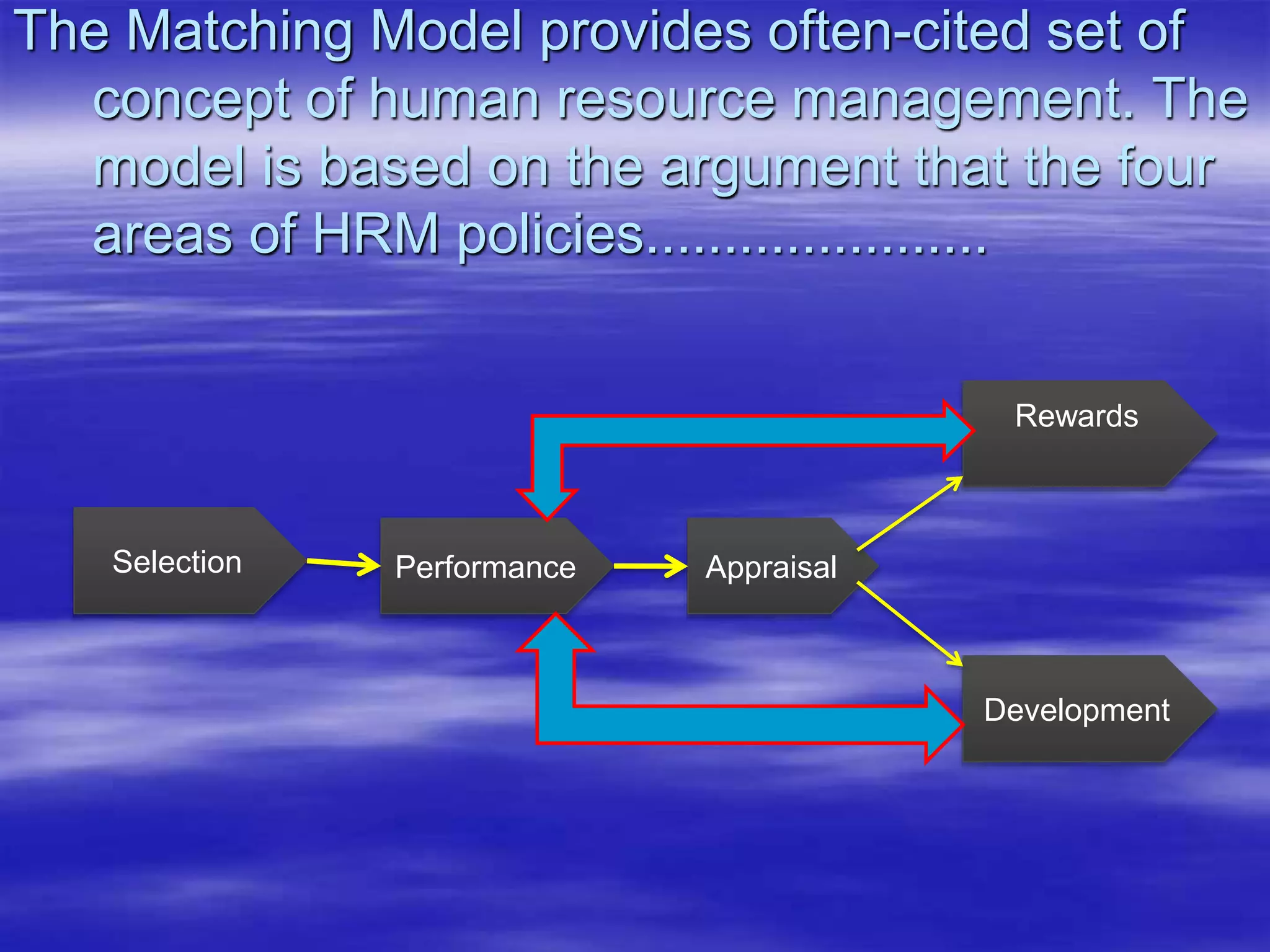
The document discusses two popular models of human resource management: the Matching Model and the Harvard Model. The Matching Model suggests that a company's strategy, structure, human resource management system, and external environment should all closely align. The Harvard Model outlines four areas of HR policy and their relationship to organizational outcomes and consequences. It proposes that HR policies should aim to achieve commitment, congruence, competence and cost effectiveness among employees.