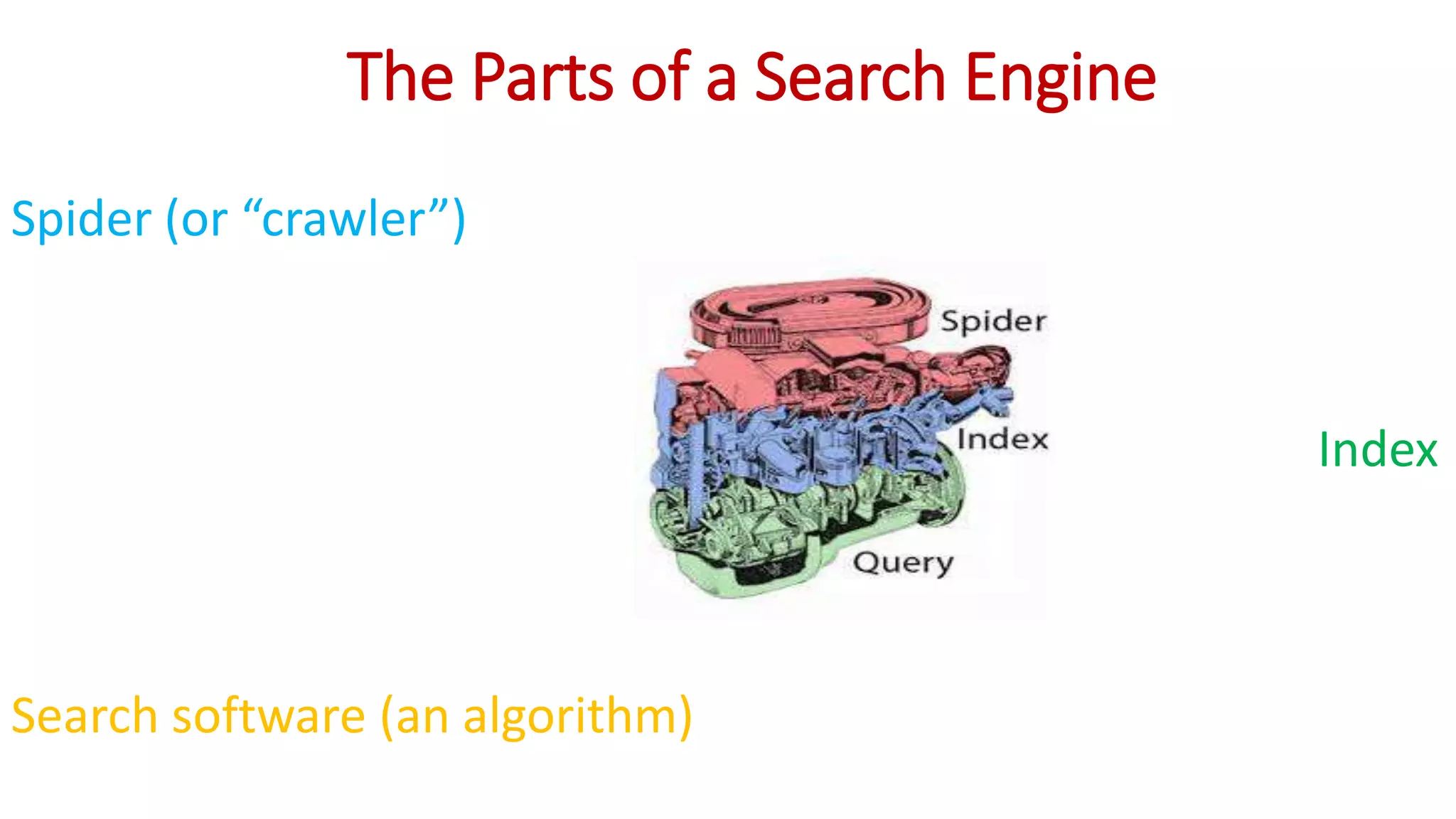
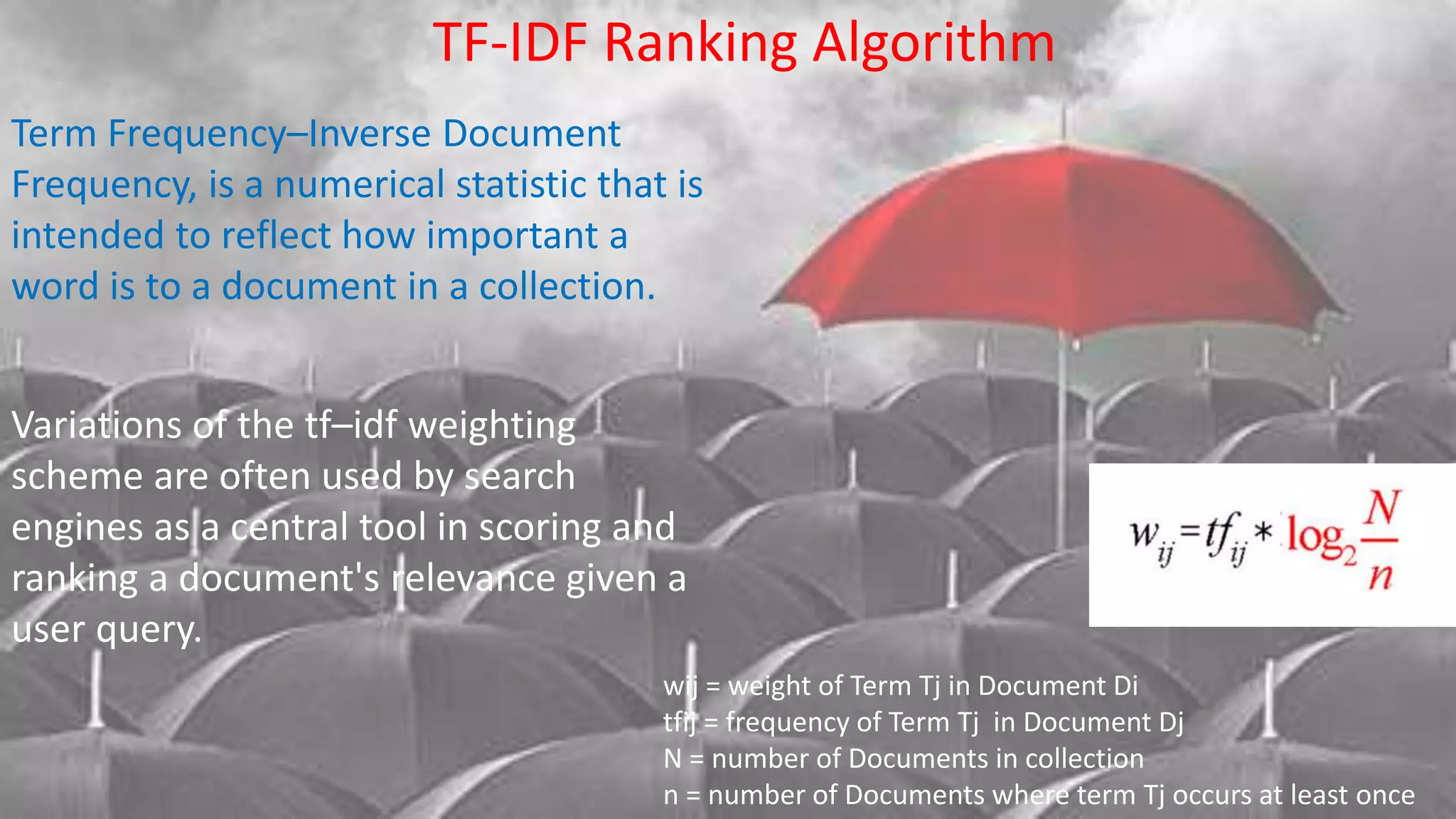
Search engines help people find information on the web. They have three main parts: spiders that crawl websites and index their content, an index that stores all the crawled web pages, and search software that finds matches to user queries in the index and ranks results by relevance. Search engines use algorithms like TF-IDF for scoring documents and PageRank to determine the importance of pages based on links from other websites. Together these components allow search engines to efficiently search the huge volume of information on the web.