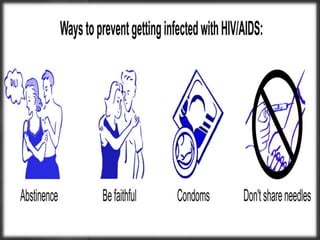
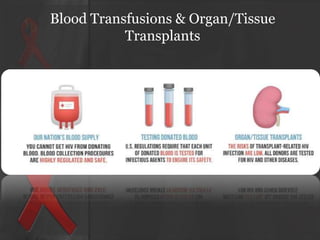
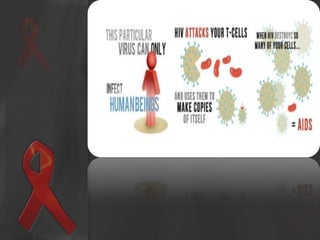
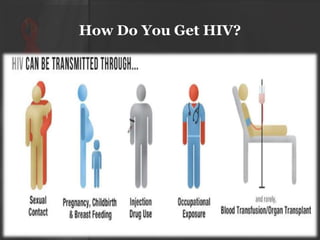
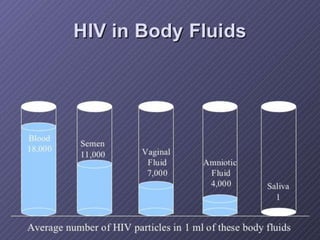
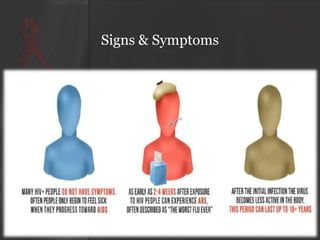
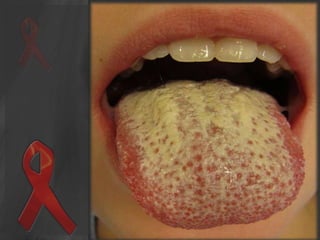
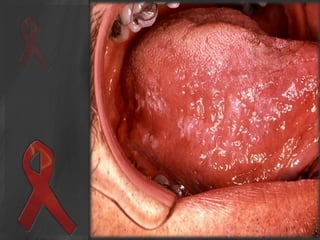
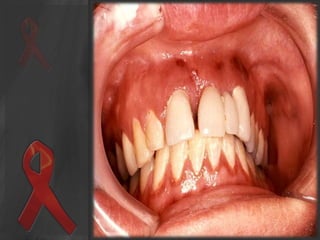
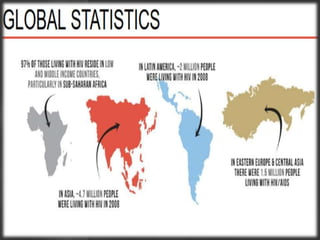
The document presents an overview of HIV/AIDS, including its definition, transmission, symptoms, and treatment options. It highlights the origins of HIV, the difference between HIV and AIDS, and the common oral manifestations associated with HIV infection. It also discusses statistics on HIV prevalence in Pakistan and emphasizes the importance of prevention methods and myths surrounding the disease.














![HIV and AIDS Estimates (2012)
PAKISTAN
• Number of people living
with HIV87,000
[50,000 - 160,000]
• Adults aged 15 to 49
prevalence rate <0.1%
[<0.1% - 0.2%]
• Adults aged 15 and up
living with HIV85,000
[48,000 - 160,000]
• Women aged 15 and up
living with HIV24,000
[14,000 - 44,000]
• Children aged 0 to 14
living with HIV -- N/A
• Deaths due to AIDS3,500
[2,100 - 6,600]
• Orphans due to AIDS
aged 0 to 17 N/A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hivaids-131121063333-phpapp01/85/HIV-AIDS-25-320.jpg)