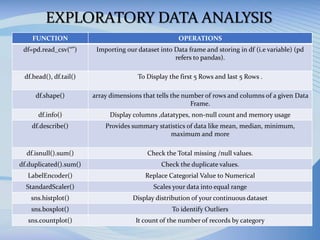
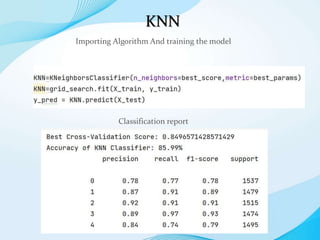
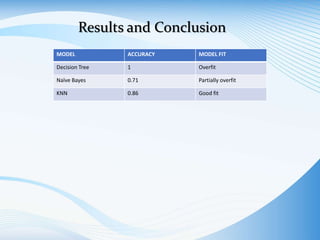
The document outlines a project aimed at developing a machine learning model to accurately identify crime hotspots in Los Angeles using LAPD crime data. It includes methodologies for data preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, and the evaluation of three classification models: Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, and KNN, concluding with a comparison of their accuracy. The initiative aims to provide actionable insights to enhance community safety and collaboration with law enforcement.