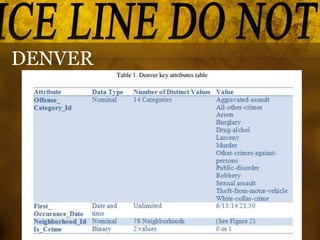
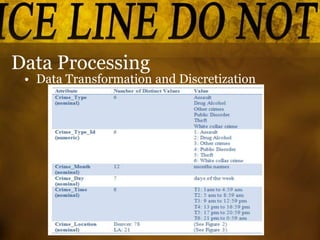
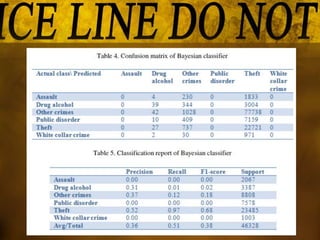
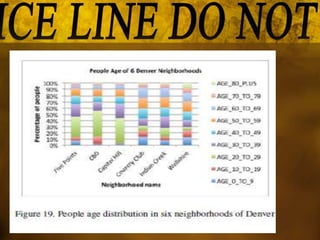
This document summarizes a study that used data mining techniques to predict crime using real-world crime datasets from Denver and Los Angeles. The goals were to identify crime hotspots and predict future crime types based on location, time, and other attributes. The models tested included the Apriori algorithm to identify frequent crime patterns, a naïve Bayesian classifier to predict crime type based on location/time features, and a decision tree classifier. Key results identified crime hotspots and showed the Bayesian classifier achieved prediction accuracies of 51-54% while the decision tree was more complex and achieved lower accuracy.