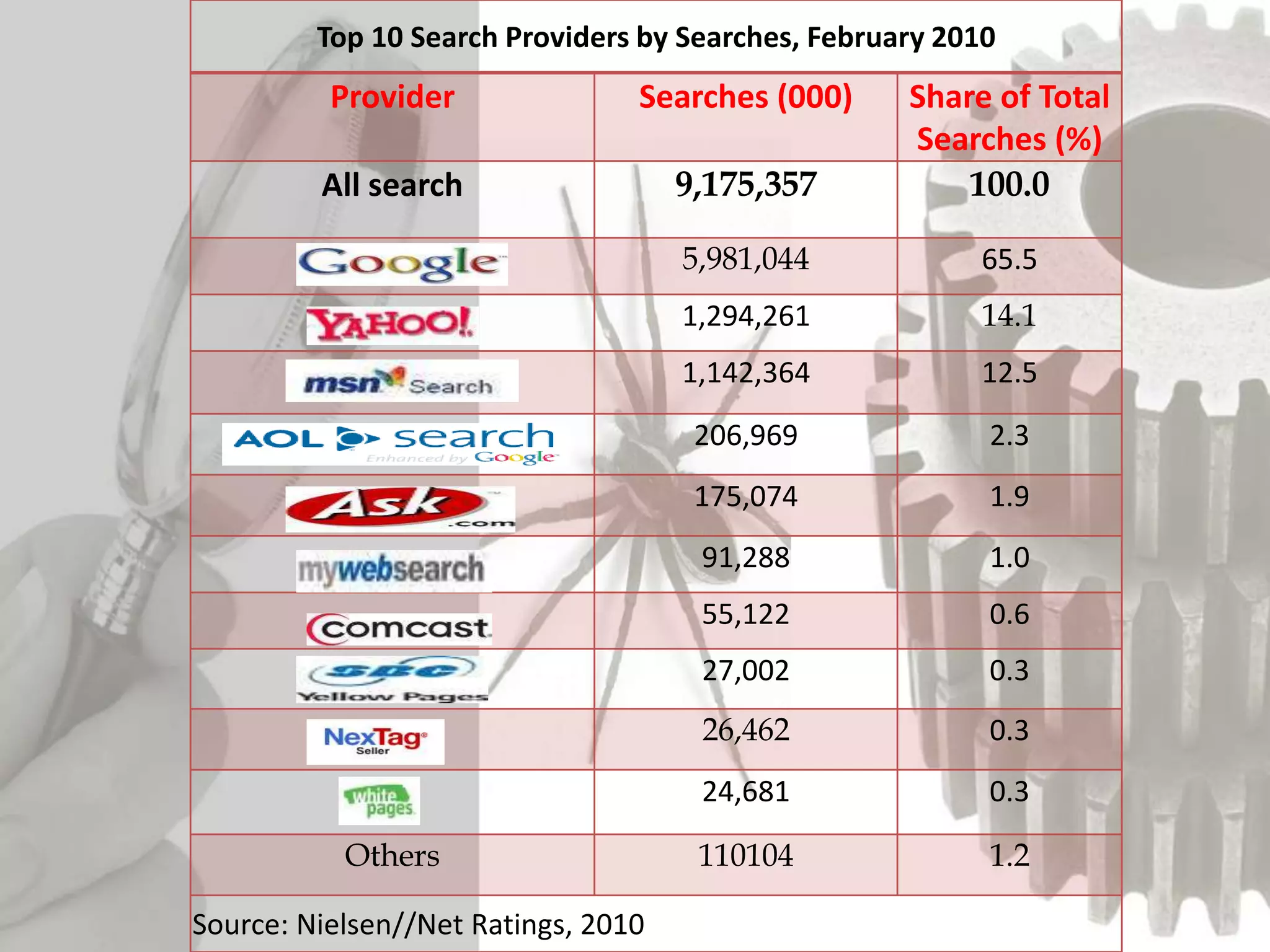
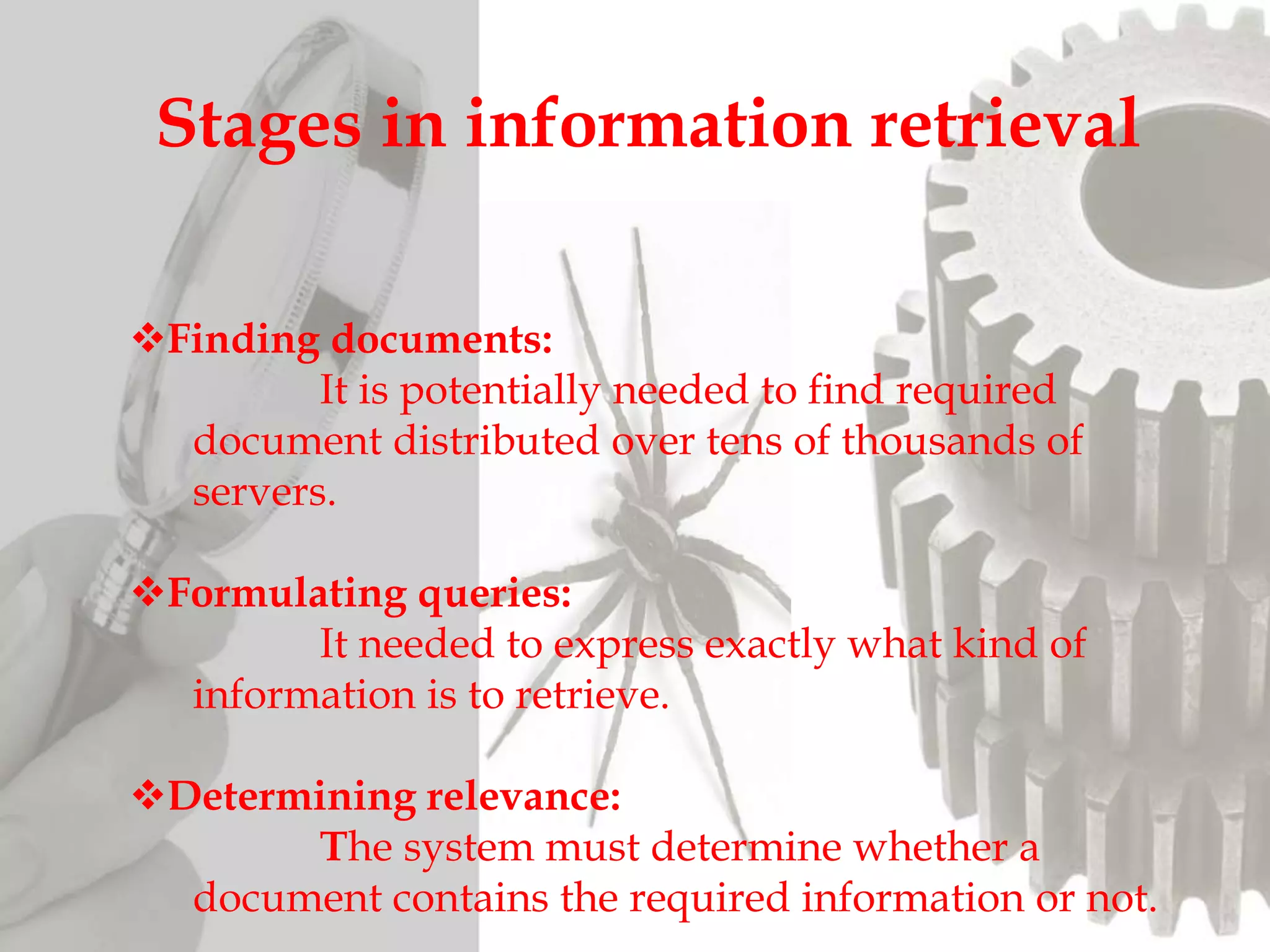
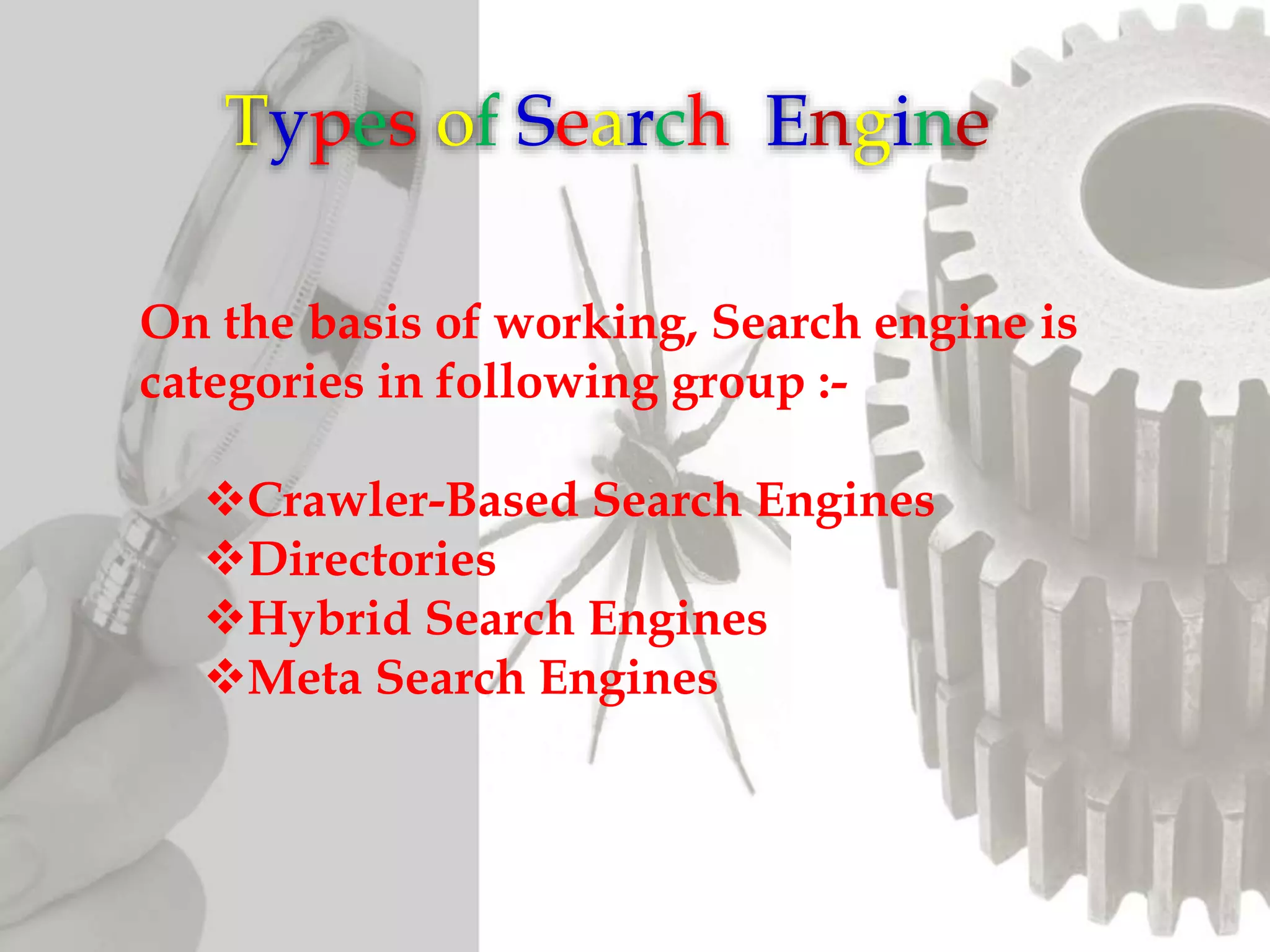
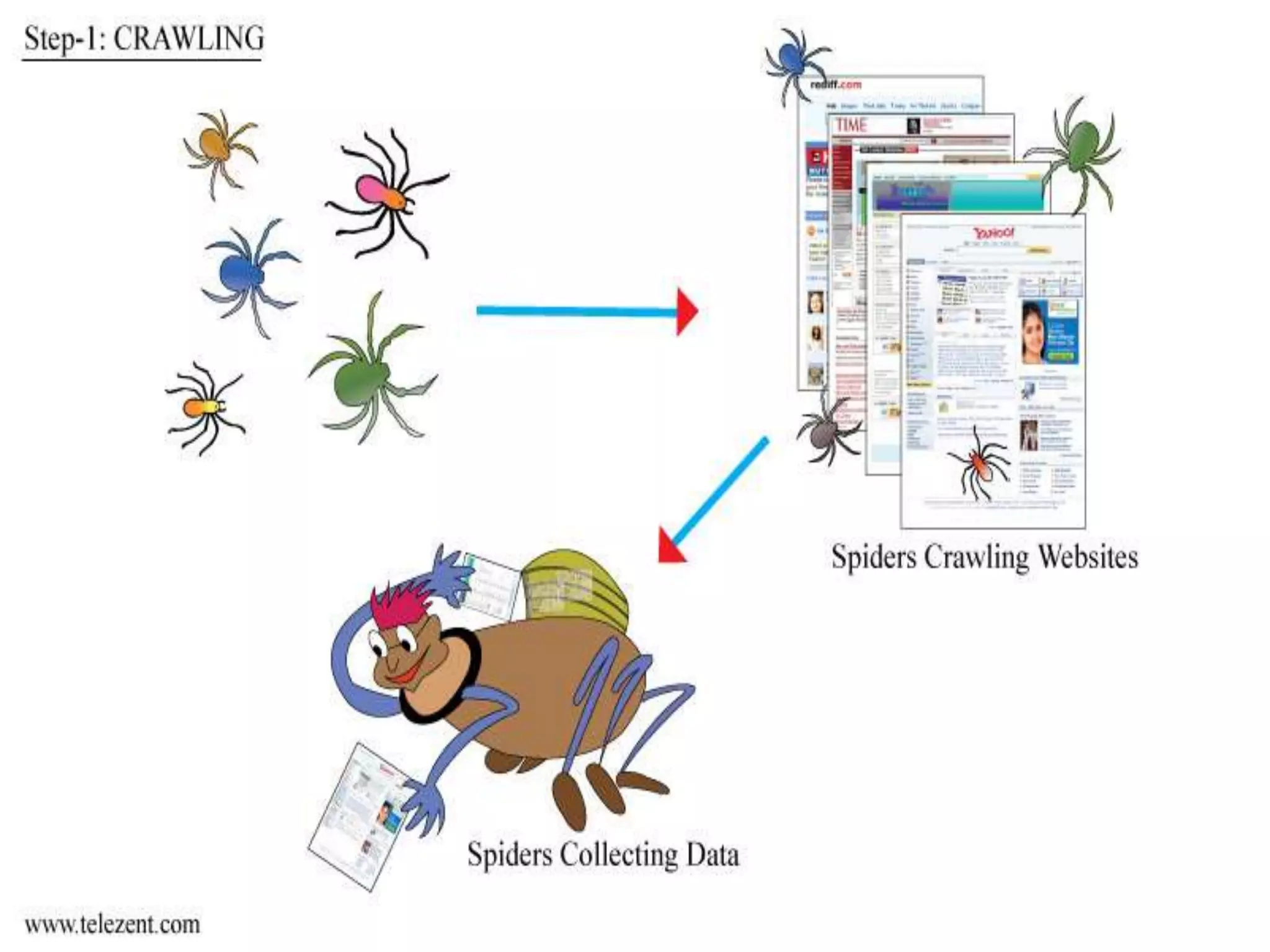
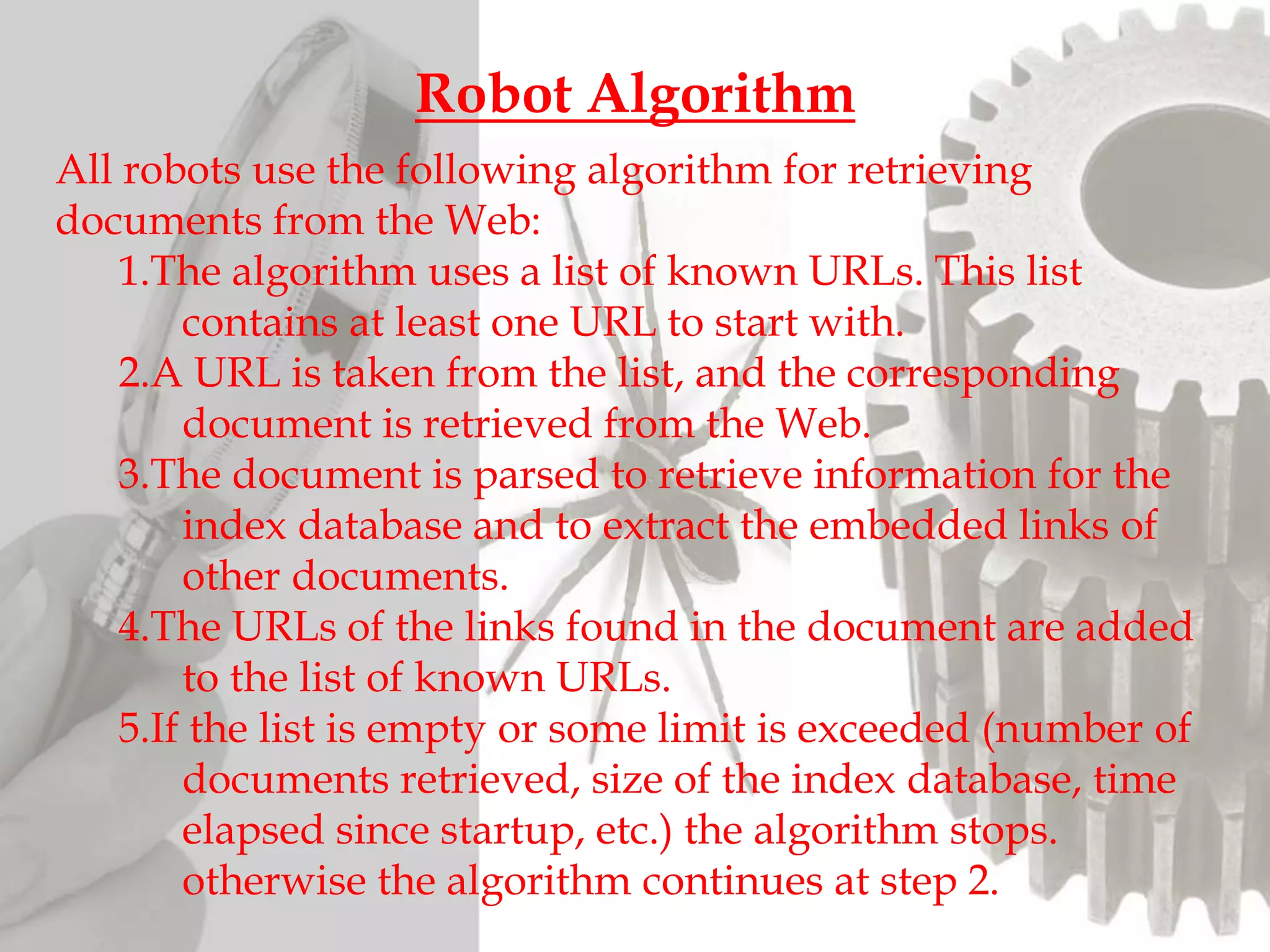
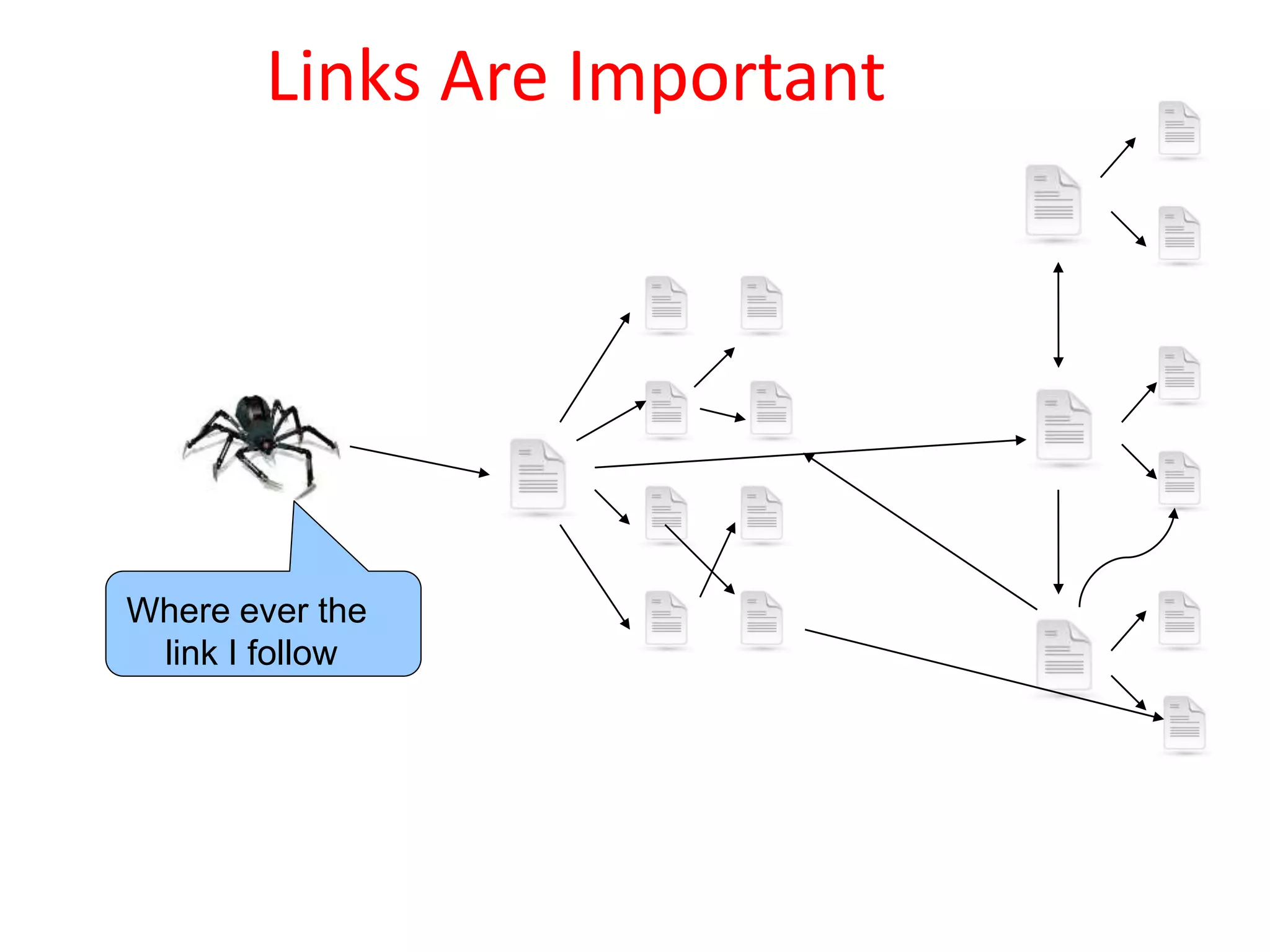
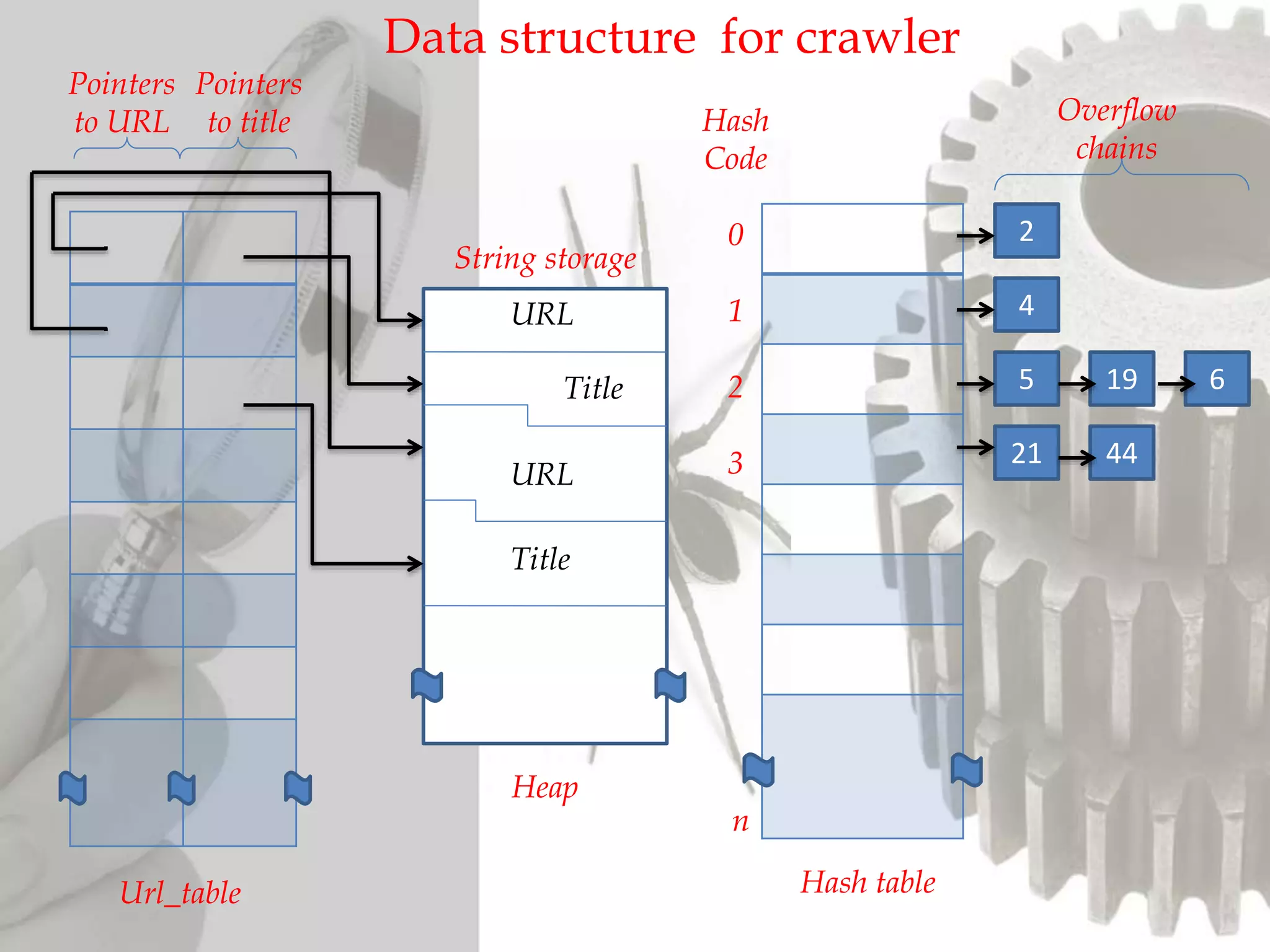
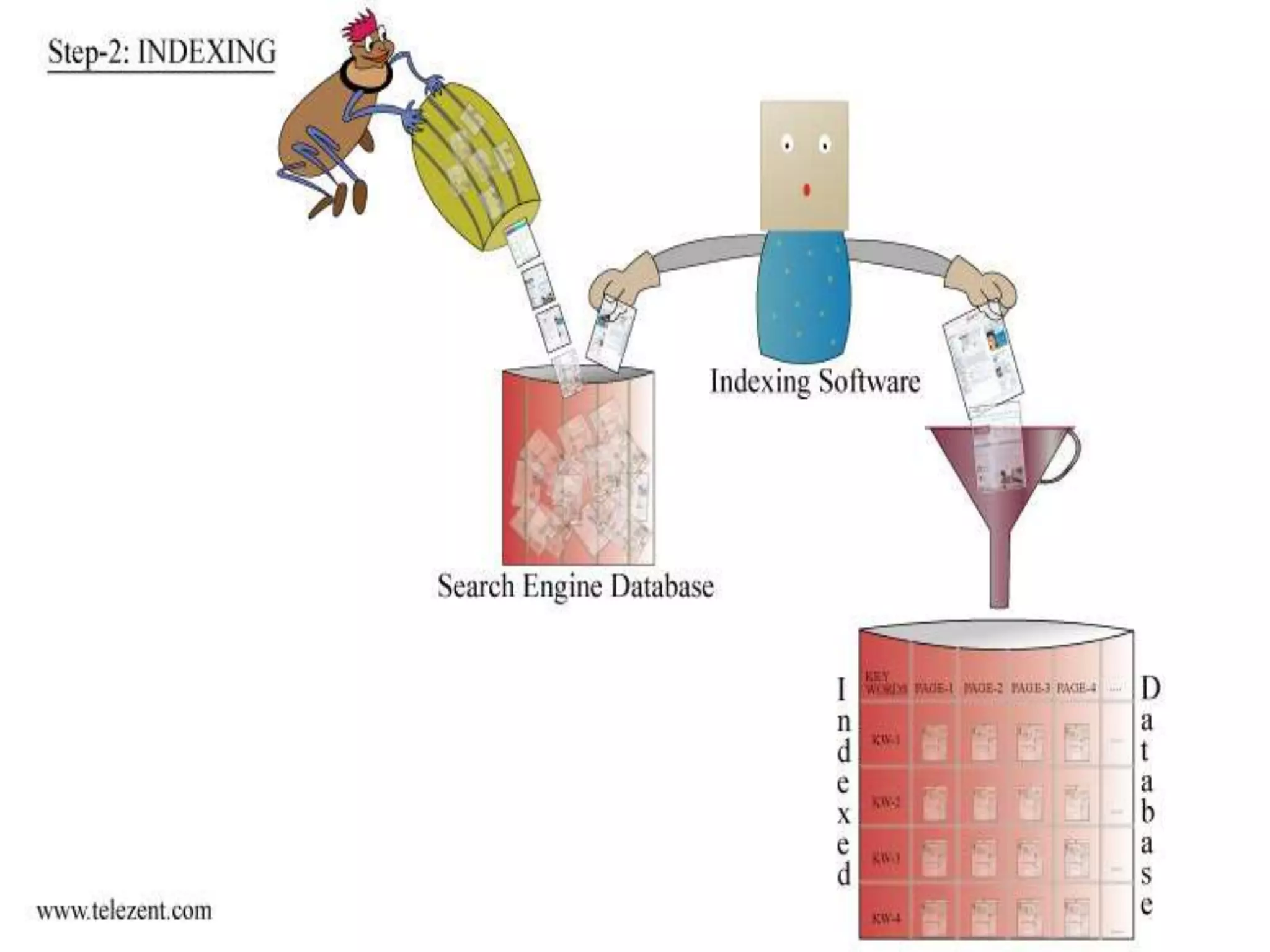
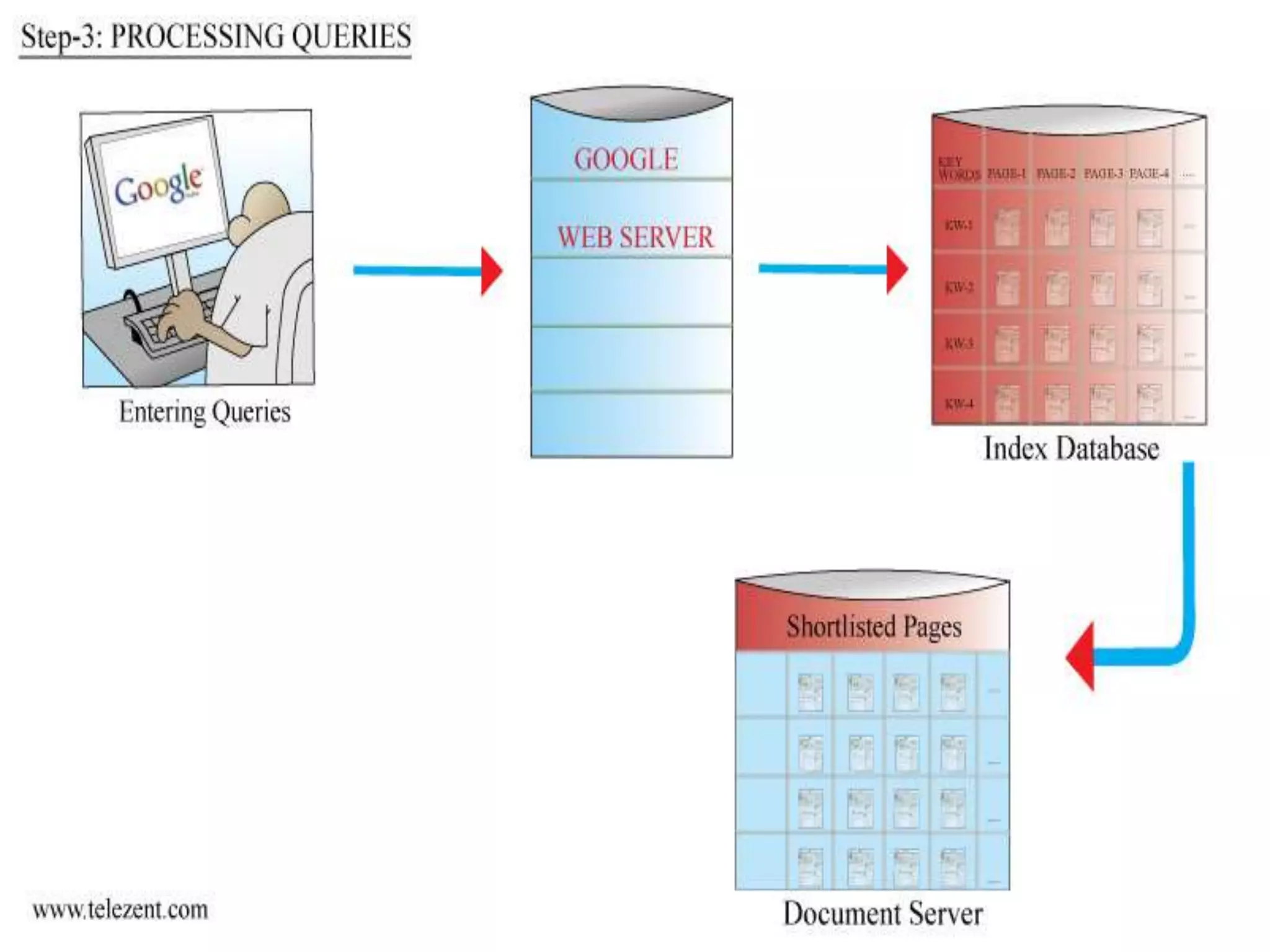
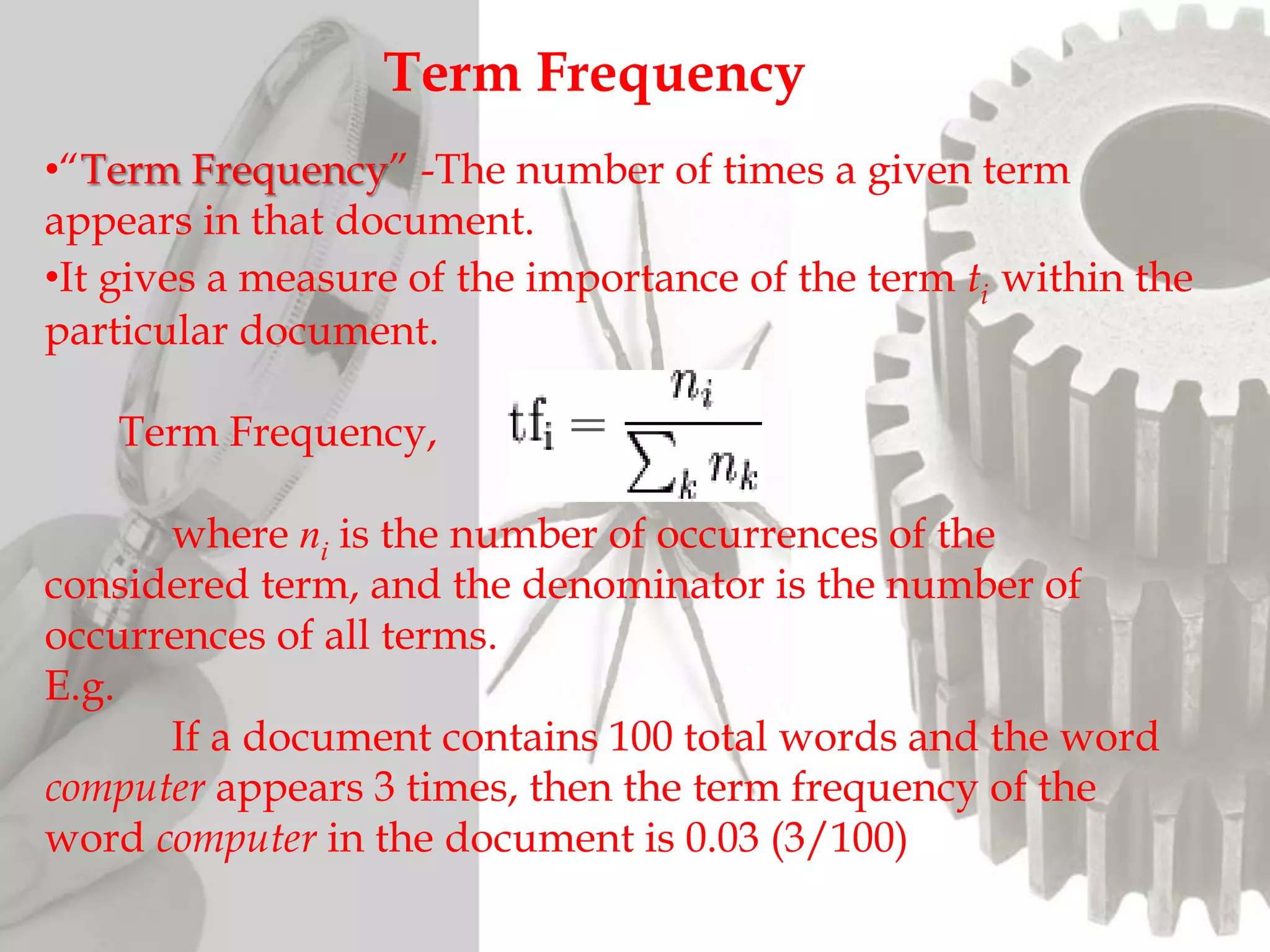
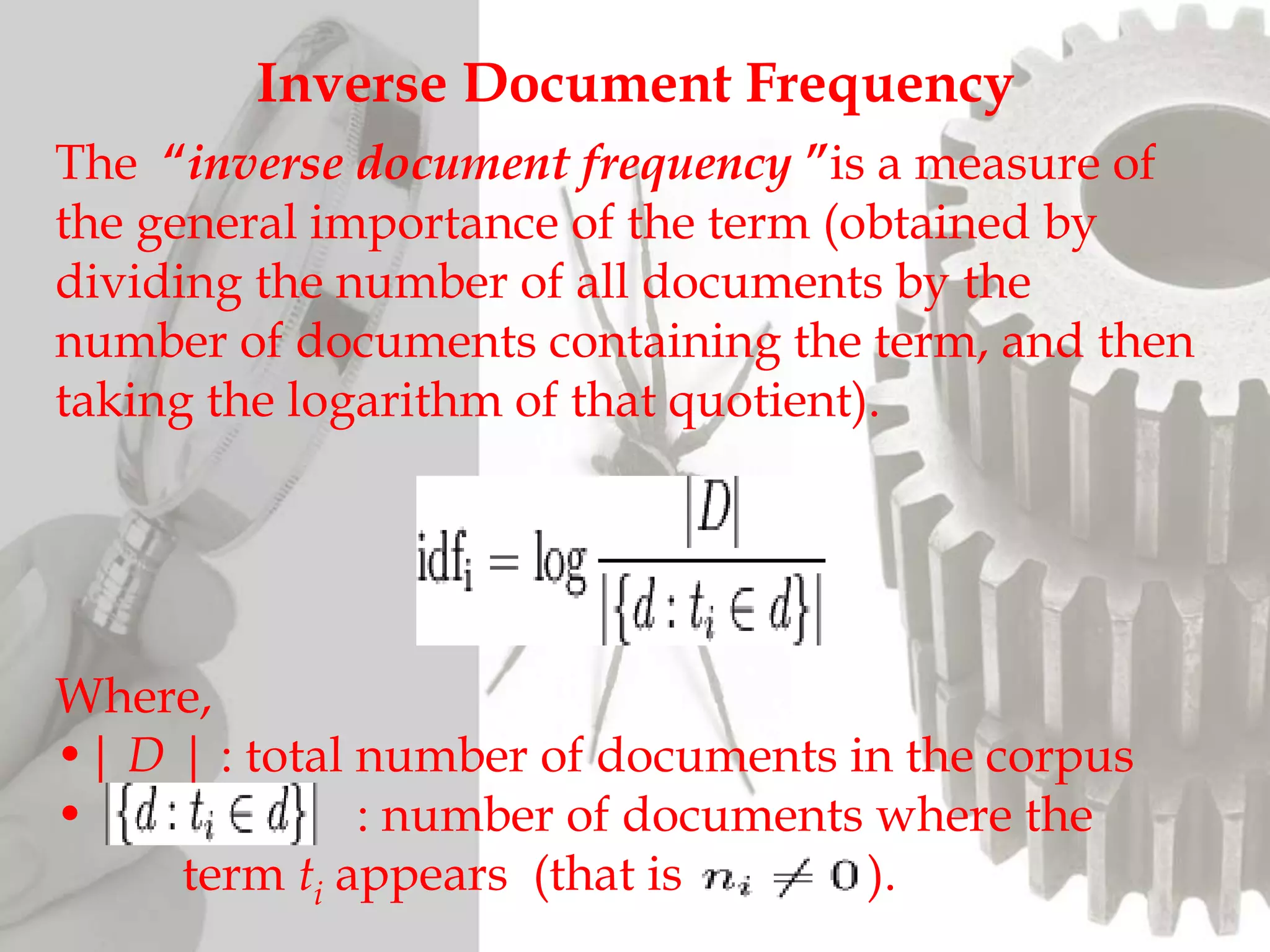
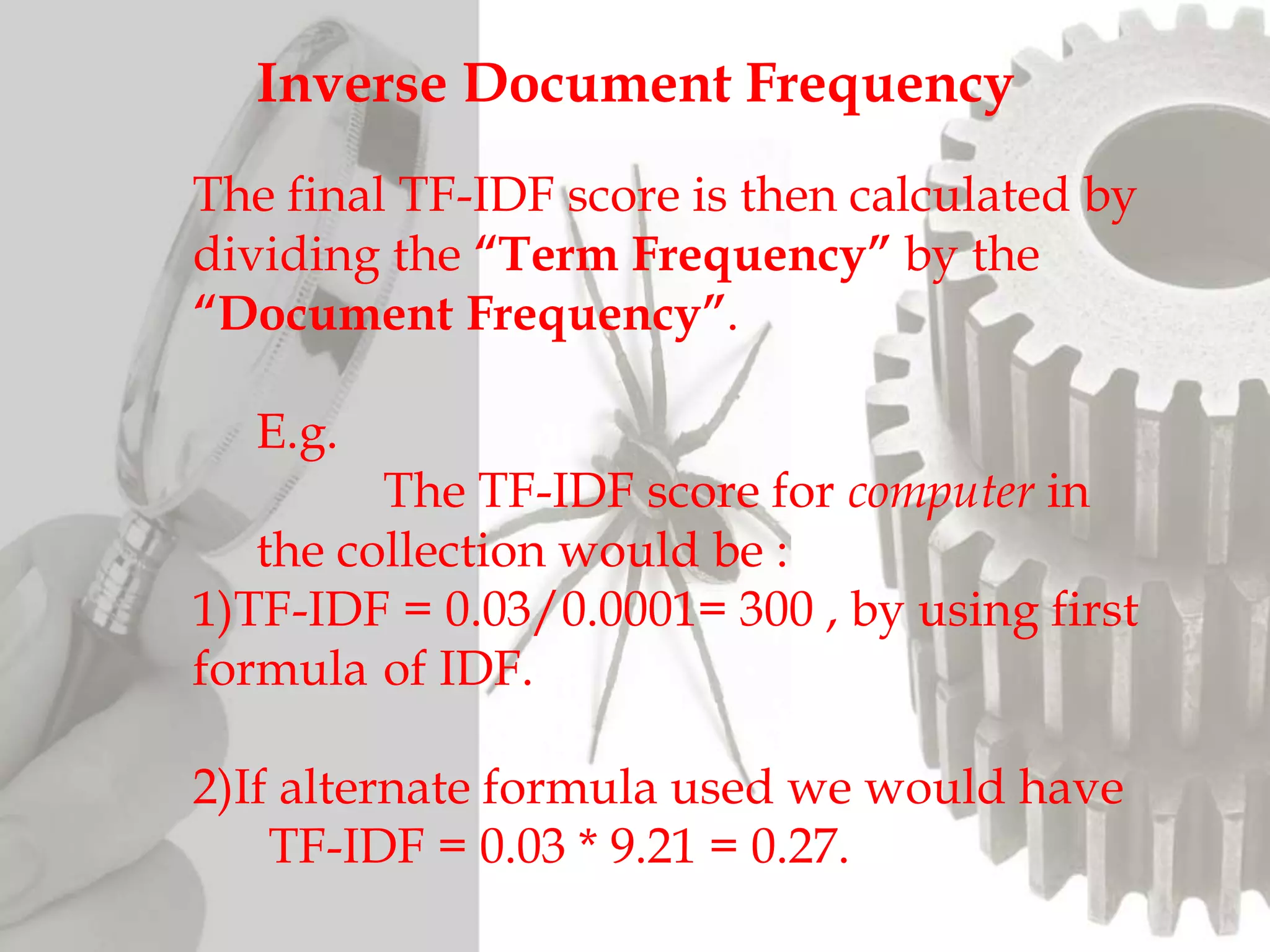
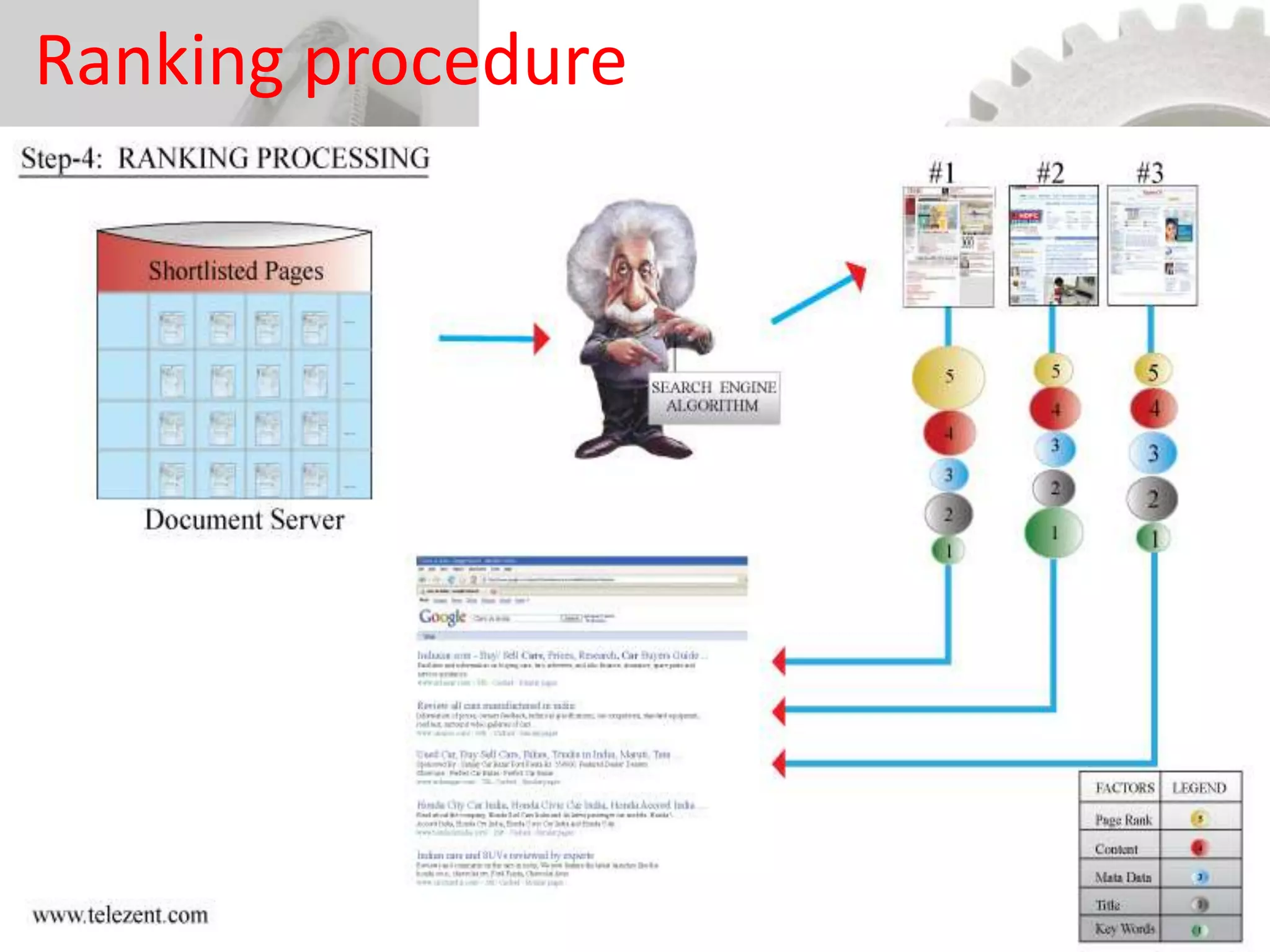
The document discusses the functioning and history of search engines, detailing their evolution from the first search engine Archie in 1990 to the introduction of algorithms that enhance search accuracy by 1998. It explains the processes of information retrieval, including how crawlers index web pages and the importance of keywords in matching user queries to relevant documents using mechanisms like tf-idf for relevance determination. Additionally, it categorizes search engines into crawler-based, directories, hybrid, and meta search engines, highlighting examples and the significance of indexing in facilitating efficient information retrieval.