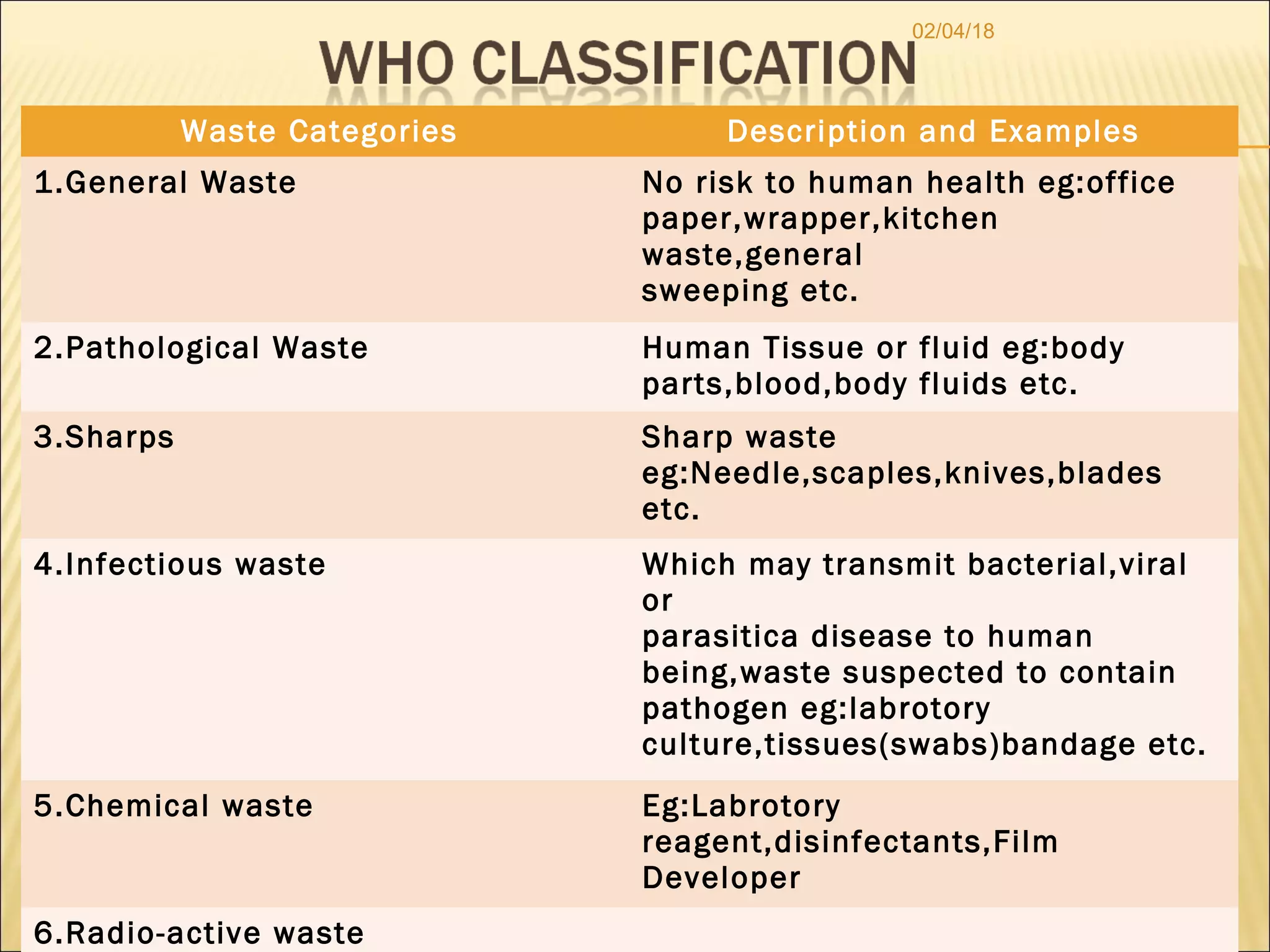
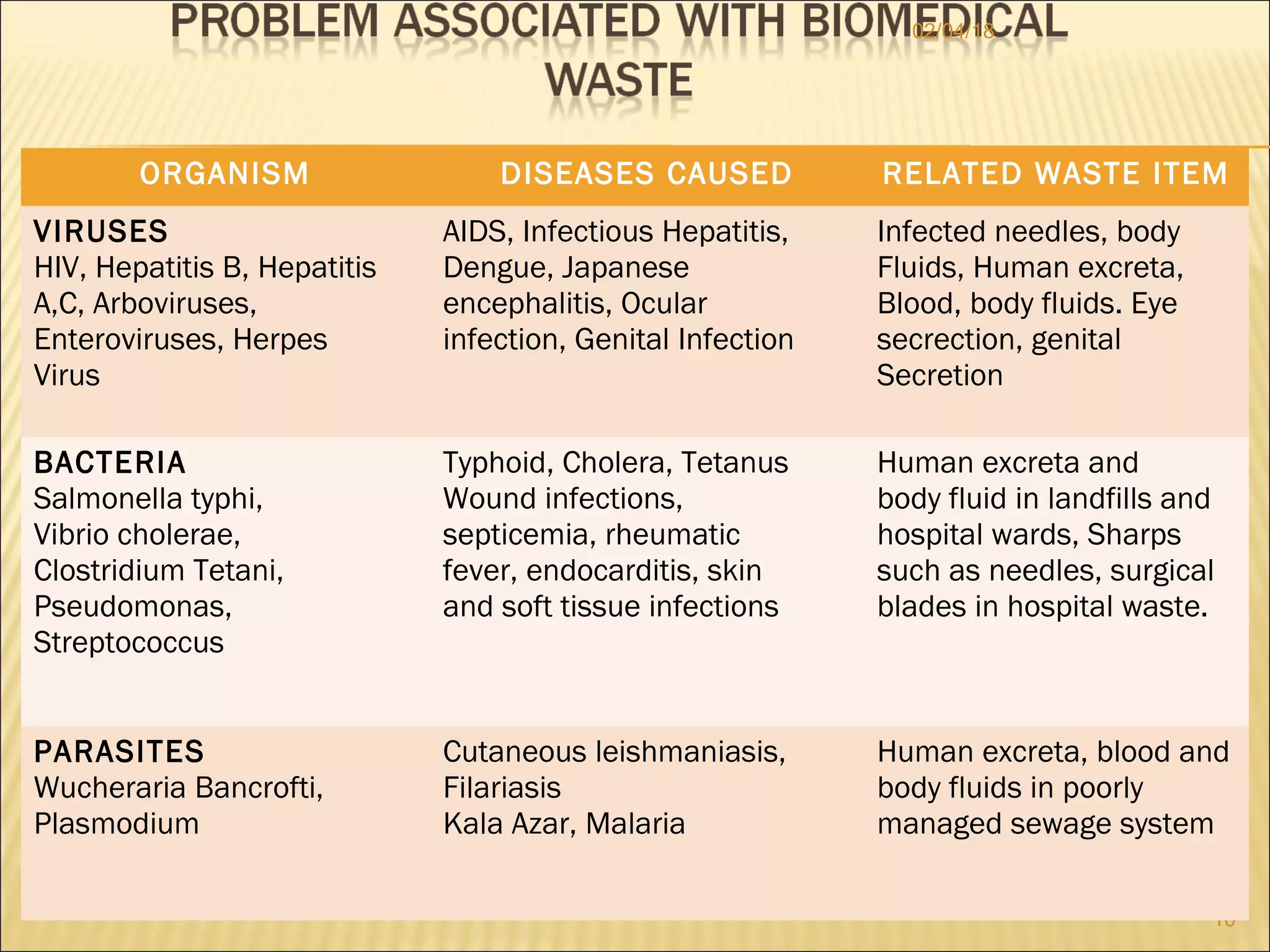
The document discusses biomedical waste management. It defines biomedical waste and explains the need for proper management due to risks to health and environment. It outlines various categories of waste like infectious, pathological, radioactive and their appropriate treatment and disposal methods like incineration, autoclaving, chemical disinfection and others. The document provides guidance on proper waste segregation, collection, storage, transportation and treatment to safely manage biomedical waste.