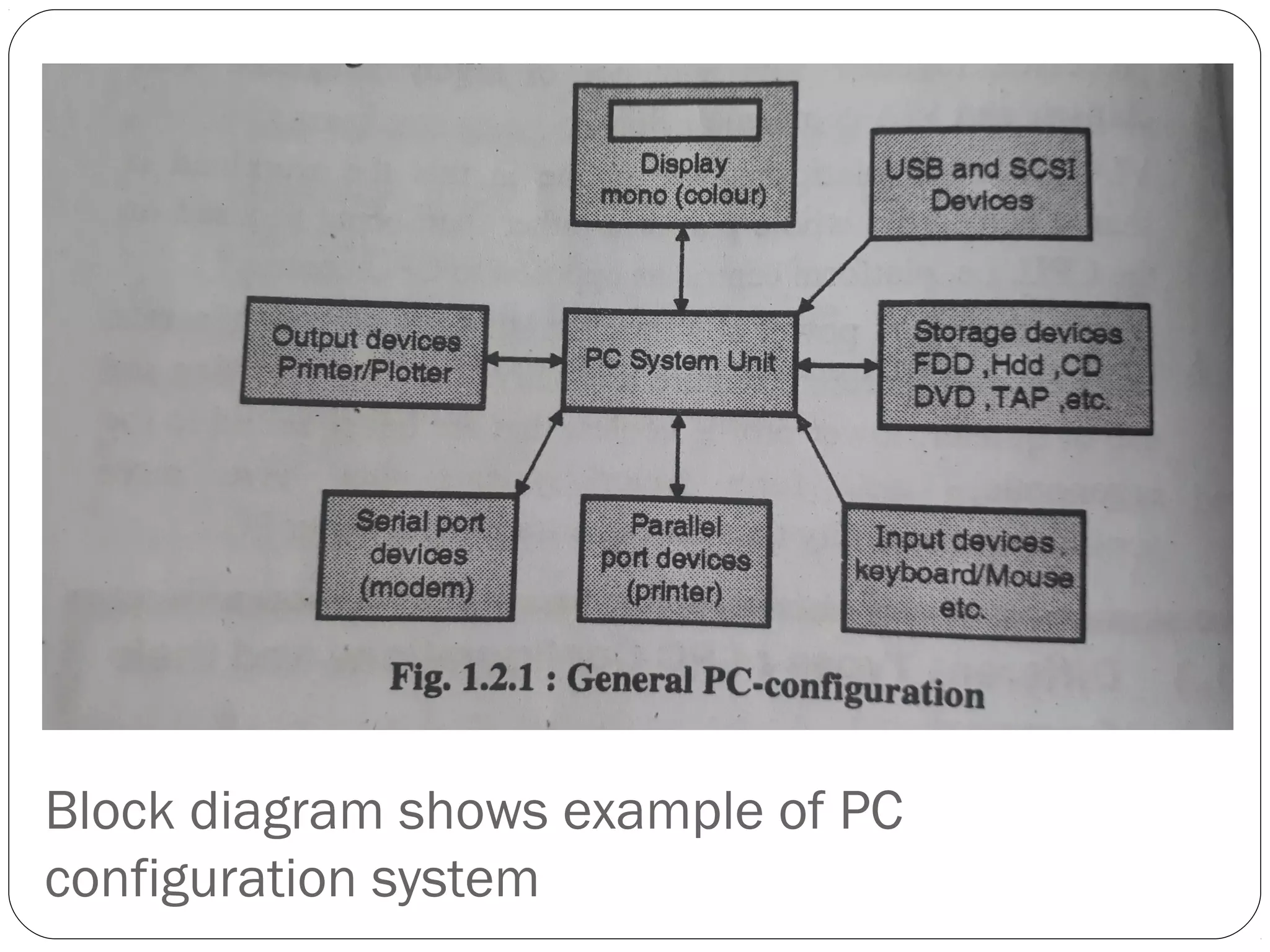
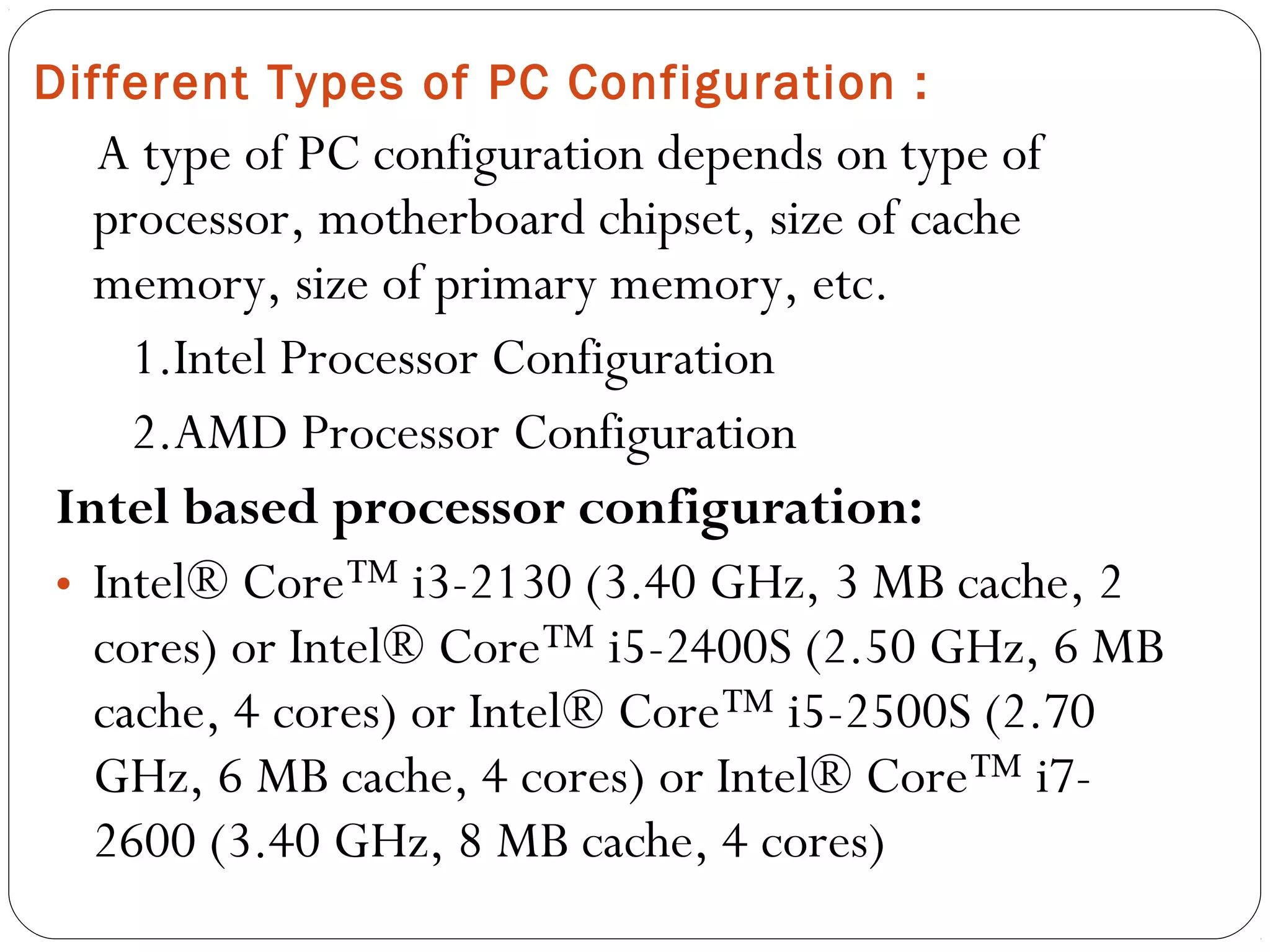
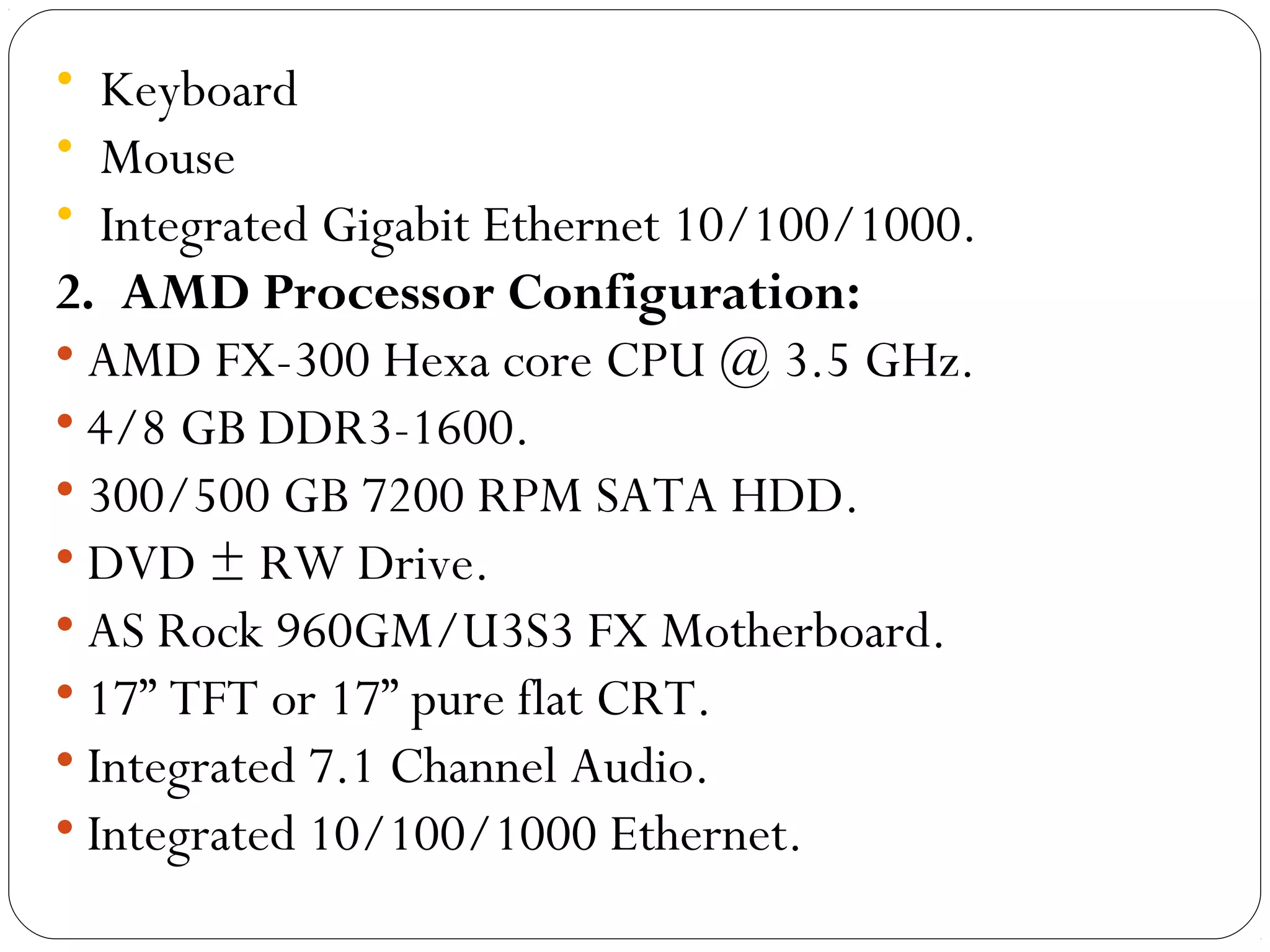
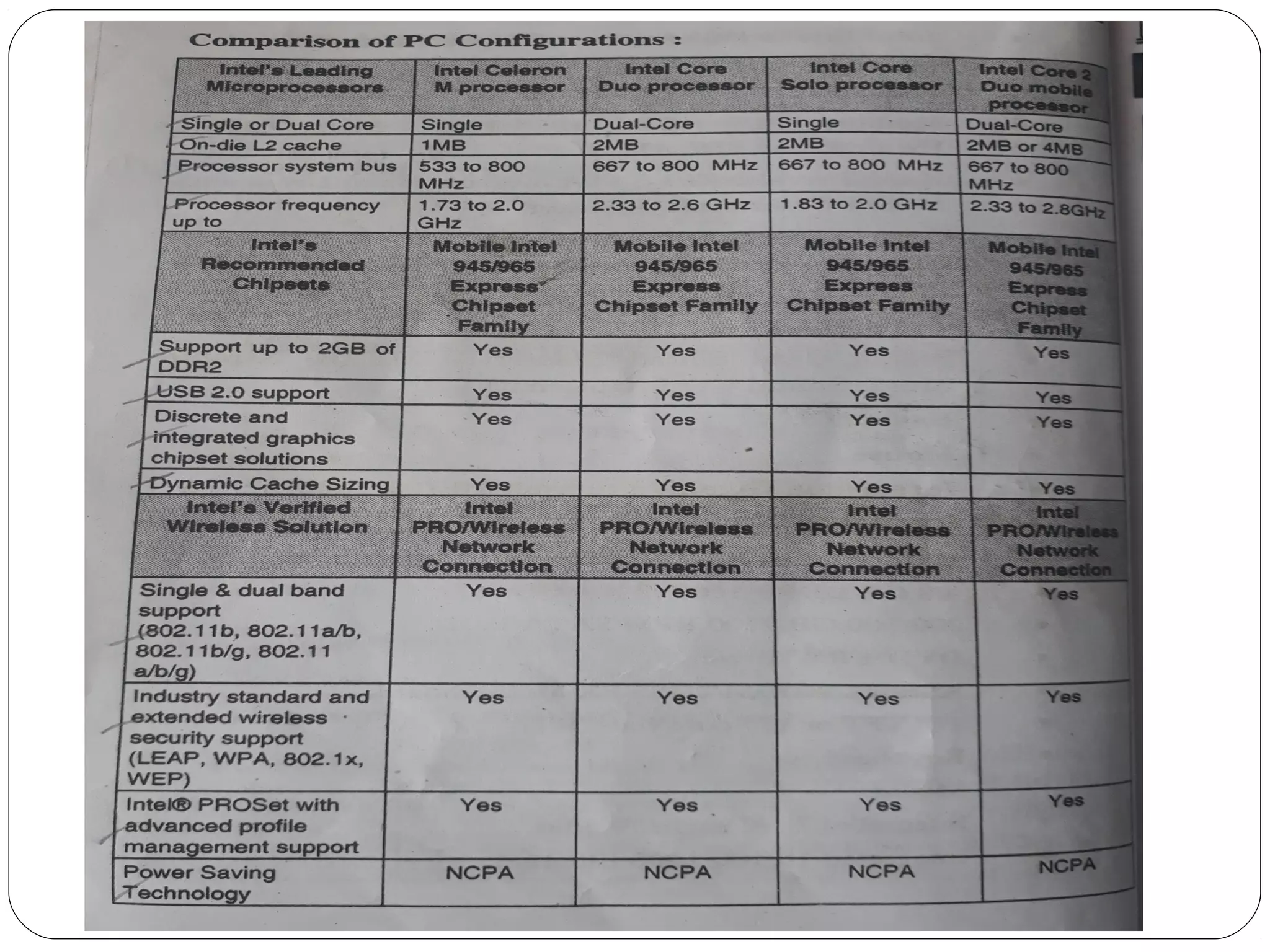
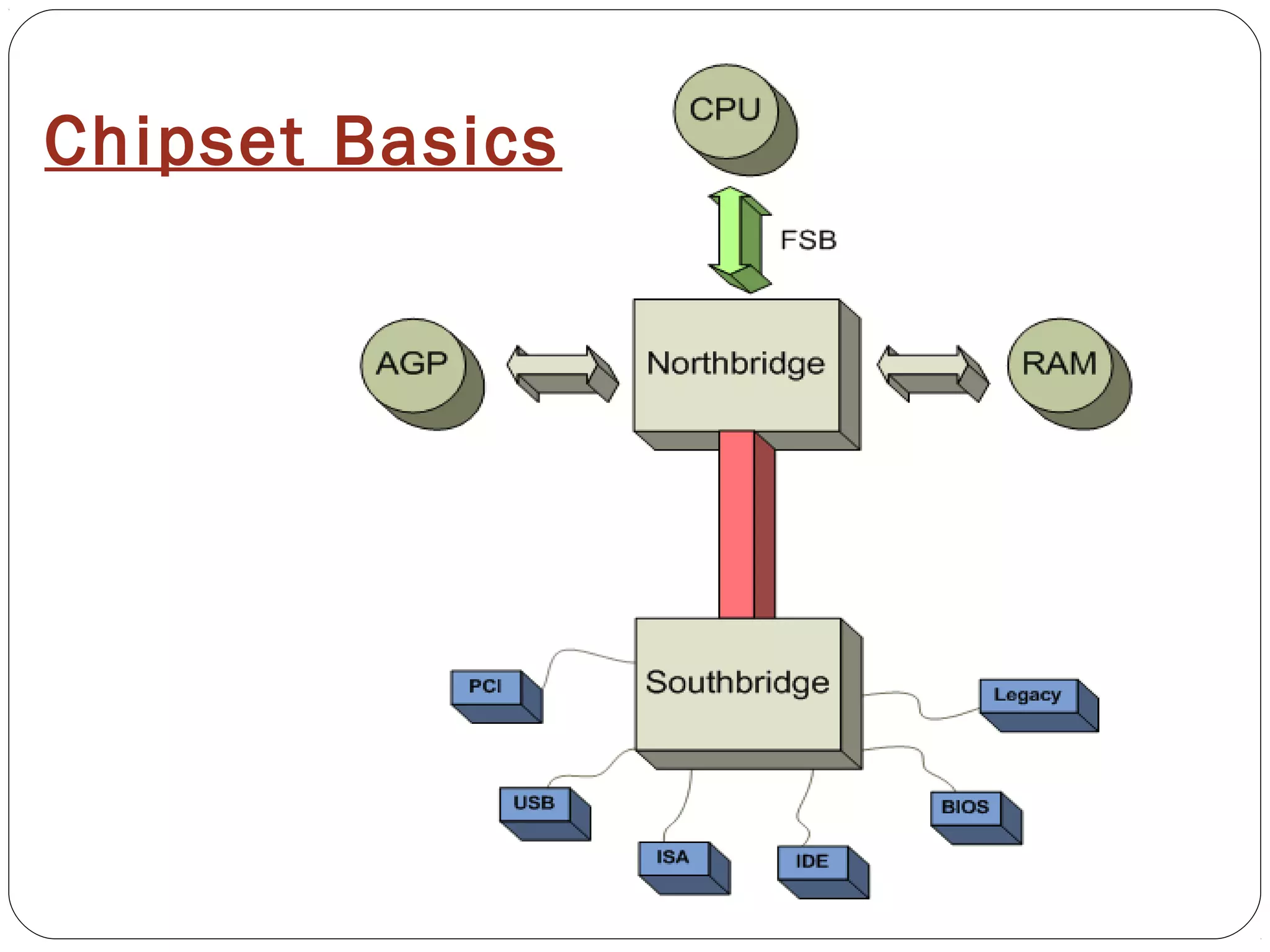
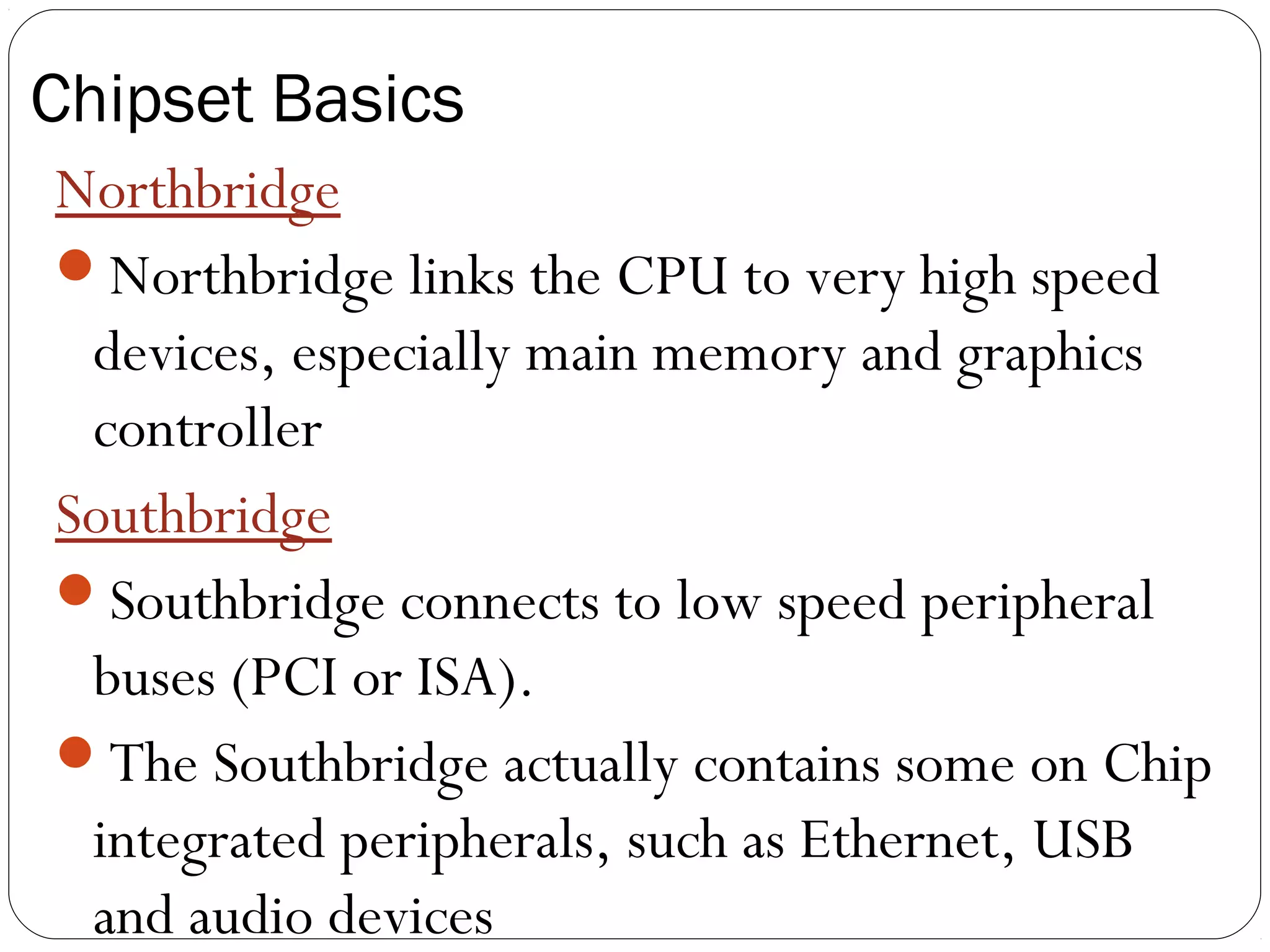
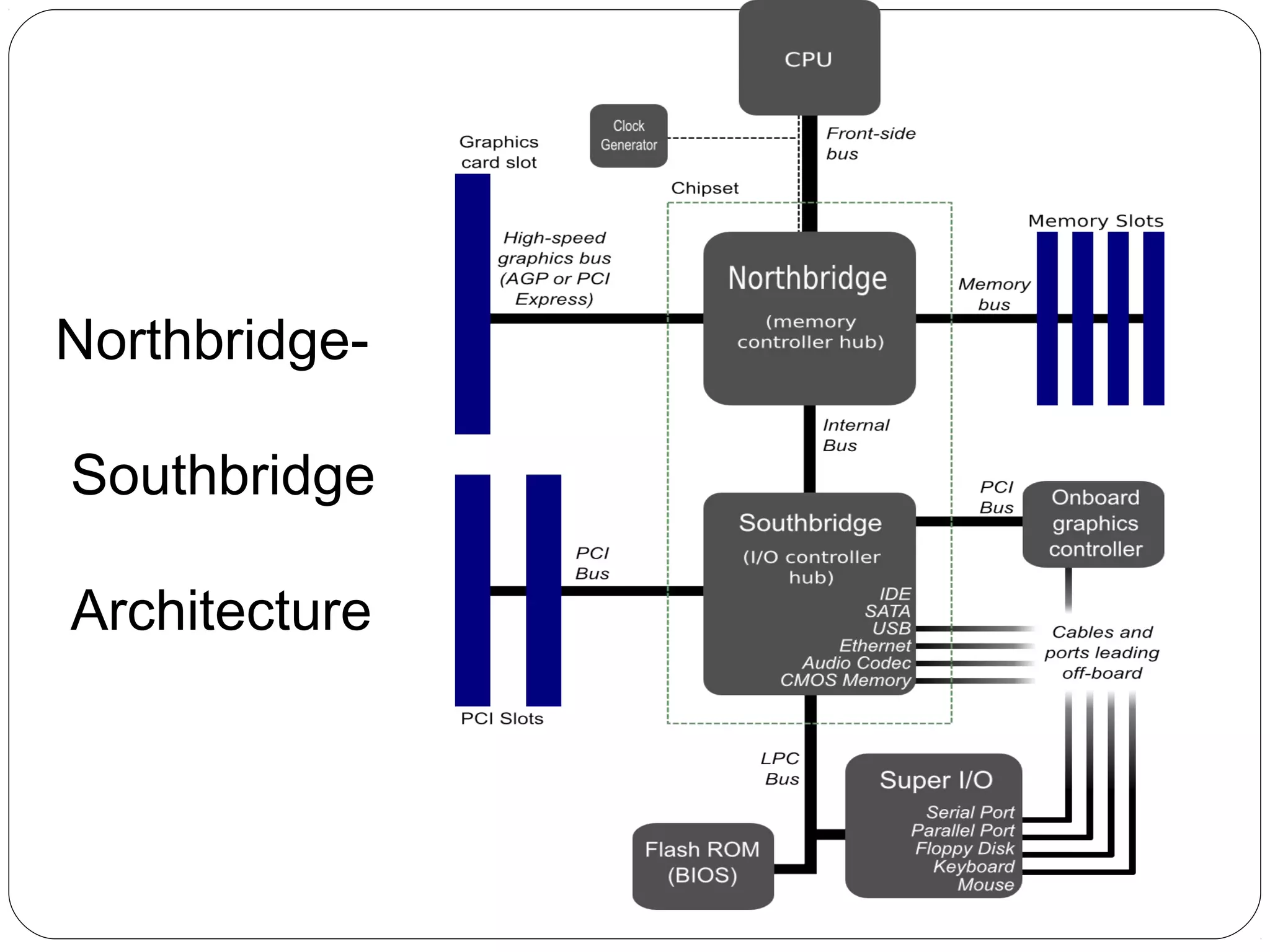
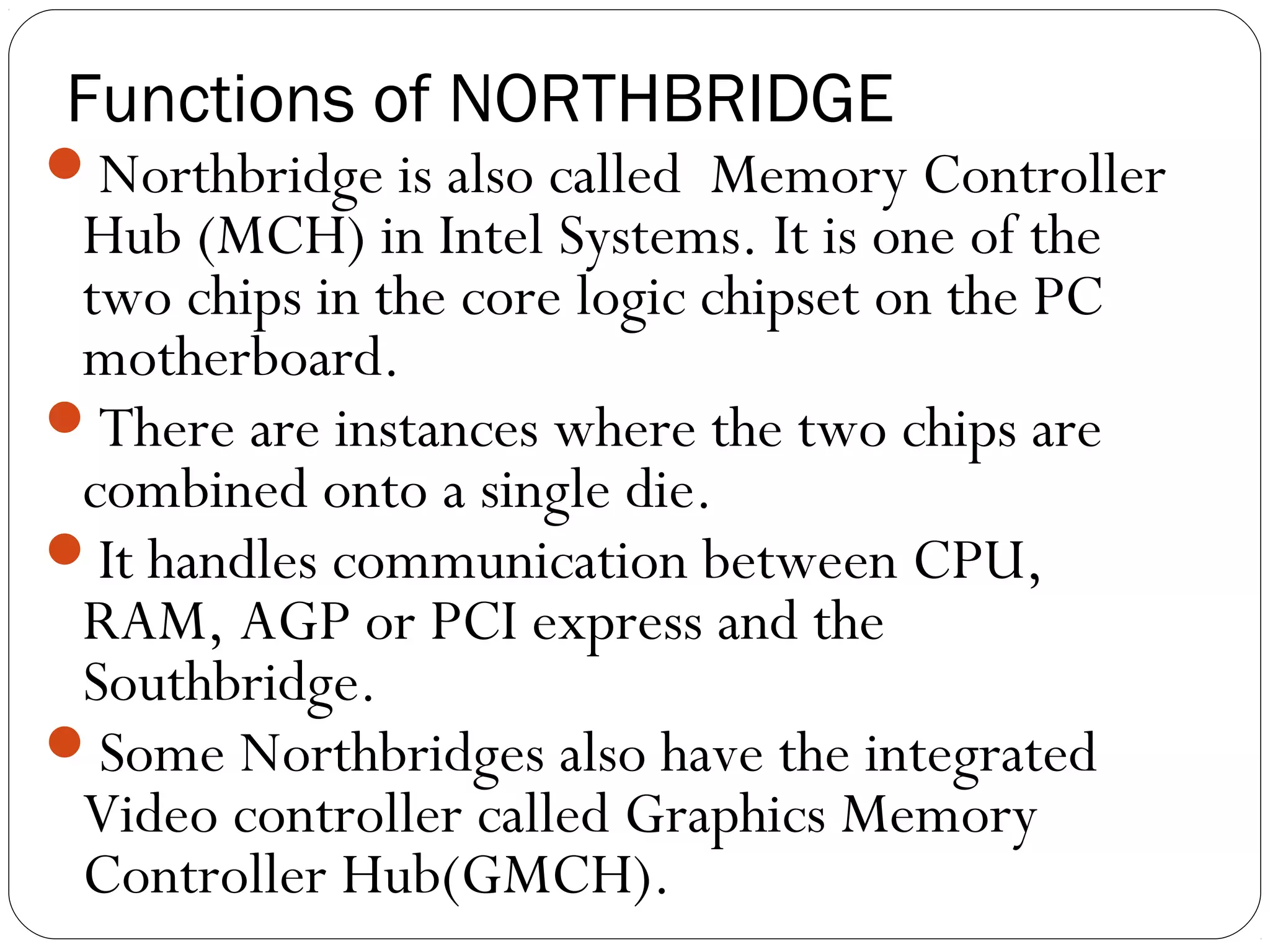
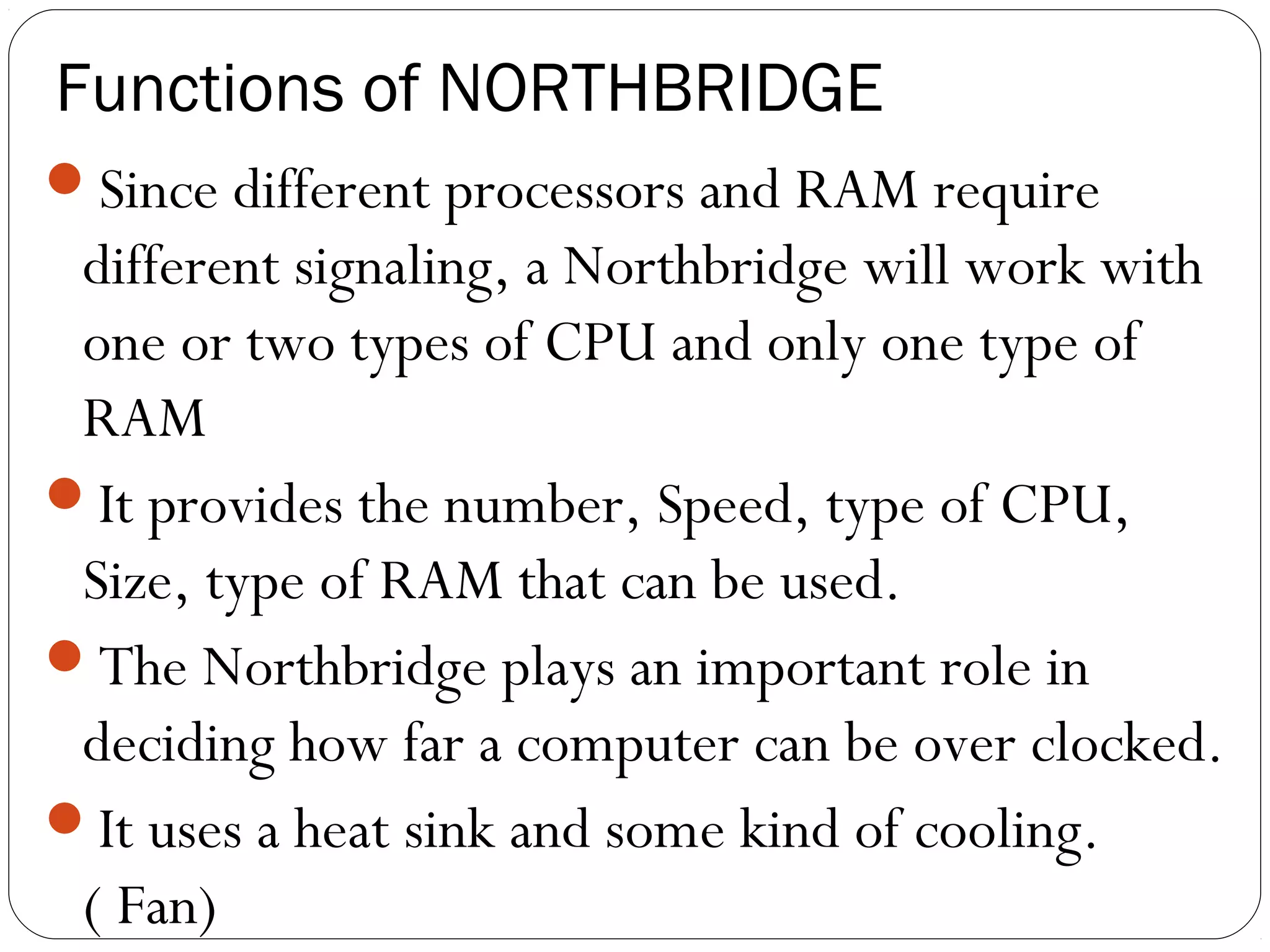
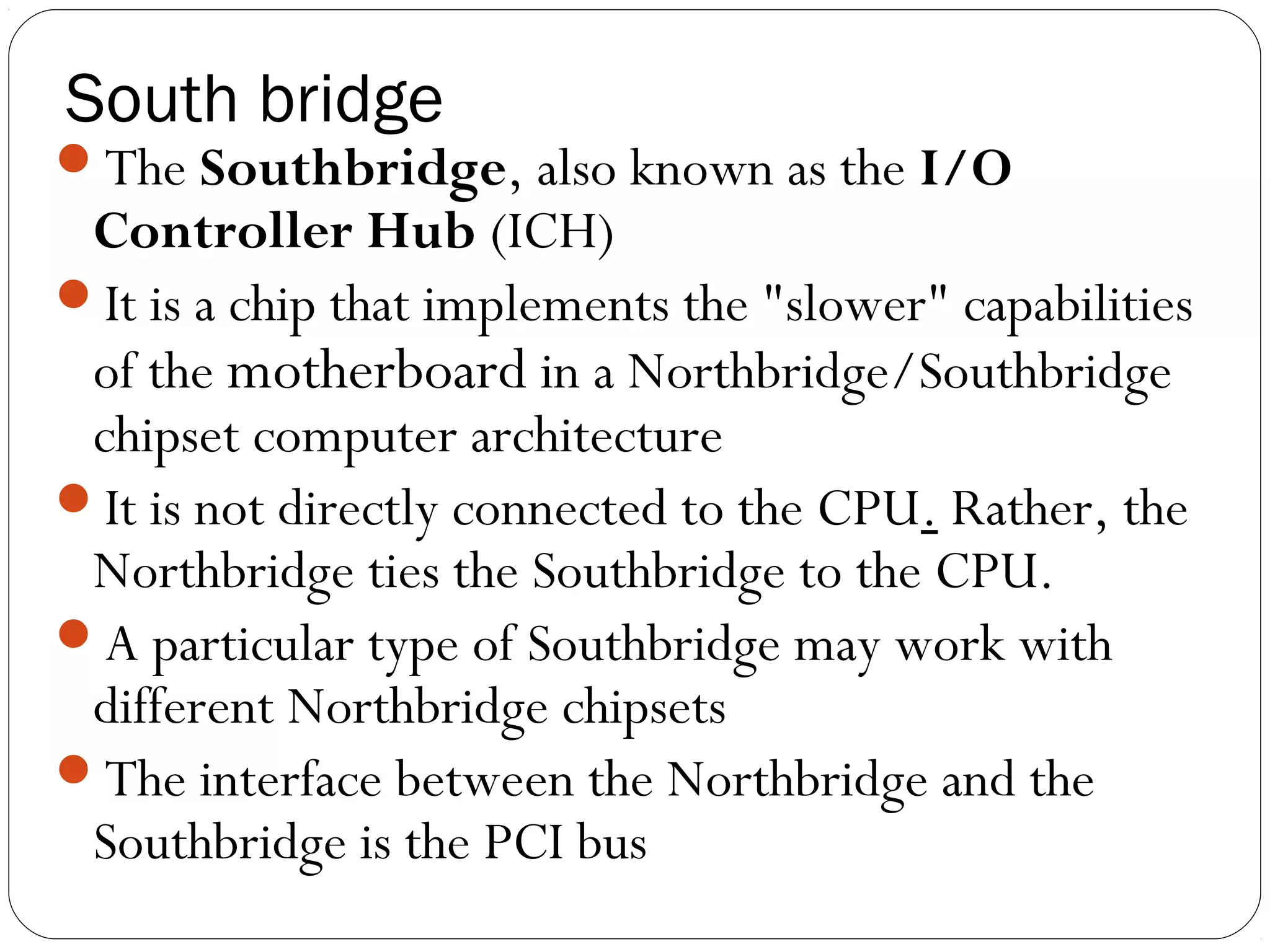
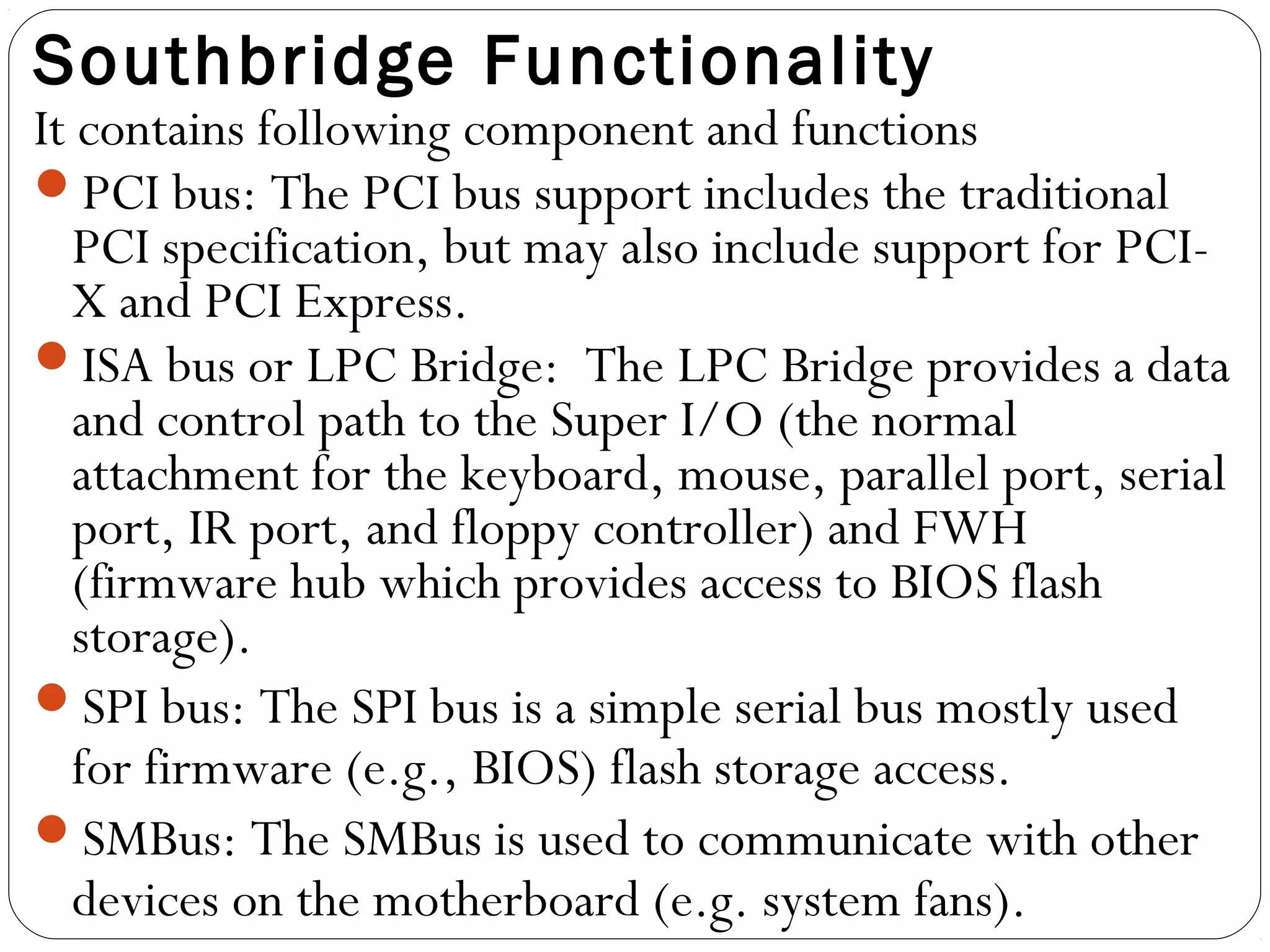
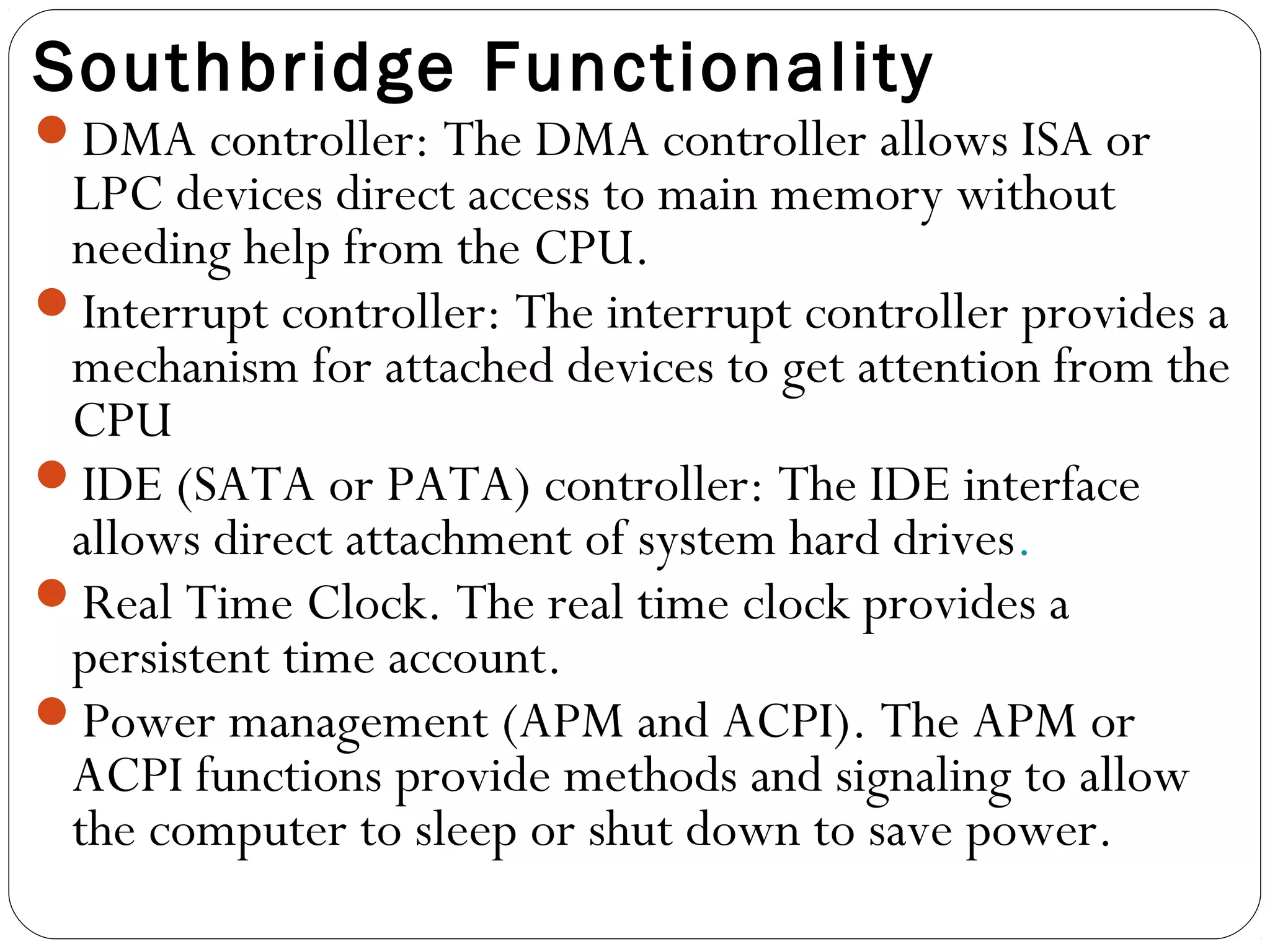
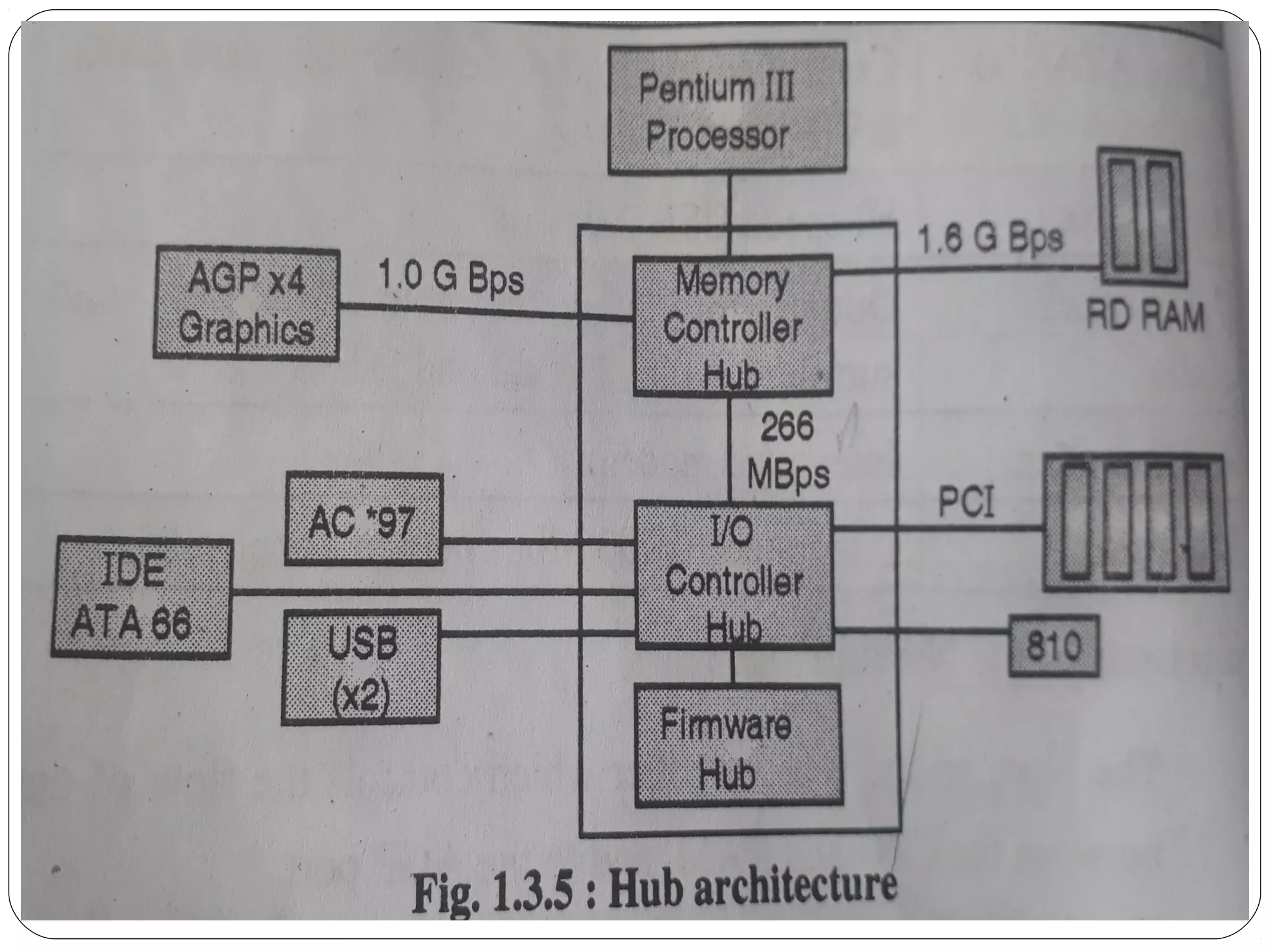
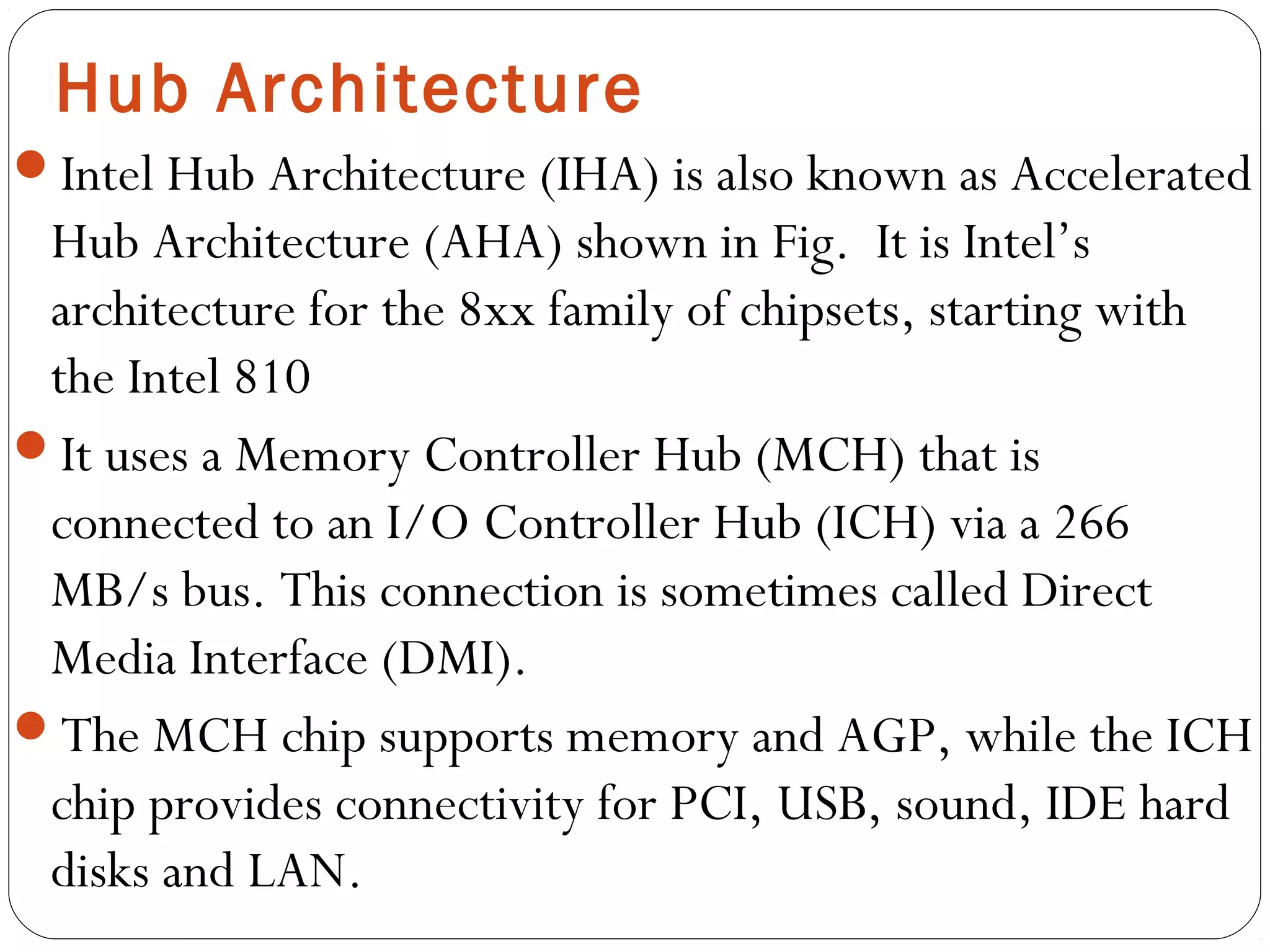
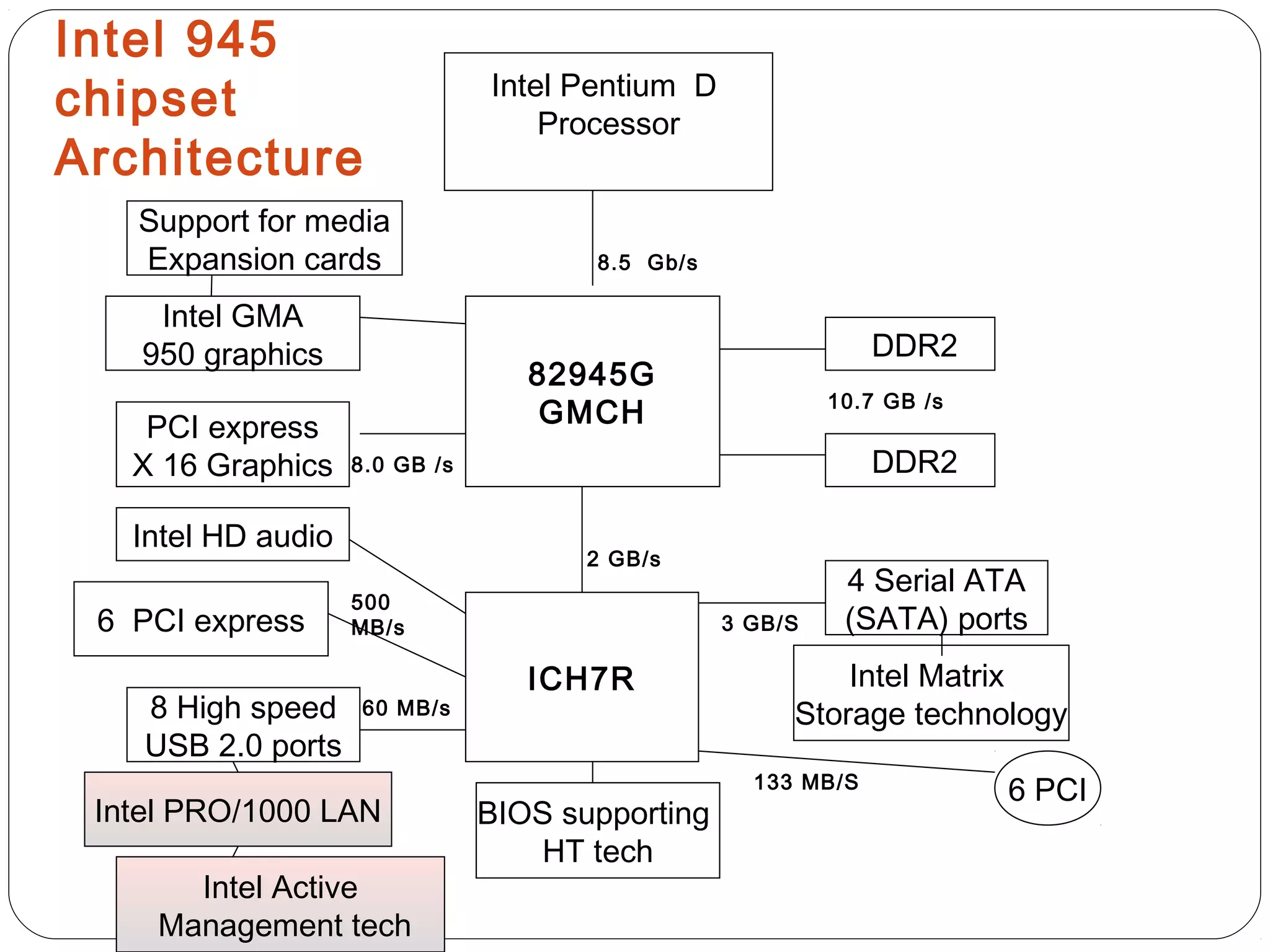
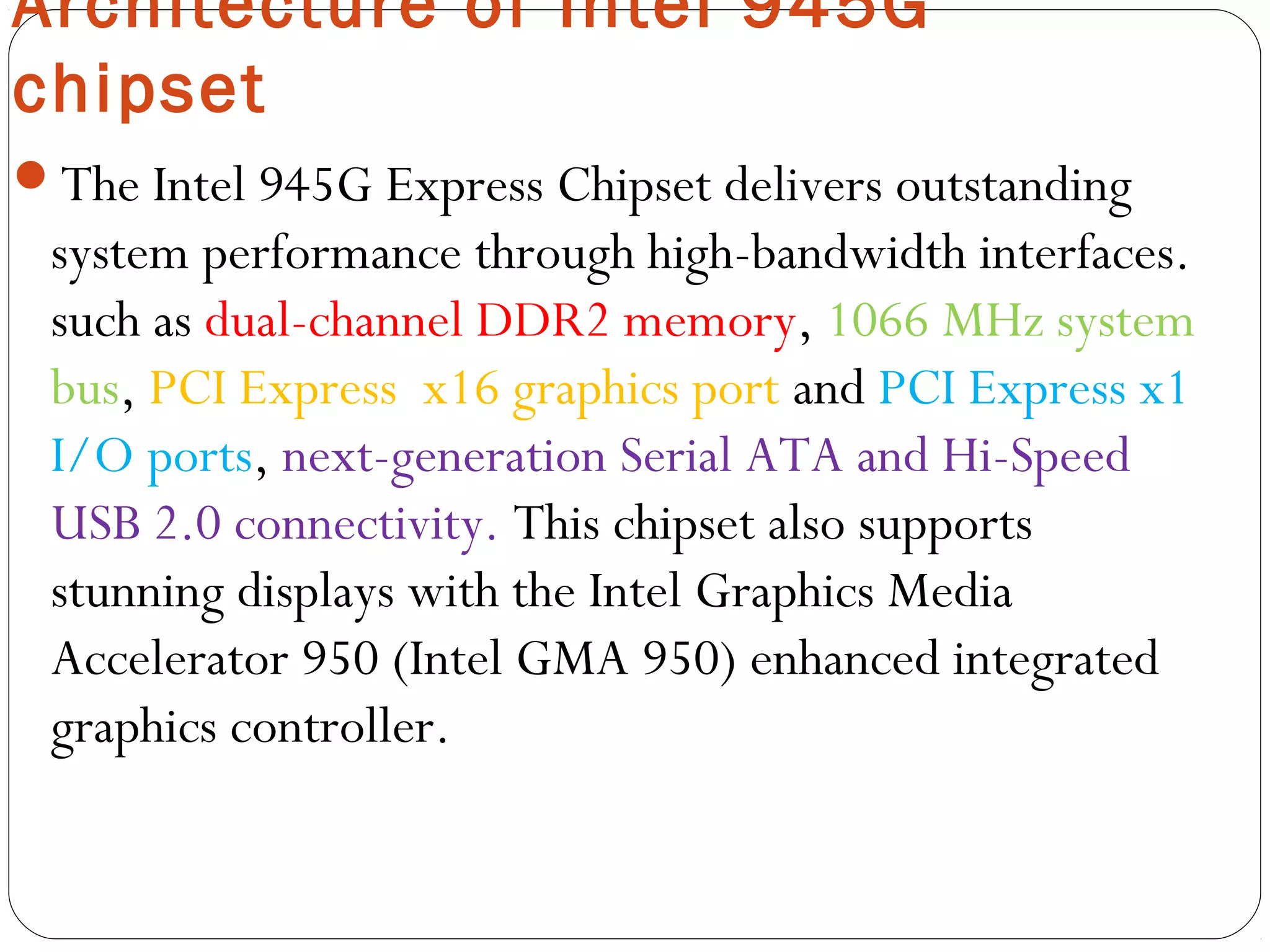
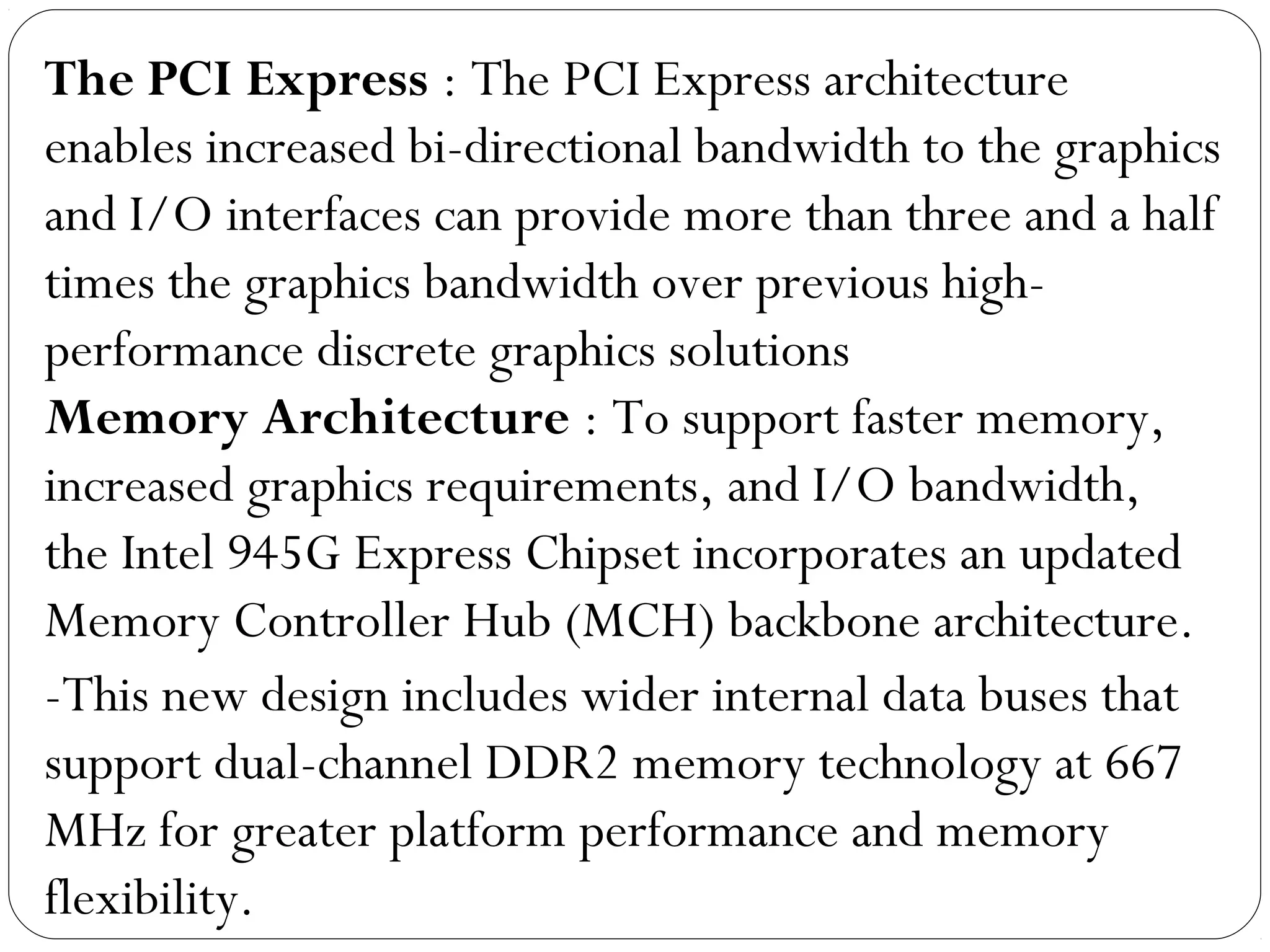
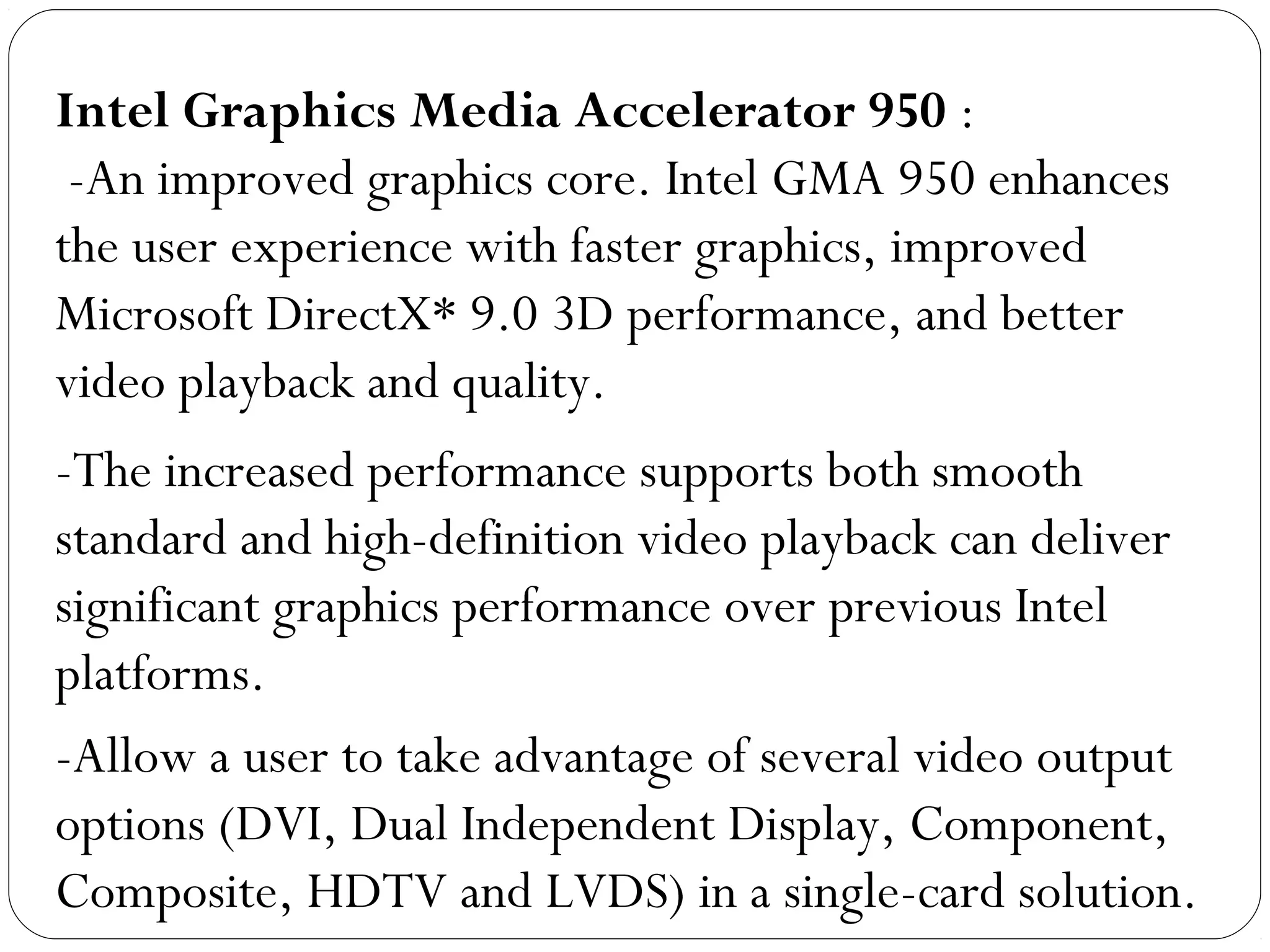
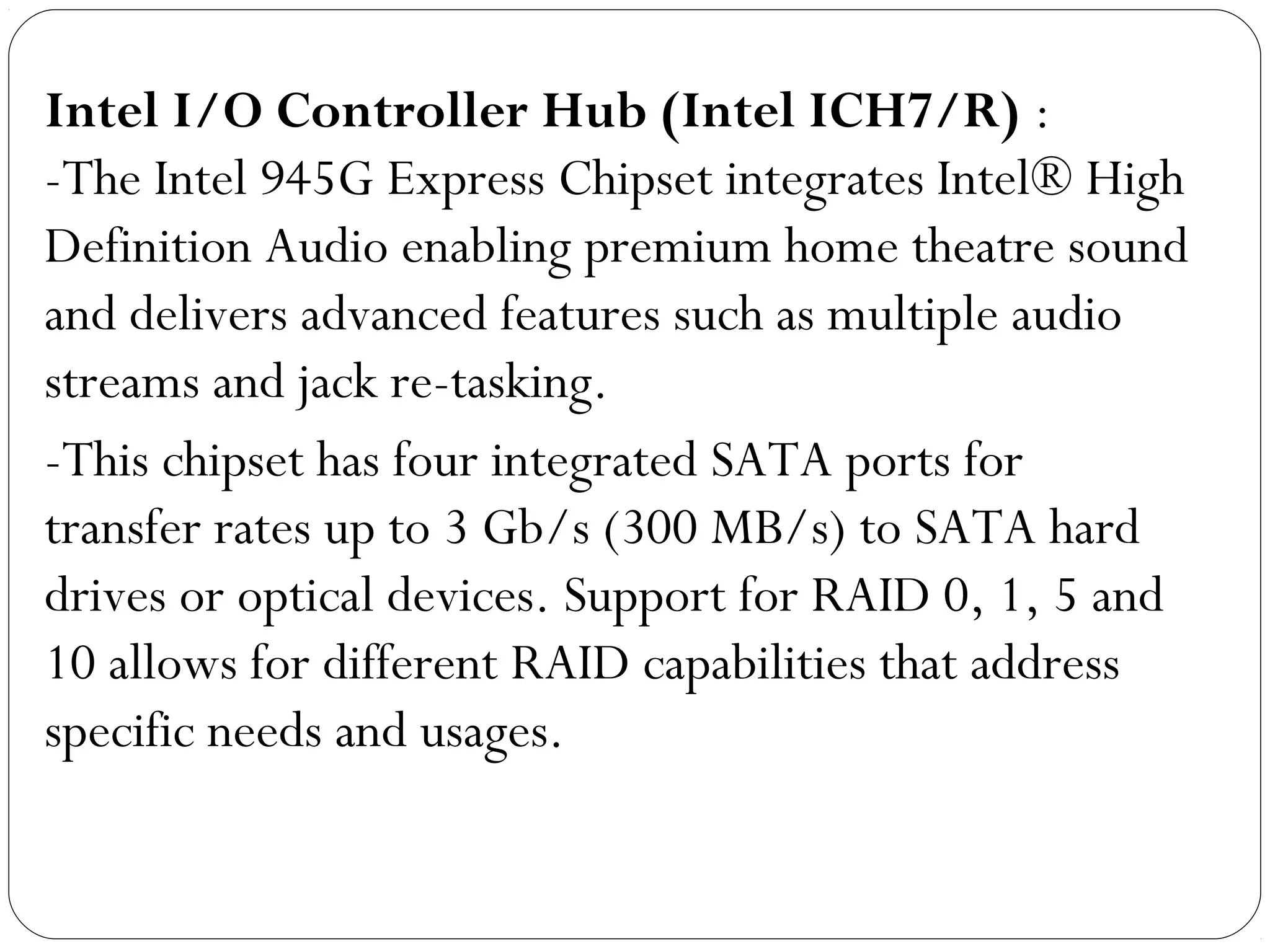
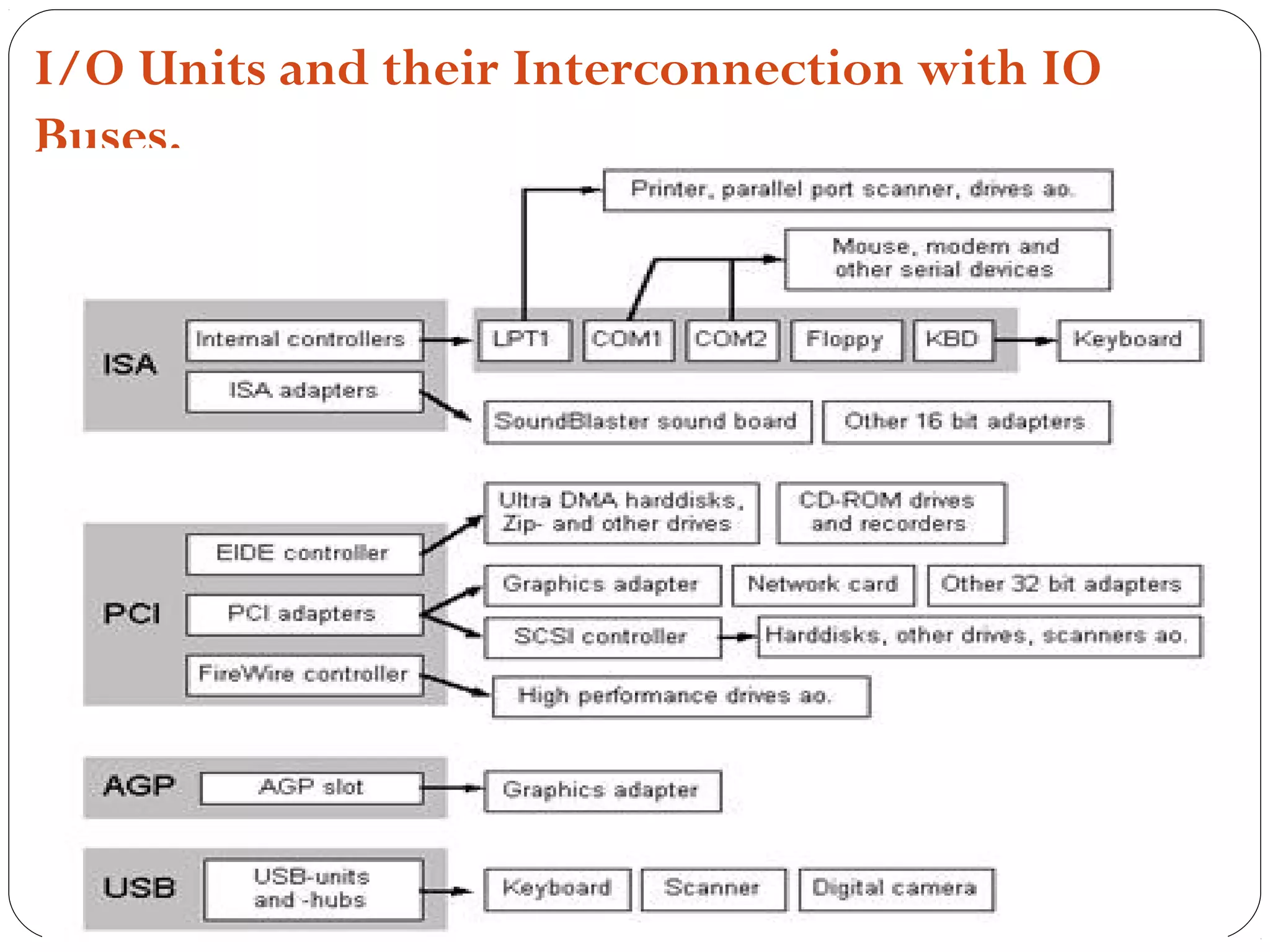
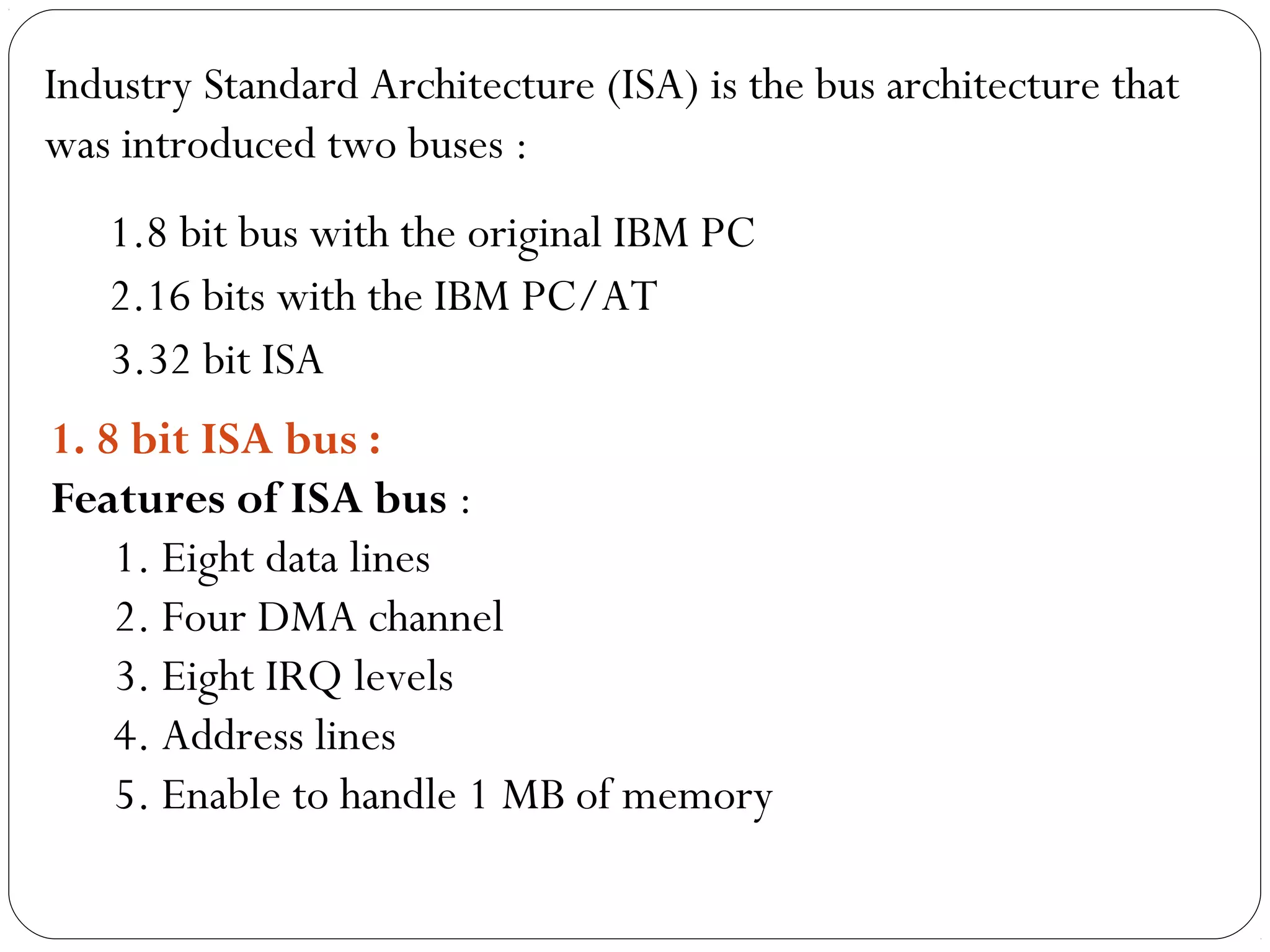
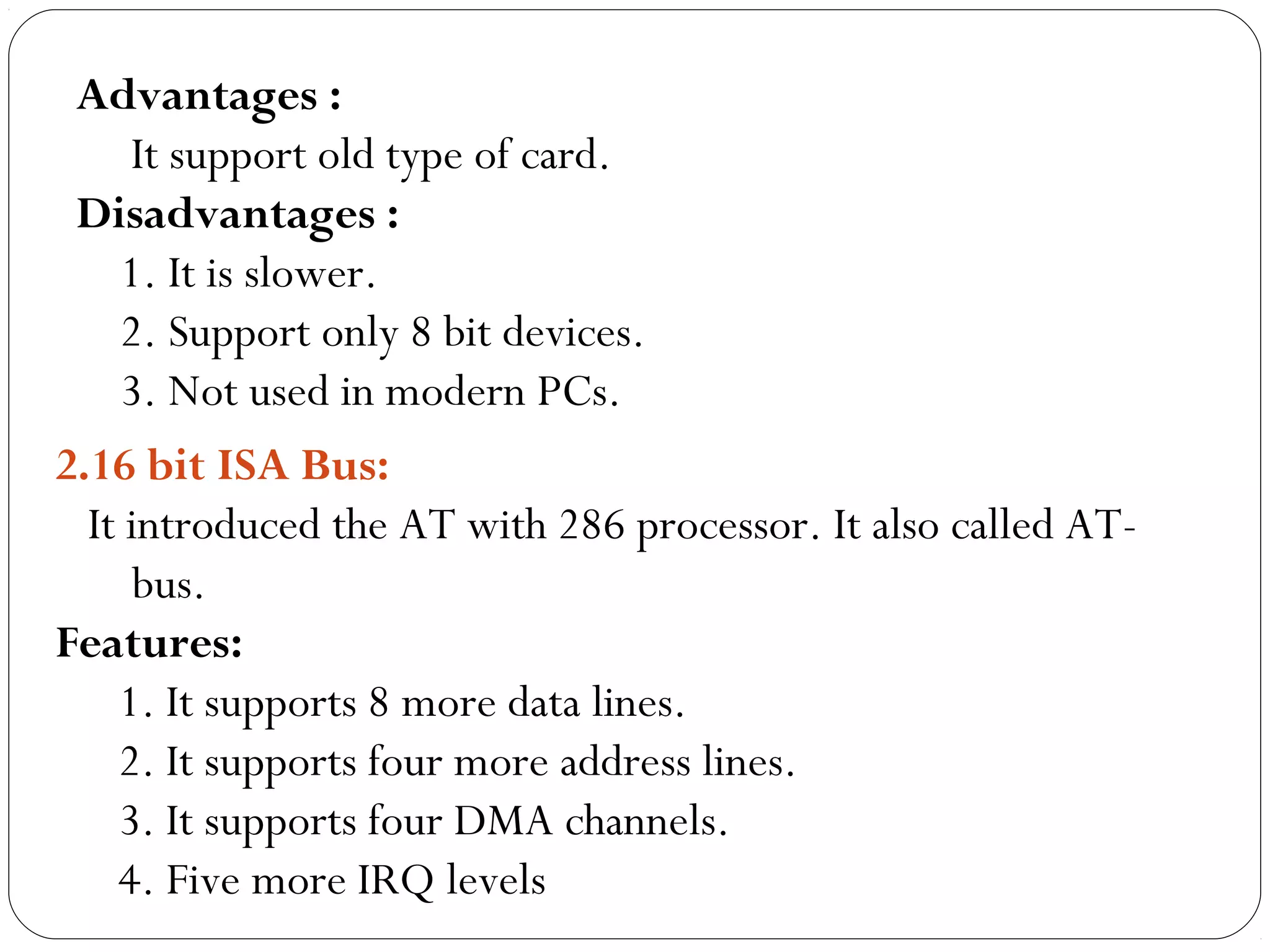
The document discusses PC configurations and components. It describes the typical parts that make up a PC like the motherboard, CPU, memory, storage, ports, and peripherals. It also discusses different types of PC configurations based on the processor and motherboard chipset used, such as Intel and AMD configurations. Chipsets and their functions are explained, focusing on the northbridge which connects to fast devices like RAM and graphics, and the southbridge which connects to slower peripherals.
![Secondary Memory
Keyboard
Mouse
Display (Monitor) CRT/TFT
Switch Mode Power Supply
USB Port]
DVD etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1chipset-120302093847-phpapp021-170913120301/75/Computer-hardware-and-networking-by-Pradeep-Kudale-3-2048.jpg)