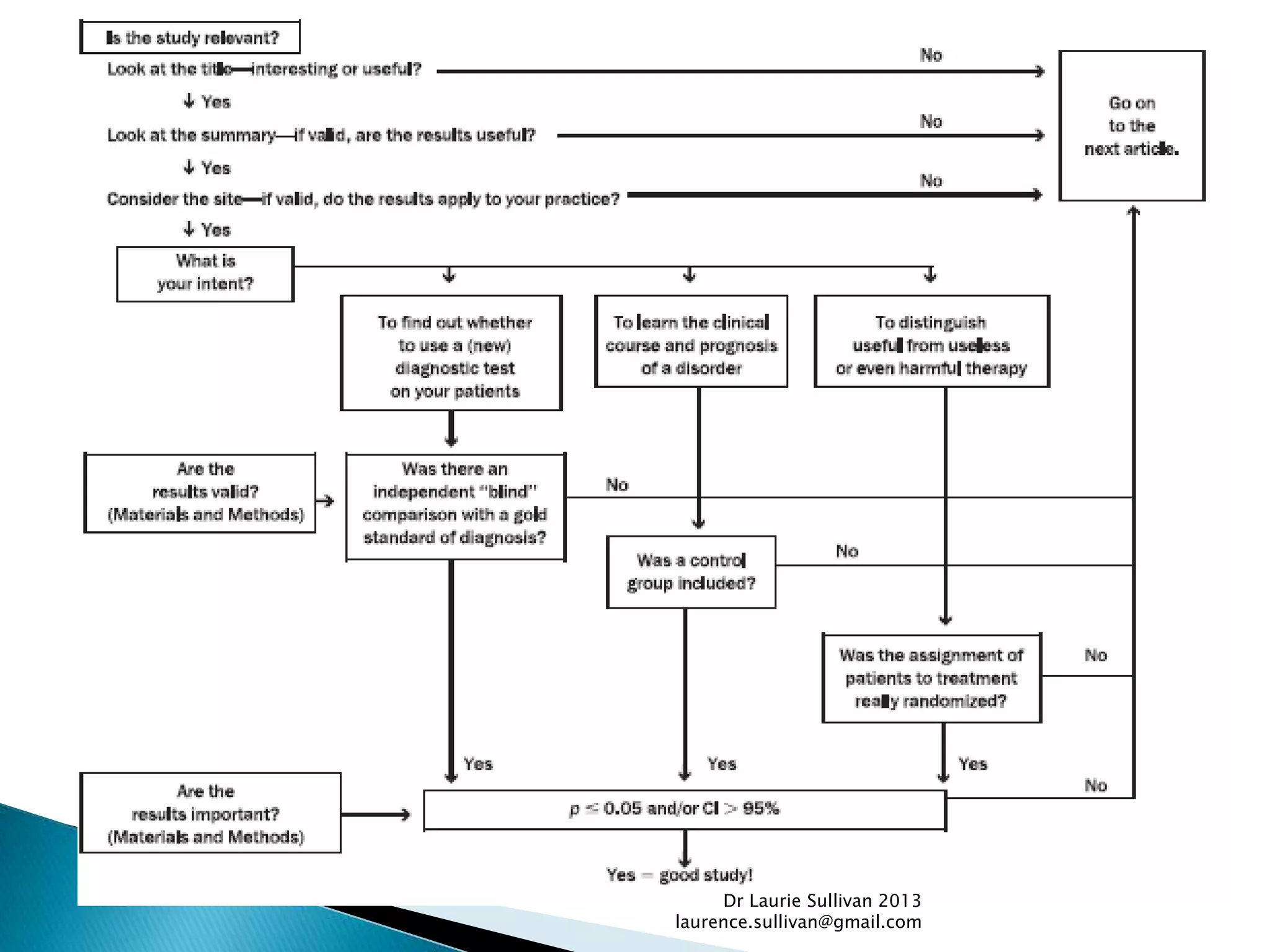
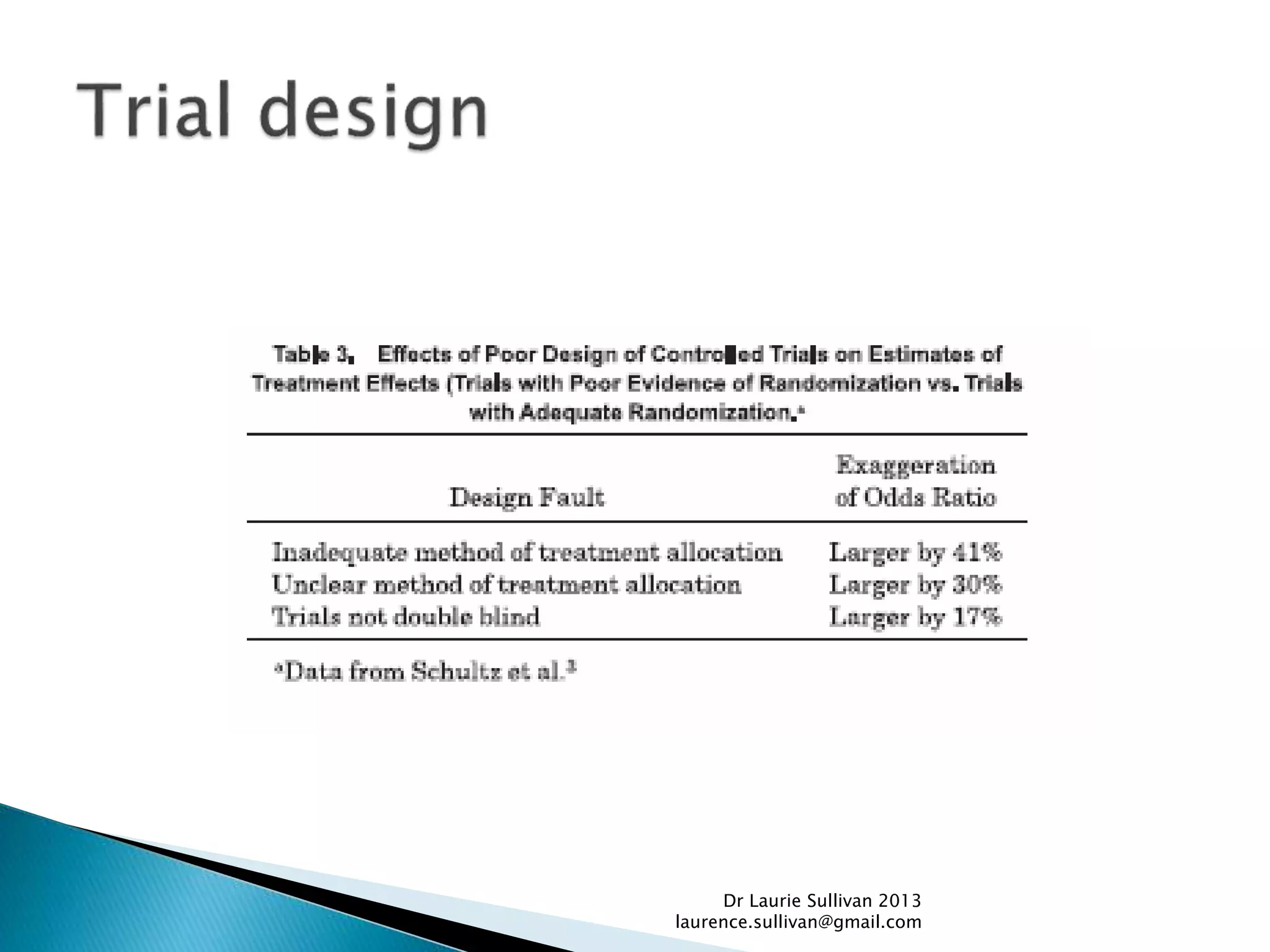
This document provides guidance on how to critically evaluate medical research papers and literature. It discusses key aspects of research papers such as the importance of lifelong learning, using evidence to support clinical practice, and evaluating new treatments. The document also provides tips on how to review different sections of papers, including evaluating the methods, abstract, conclusions, and statistical analysis. Overall, the document aims to teach physicians how to properly assess the validity and reliability of medical research.