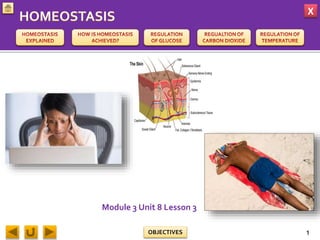
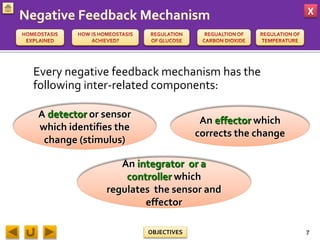
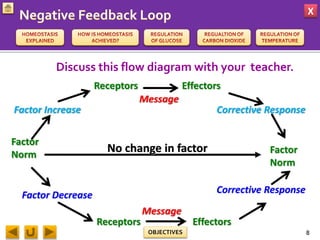
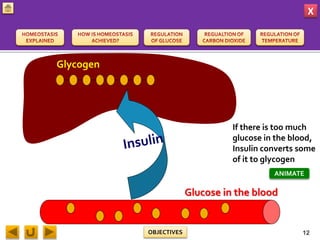
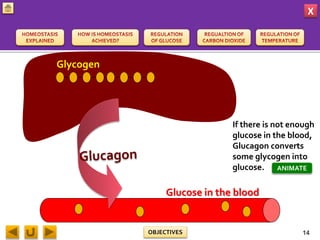
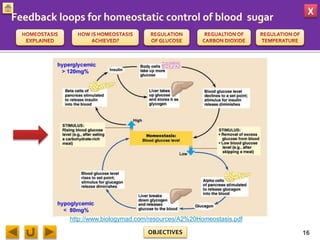
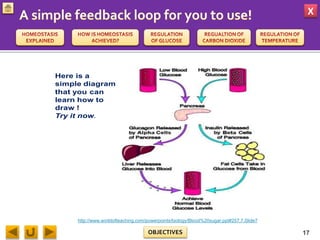
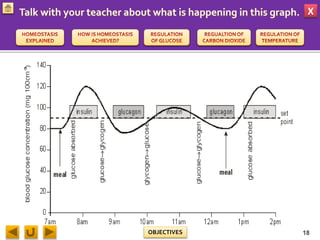
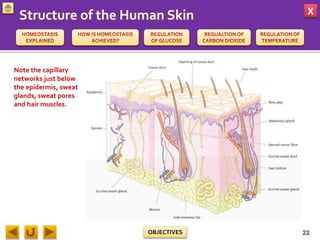
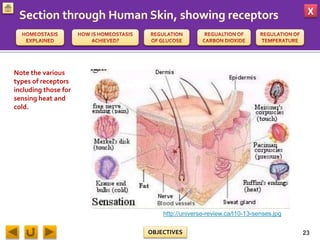
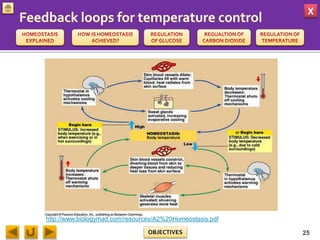
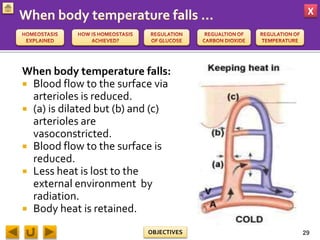
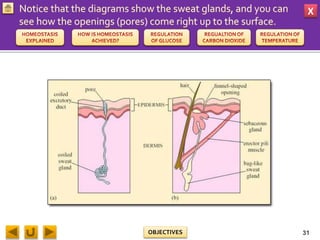
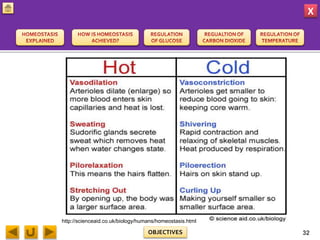
This document provides information about homeostasis and examples of homeostasis in mammals. It begins by defining homeostasis as the maintenance of a stable internal environment regardless of external changes. It then outlines the objectives of explaining key terms, regulatory mechanisms, and giving examples using diagrams. Several examples of homeostasis in mammals are provided, such as temperature regulation and glucose regulation, along with diagrams illustrating the negative feedback loops involved. Sensors, effectors, and integrators that make up these feedback mechanisms are also described.