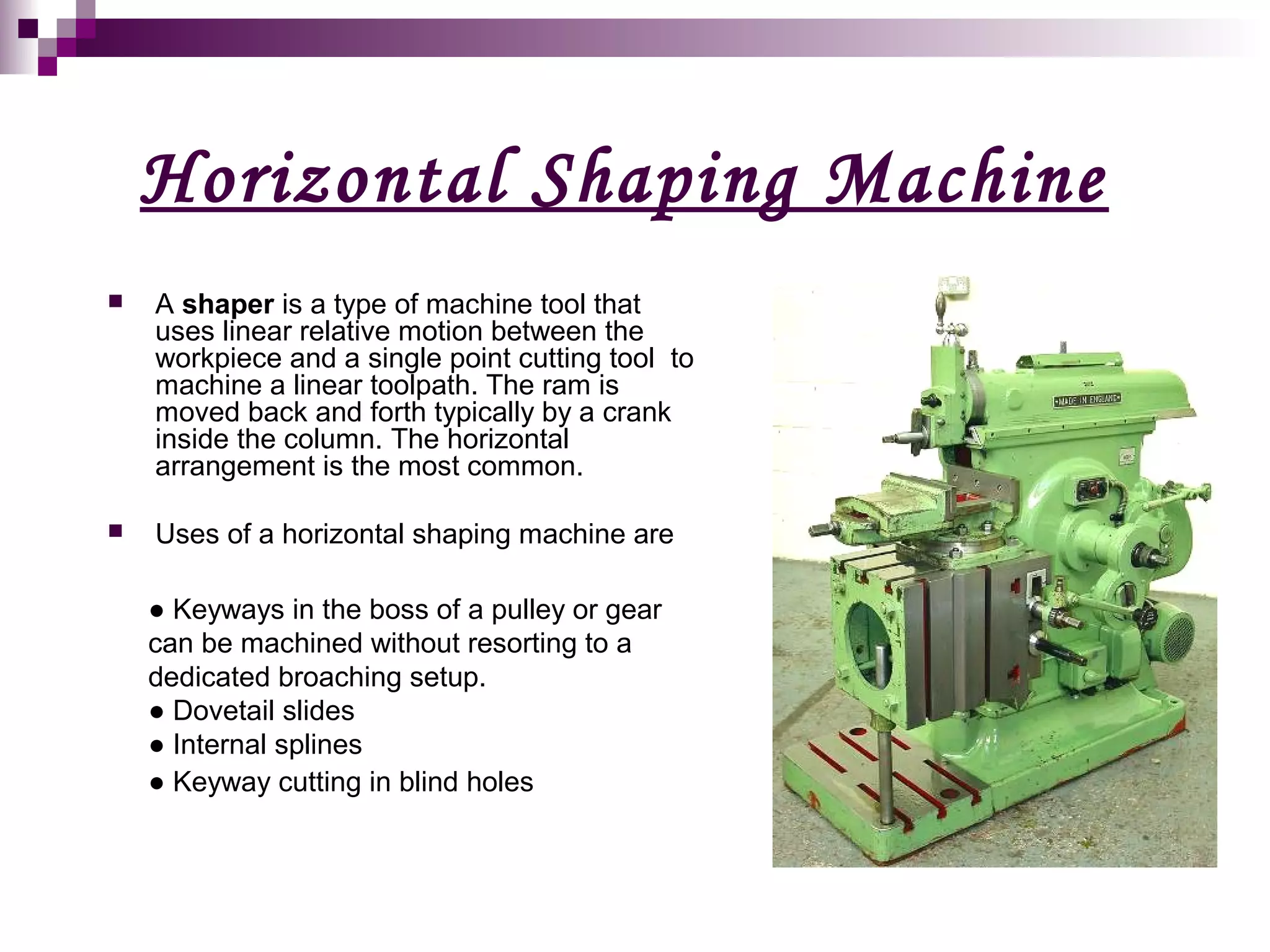
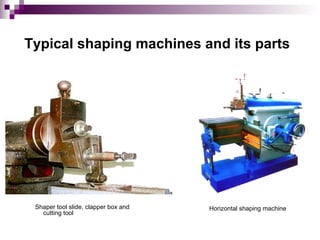
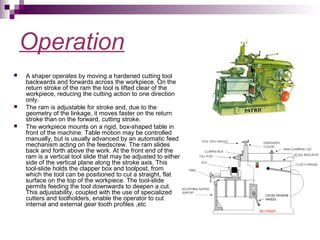
The document describes a horizontal shaping machine, which is a type of machine tool that uses linear motion between a single point cutting tool and workpiece to machine linear toolpaths. It operates by moving the cutting tool back and forth across the workpiece on the forward stroke only, while lifting the tool on the return stroke. Keyways, dovetails, splines, and keyways in blind holes can all be machined using a horizontal shaping machine by adjusting the position of the cutting tool.