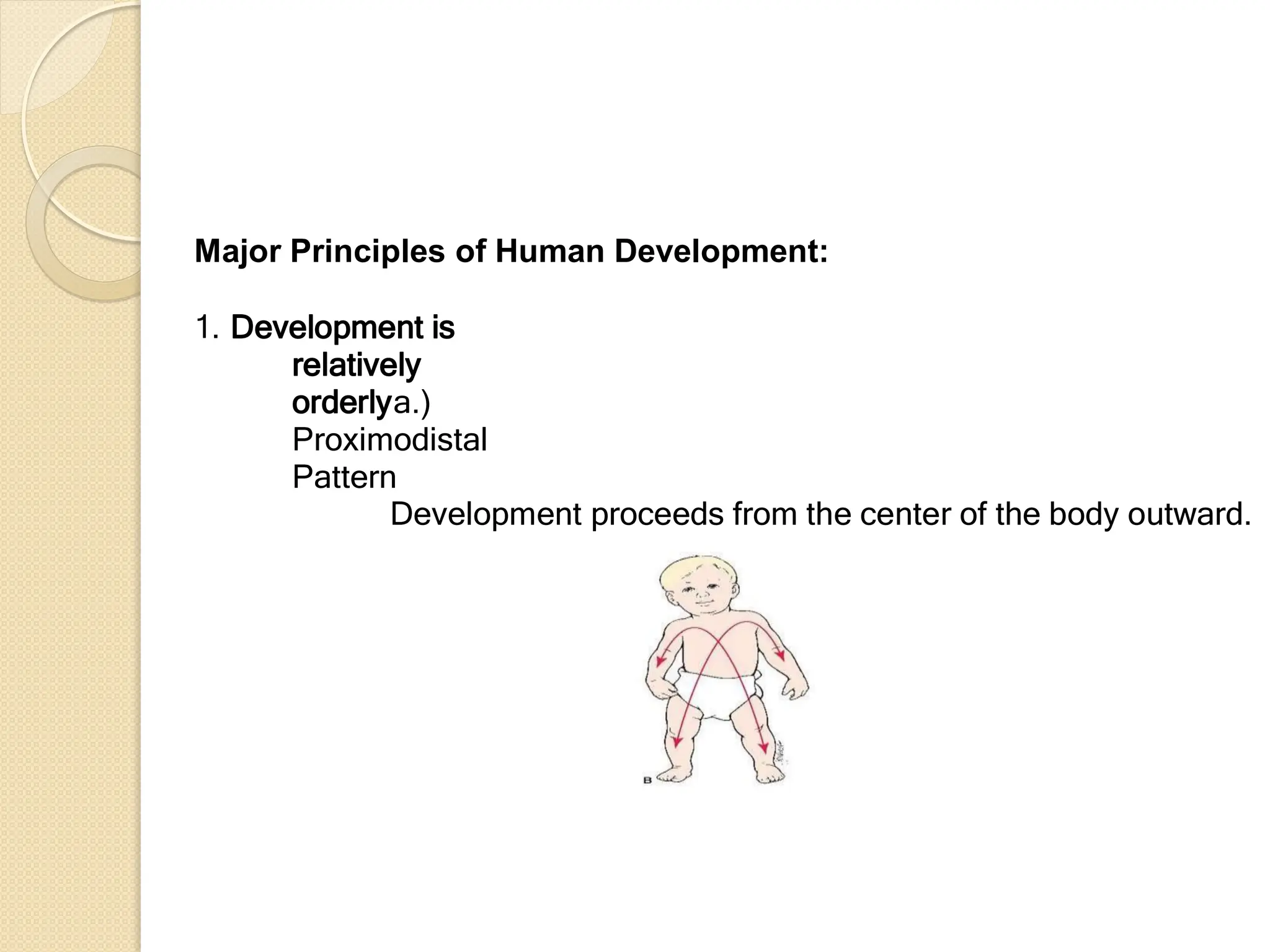
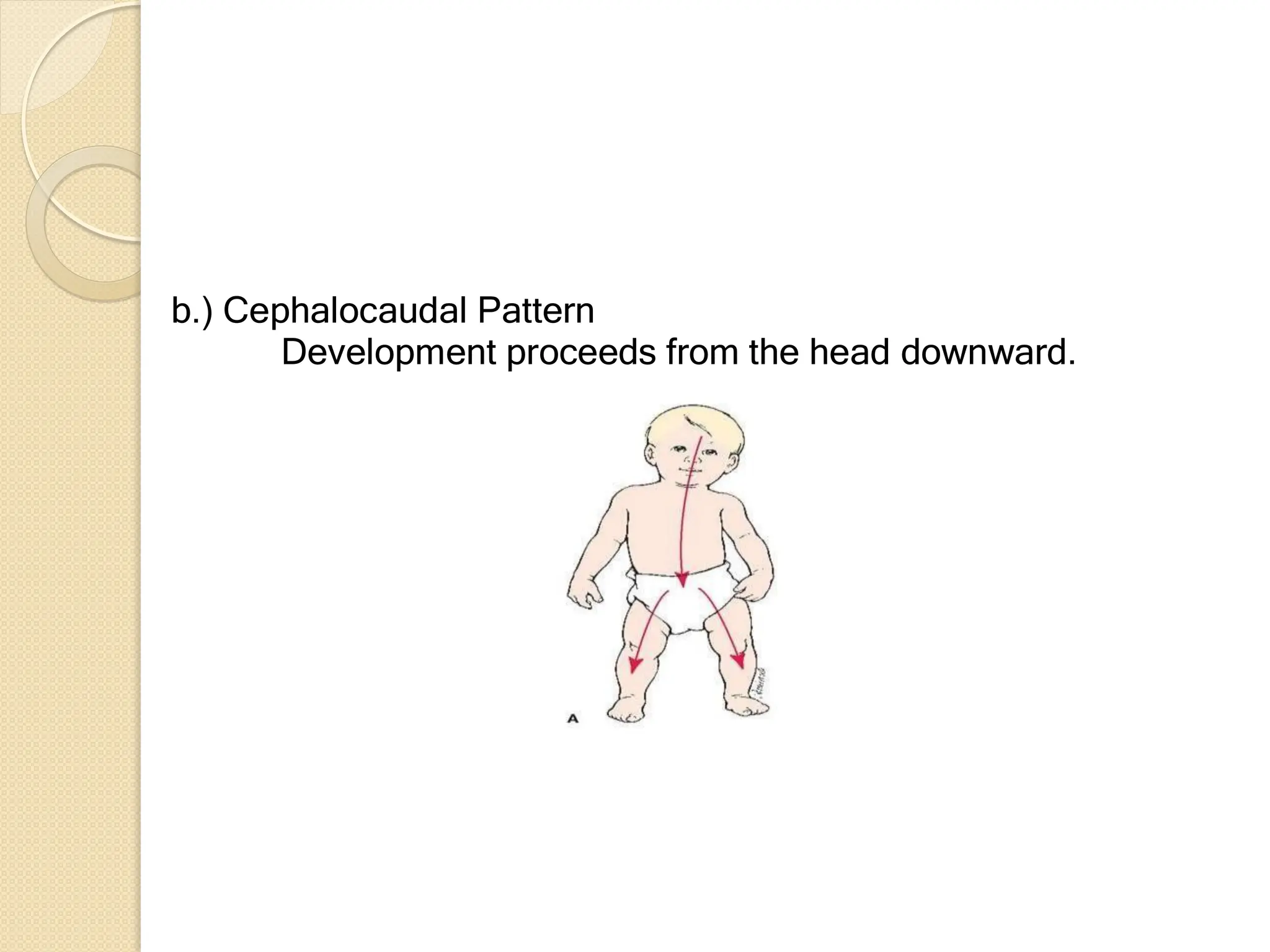
Chapter 1 of the document discusses the meaning, concepts, and approaches of human development, emphasizing that development begins at conception and continues throughout life, encompassing growth and decline. It outlines major principles of development, including orderly progression, dependency on maturation and learning, and the continuous nature of development, while highlighting key aspects such as physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development. The chapter also contrasts traditional and life-span approaches to understanding development, stressing the significance of individual differences and the impact of early experiences on later growth and learning.