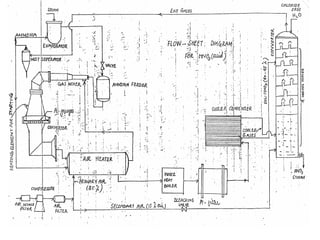
The document discusses nitric acid manufacturing, highlighting its properties, such as being transparent, yellowish, hygroscopic, and corrosive. It outlines various production methods including reactions with Chile saltpeter, electric oxidation of air, and high-pressure techniques used in single and dual pressure plants. Additionally, it describes the role of catalysts and the concentration methods for nitric acid, stressing the competitive costs of different plant types.