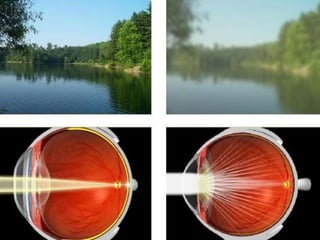
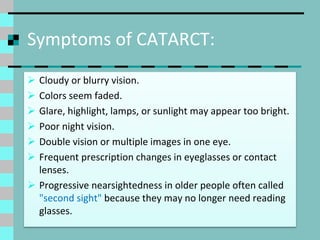
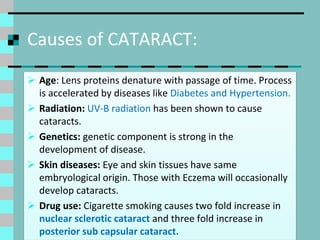
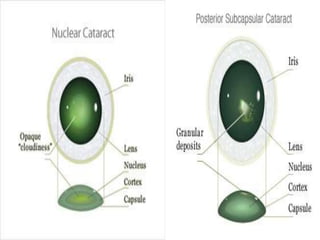
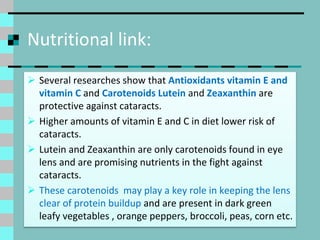
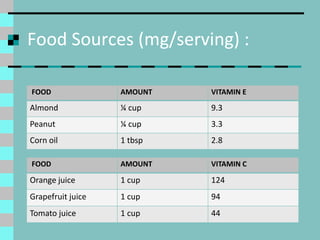
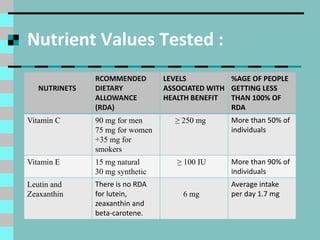
Cataracts are a clouding of the lens inside the eye that leads to decreased vision. They are the leading cause of blindness worldwide. Protein clumps in the lens cause it to become yellowed or brown, impairing vision. Symptoms include blurry or cloudy vision, sensitivity to light, and difficulty seeing at night. Cataracts are most often age-related as lens proteins deteriorate over time but can also be caused by genetics, radiation exposure, diabetes, smoking, and other eye or skin conditions. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E and nutrients like lutein and zeaxanthin found in green leafy vegetables and orange peppers may help prevent cataracts by protecting the lens from protein buildup