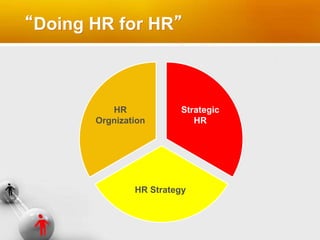
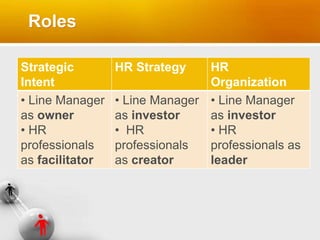
HR professionals are encouraged to apply HR principles to themselves and the HR function in order to be more credible and effective business partners. This involves managing strategic HR, HR strategy, and the HR organization. Strategic HR involves translating business strategies into organizational capabilities through HR practices. Developing an HR strategy establishes the effectiveness and efficiency of HR practices. Examining the HR organization diagnoses strengths and weaknesses to improve how HR services are delivered. HR professionals must model the principles they advocate for others to be truly successful.