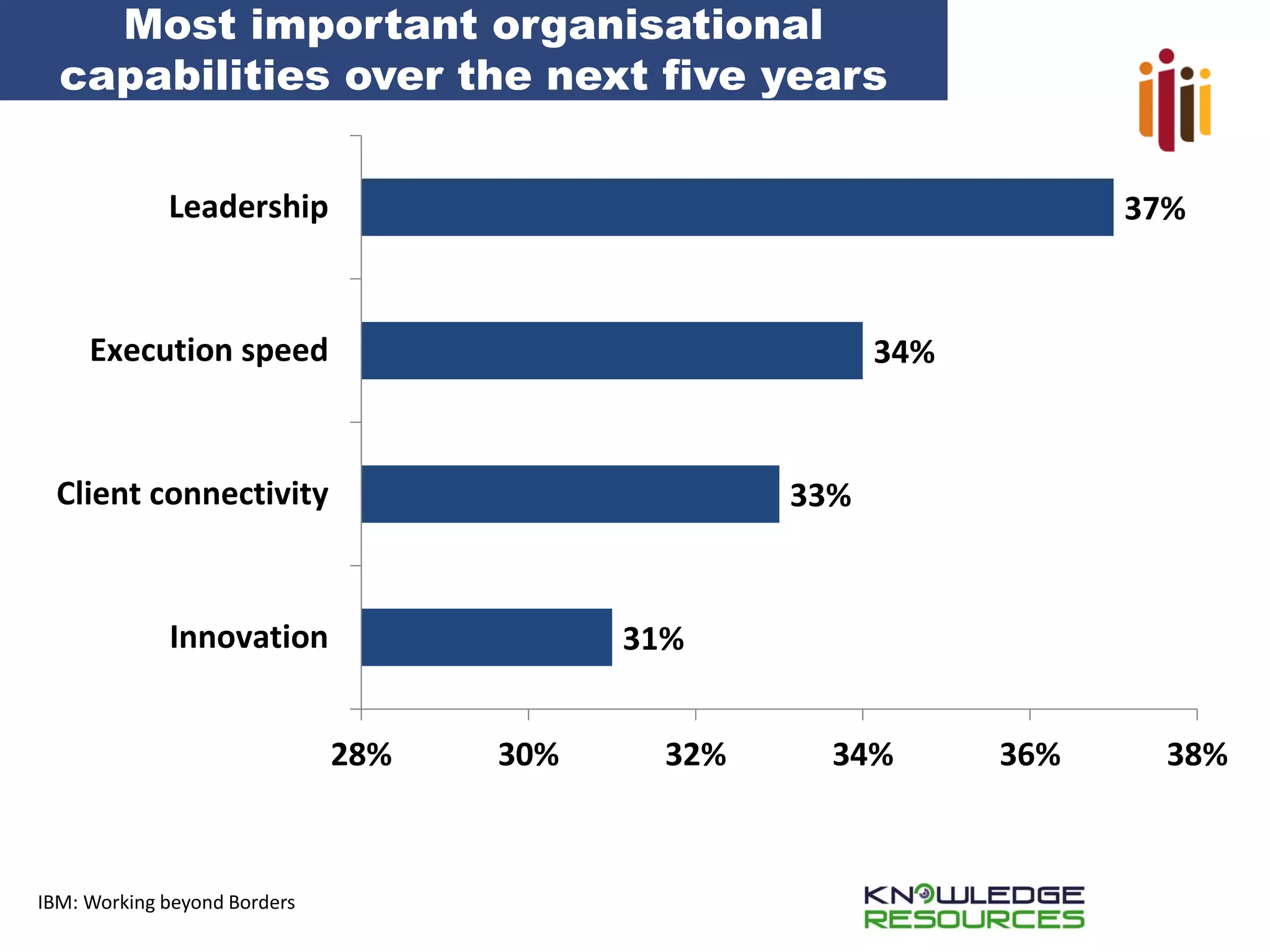
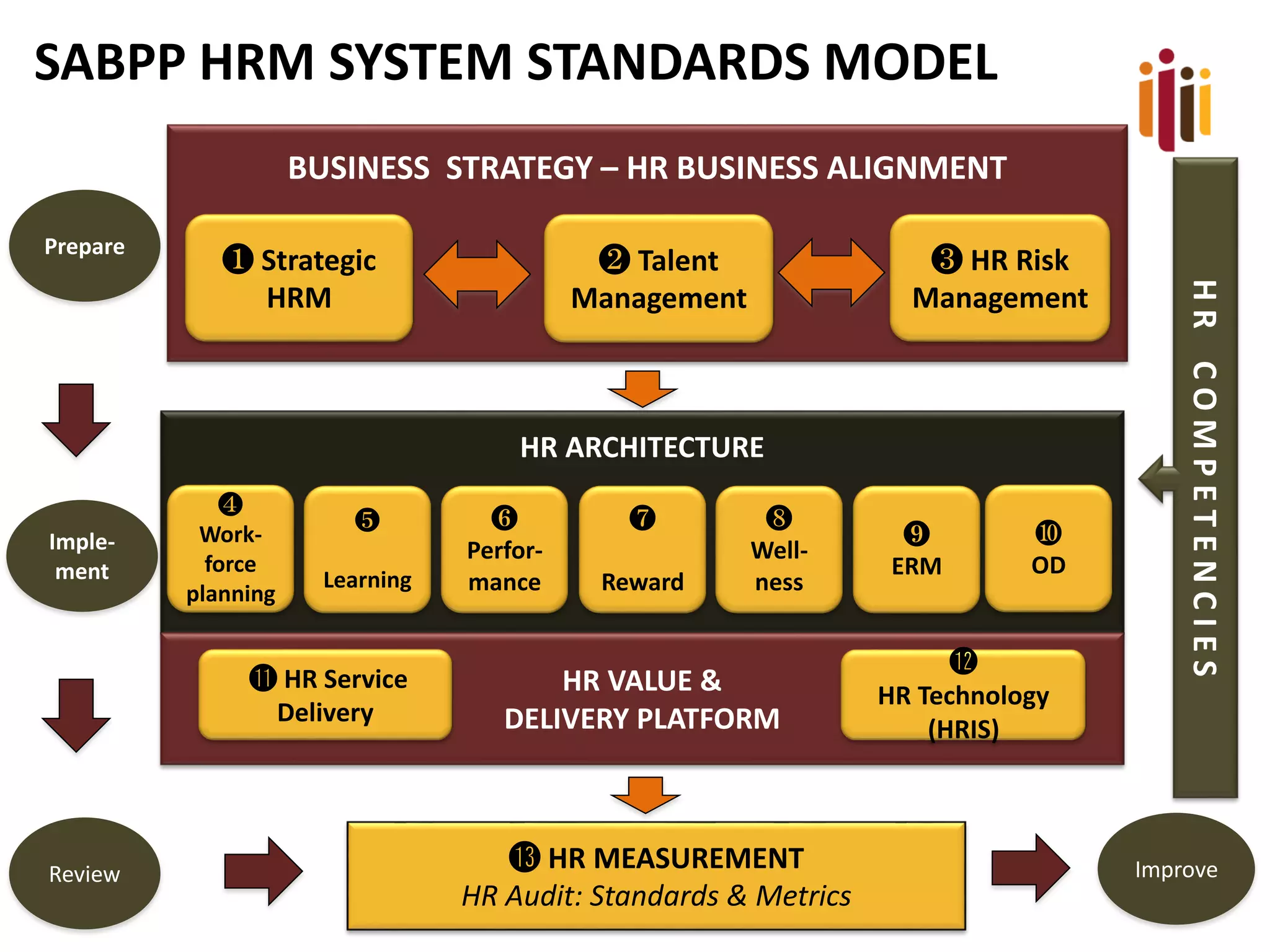
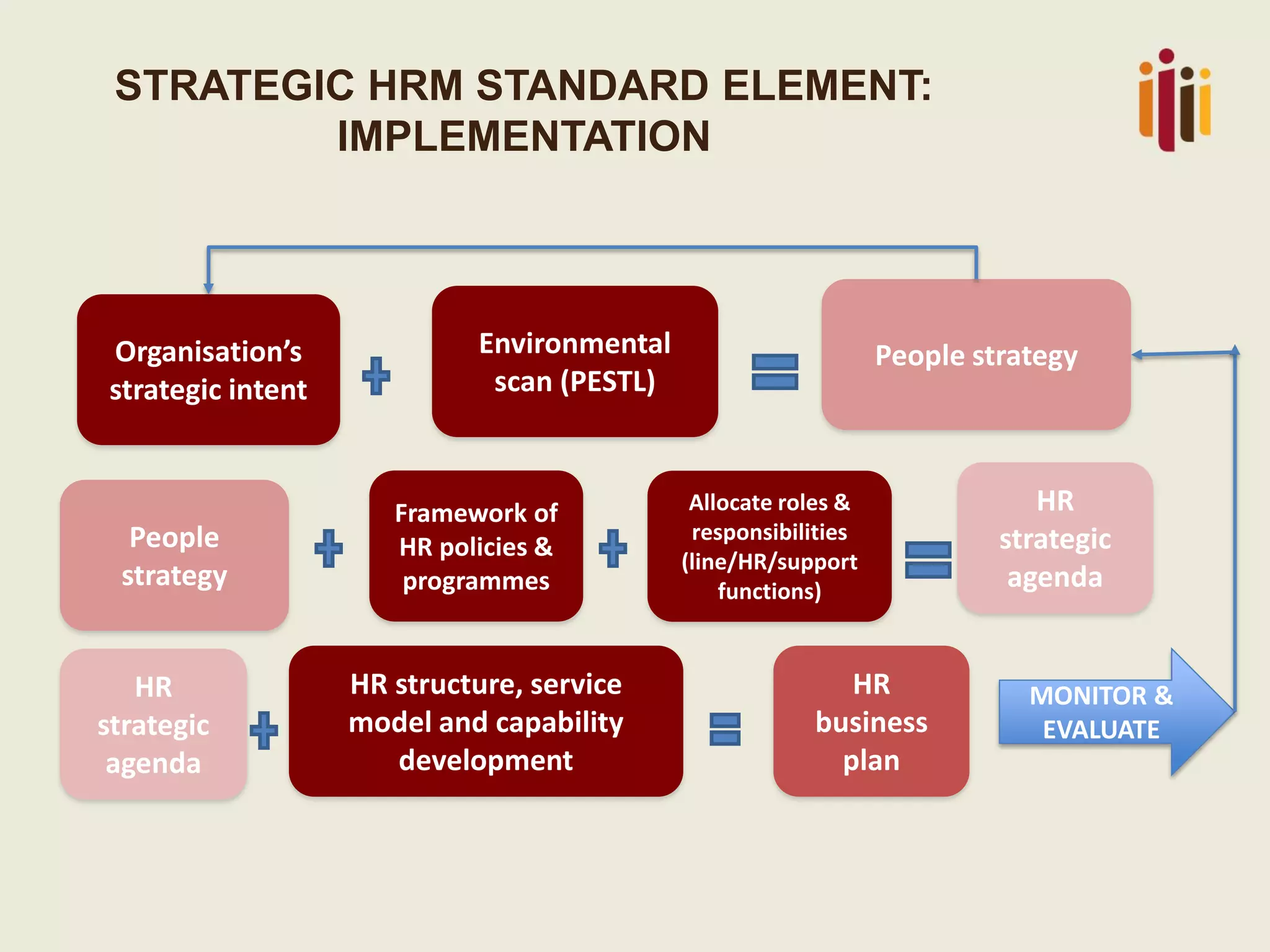
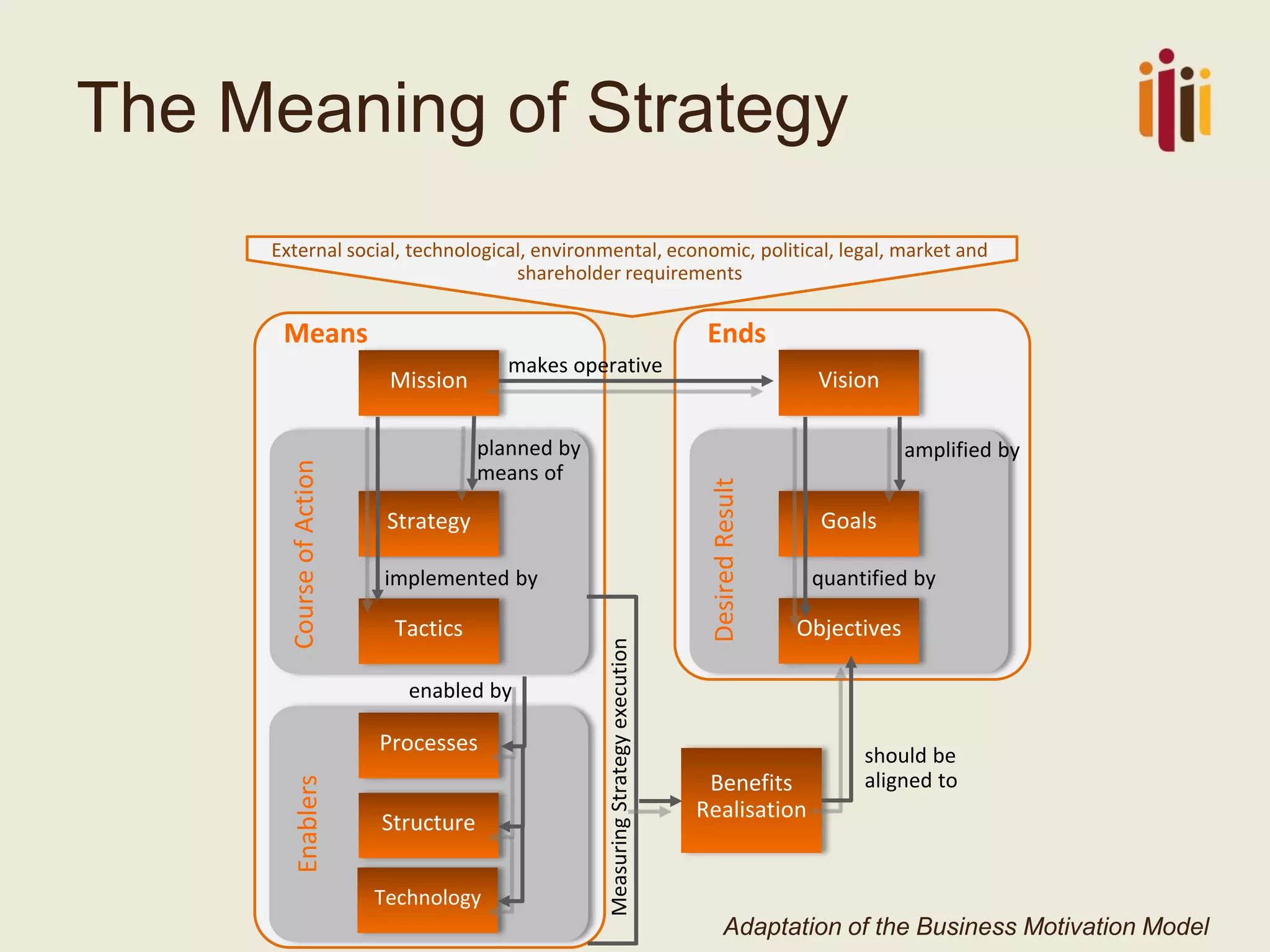
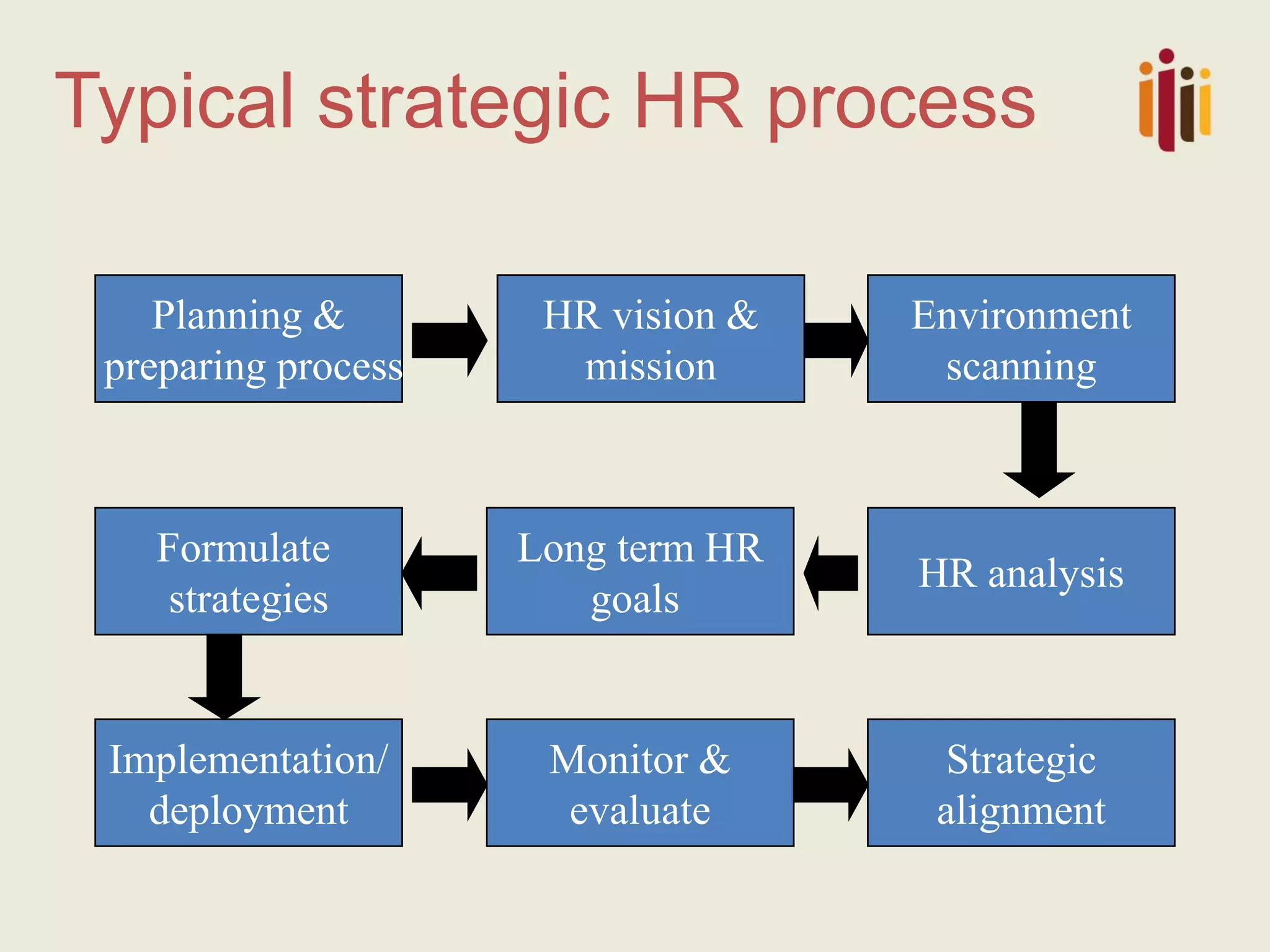
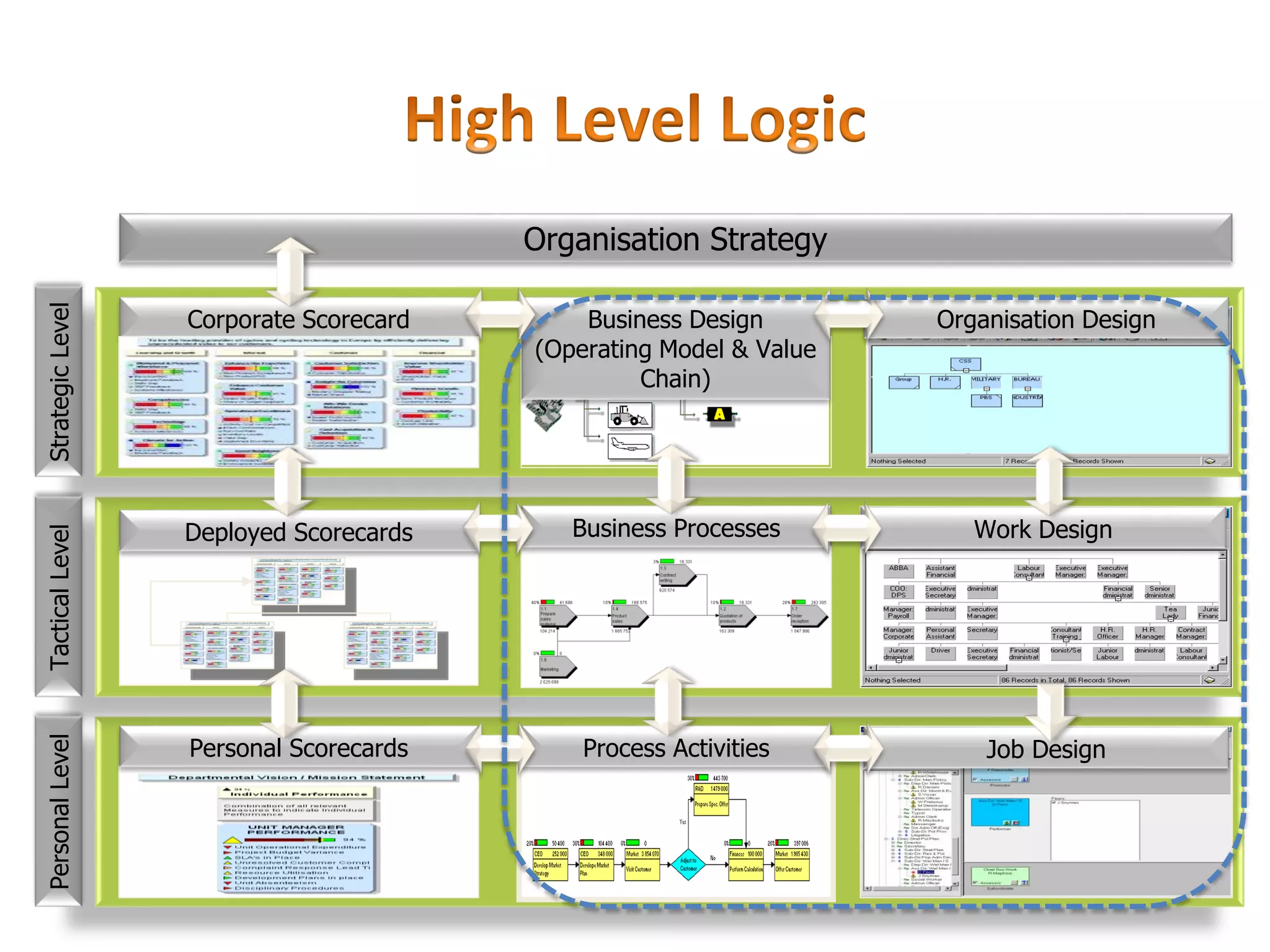
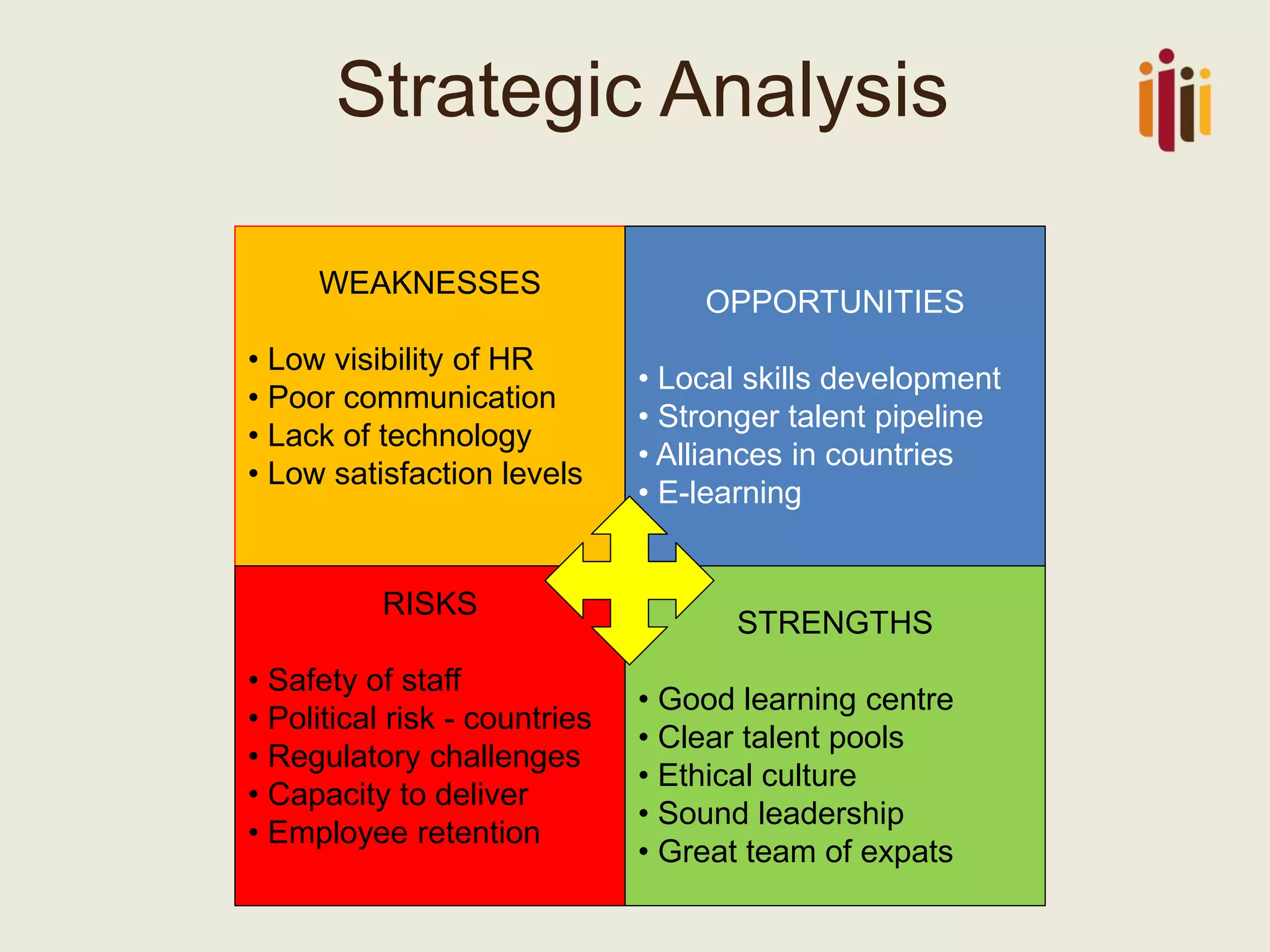
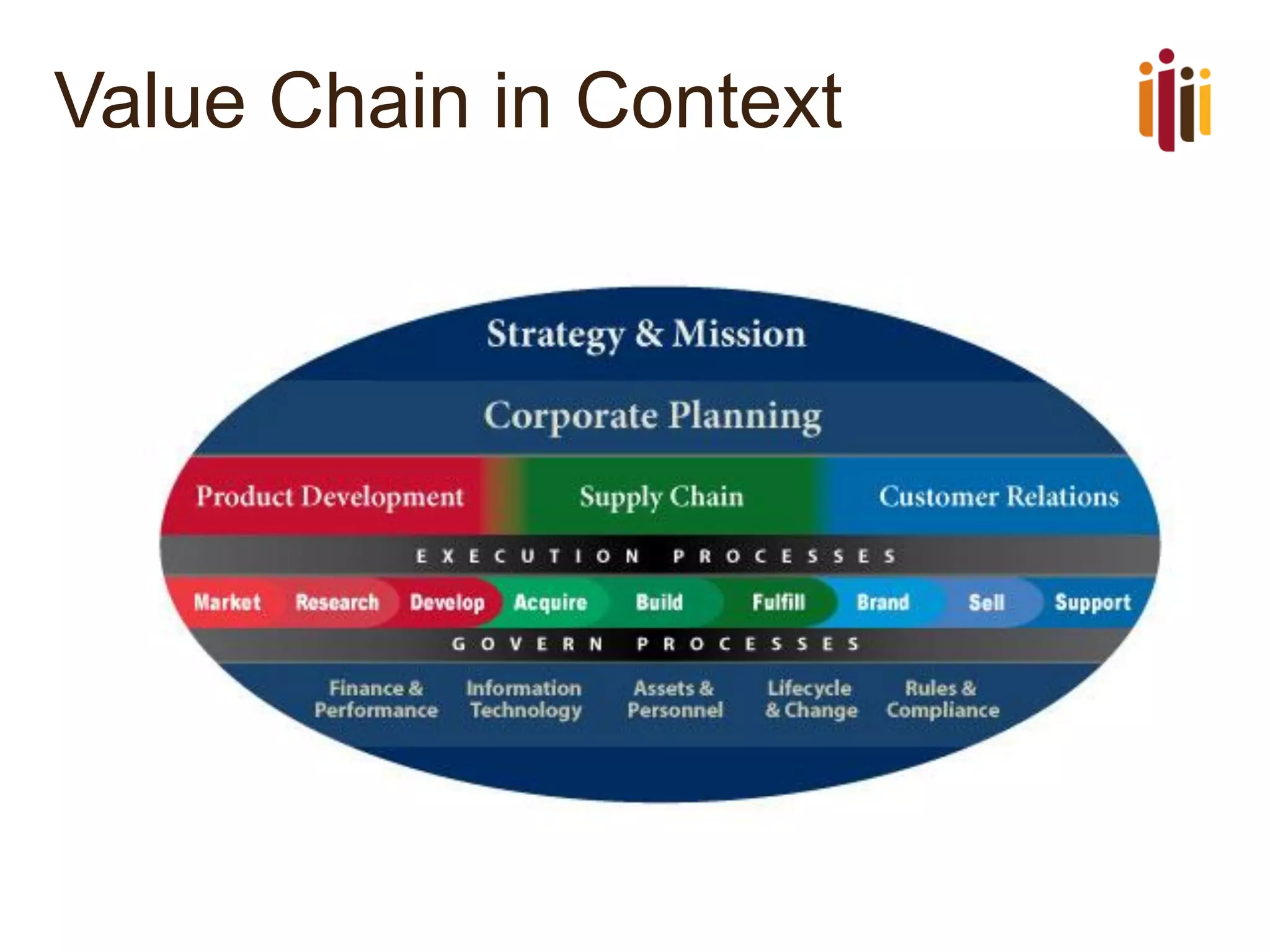
The document discusses the critical role of strategic human resource management (HRM) in aligning HR strategies with organizational objectives, emphasizing the need for HR to be integral to strategic planning. It outlines key priorities for HR, including talent management, employee engagement, and performance metrics, while addressing the importance of adapting HR strategies in response to changing business environments. The document concludes that HR professionals must transition from operational roles to strategic thinkers to ensure effective execution of HR strategies and drive organizational success.