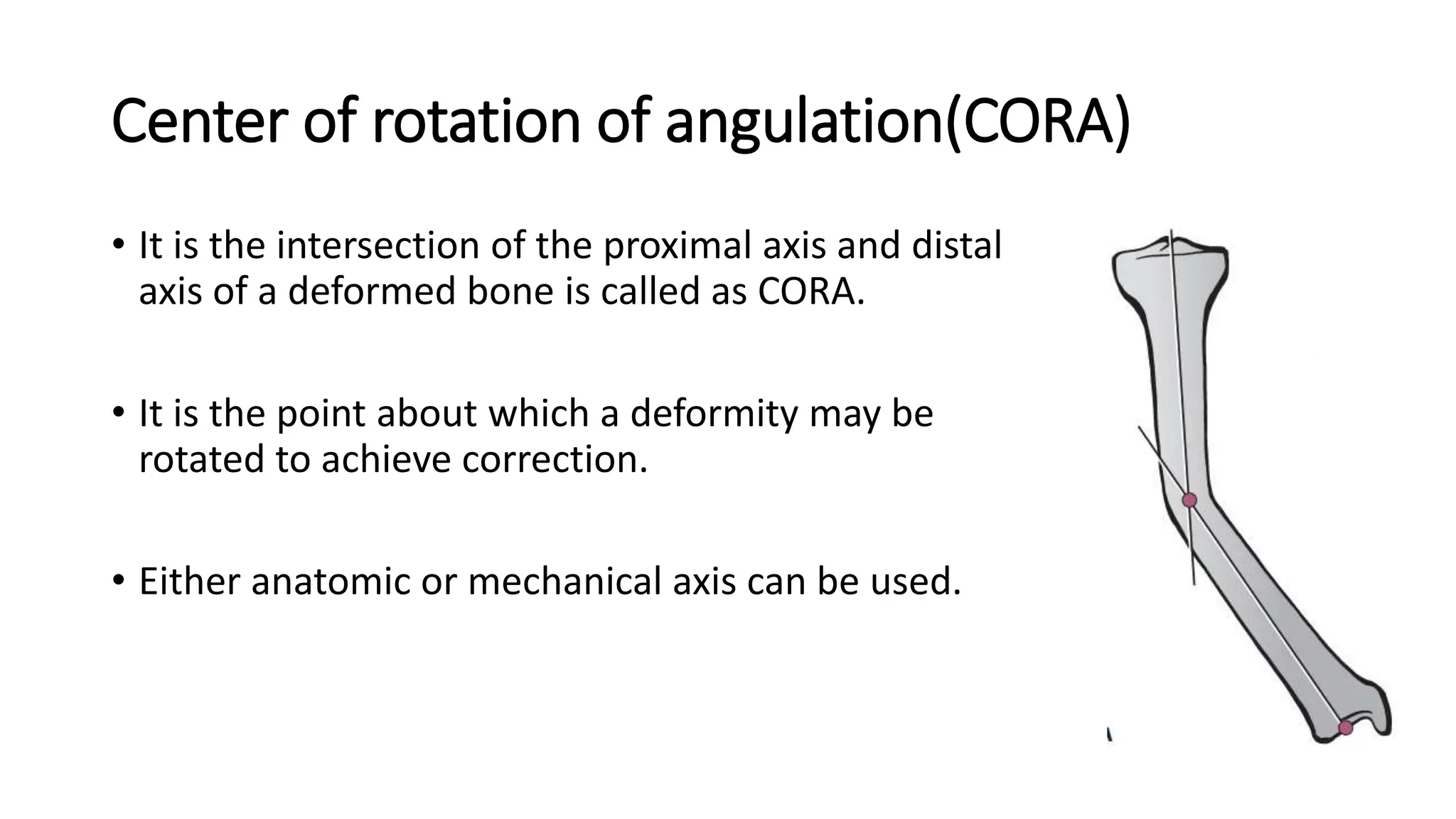
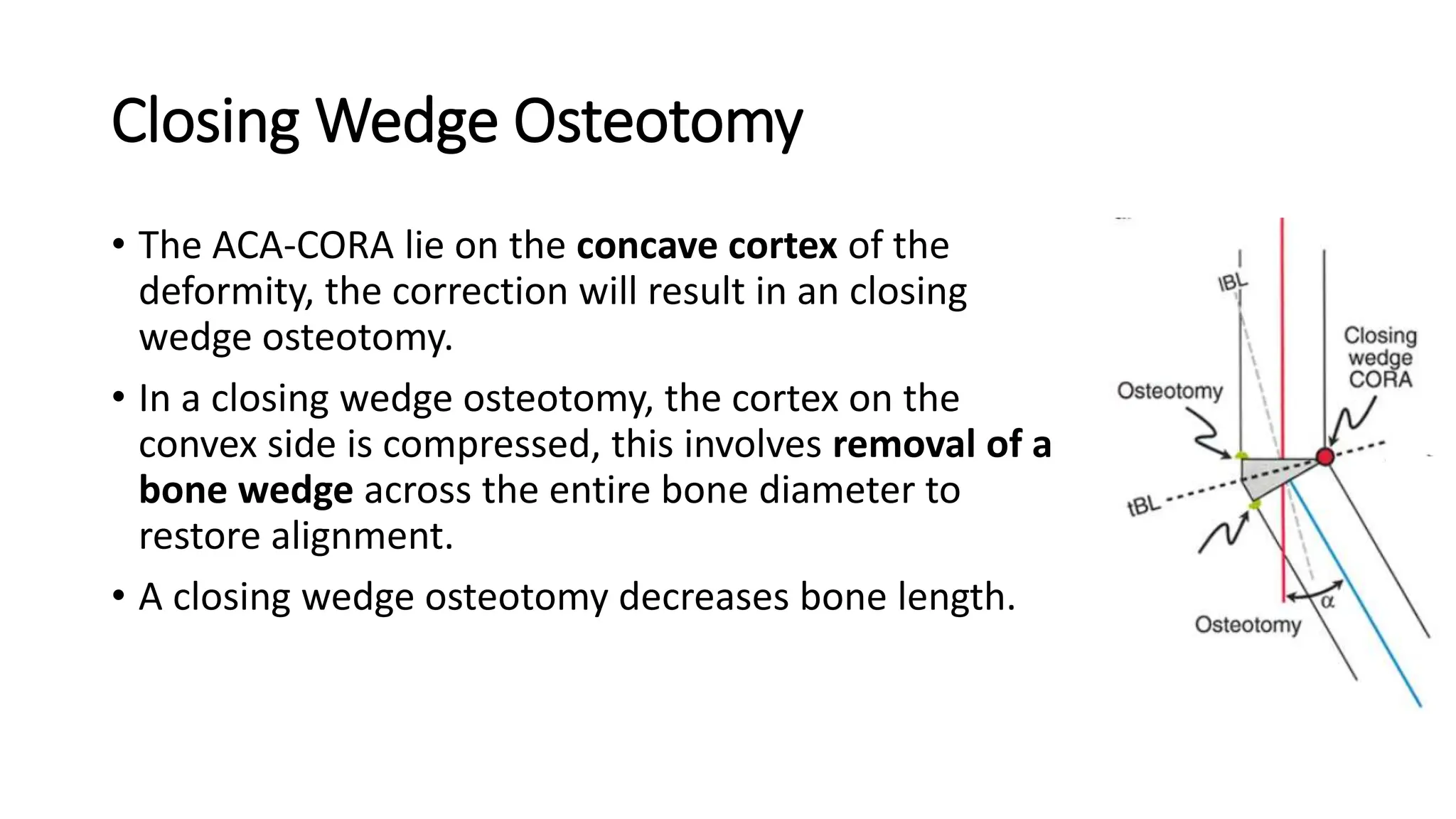
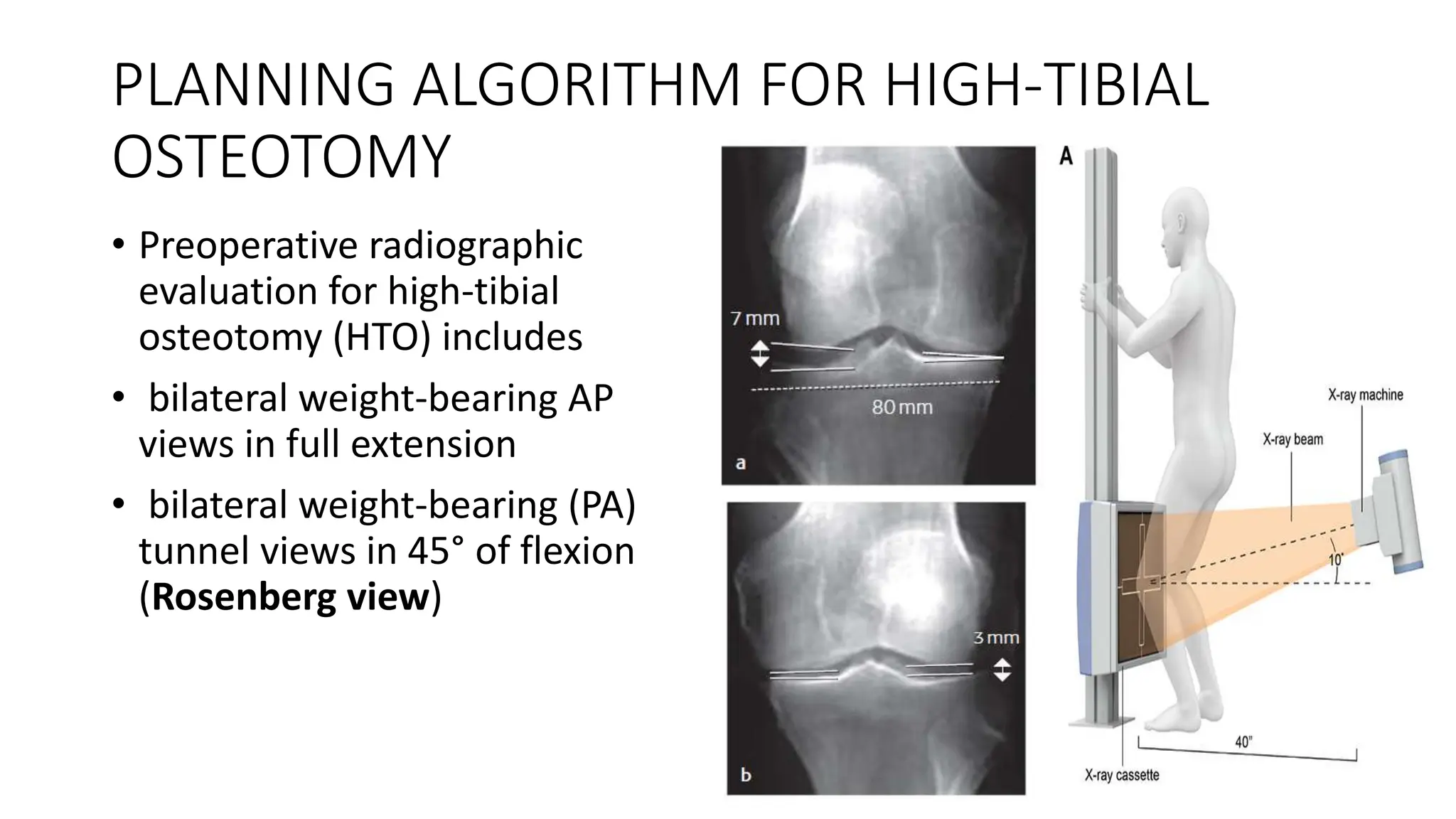
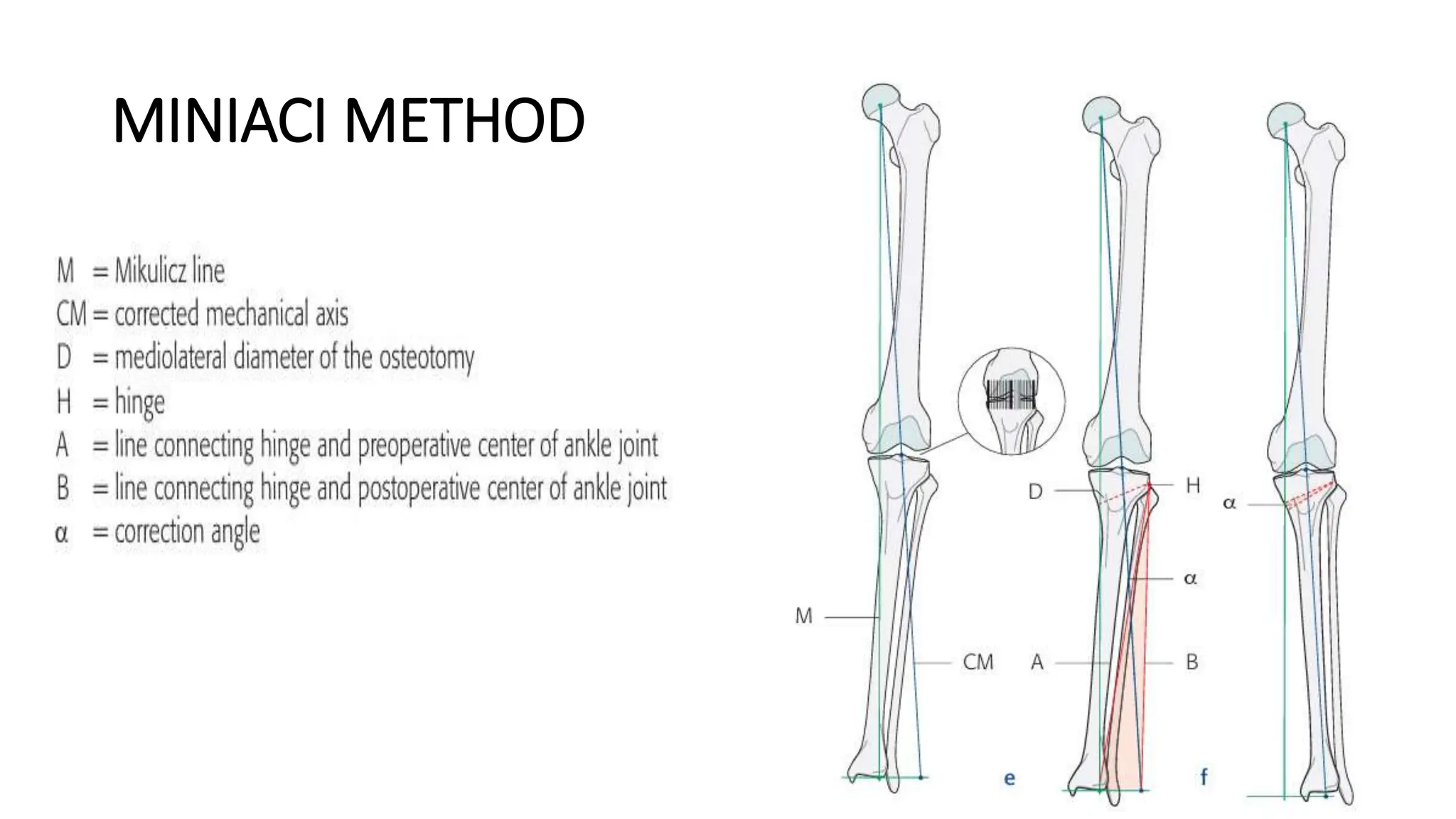
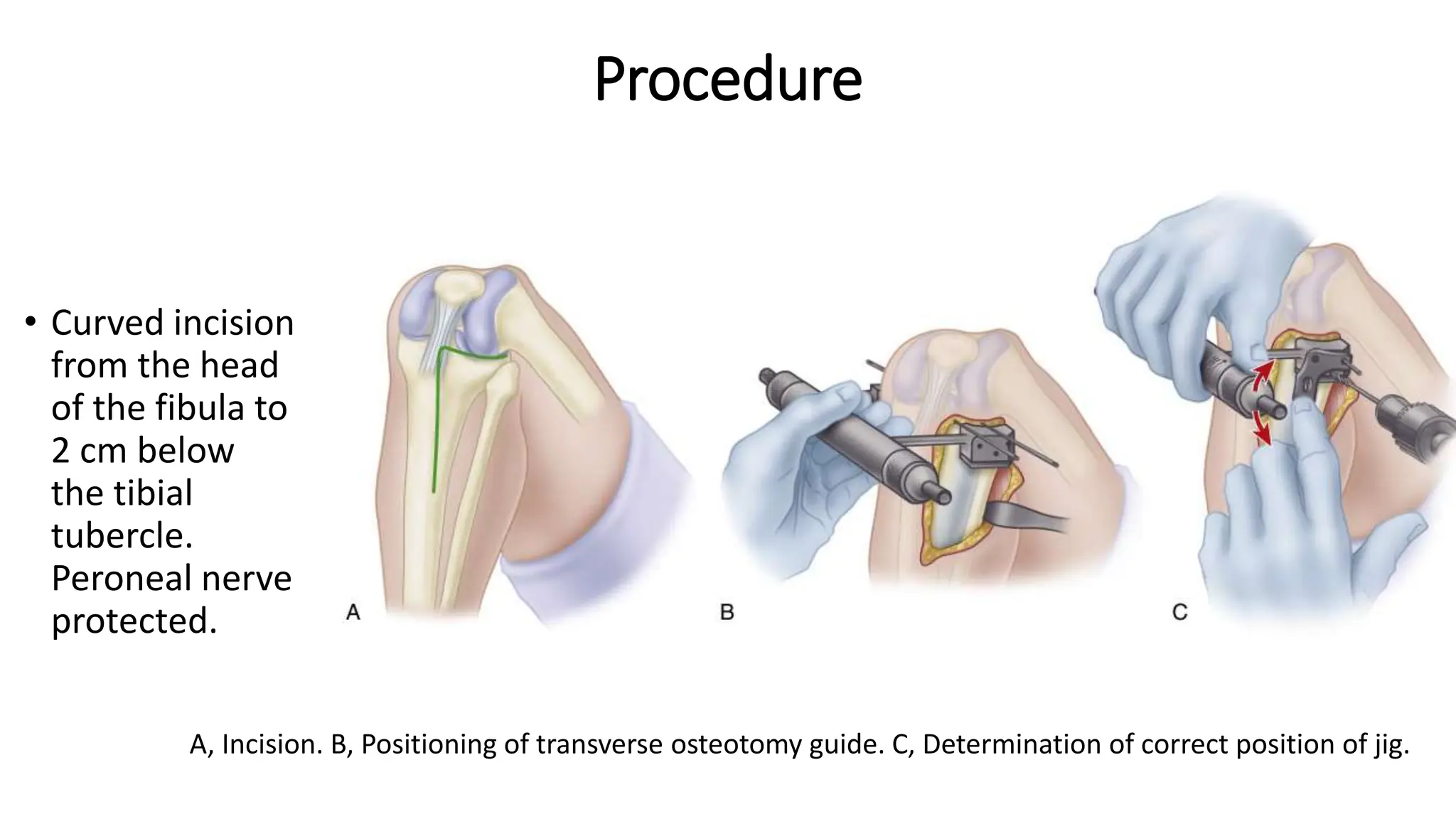
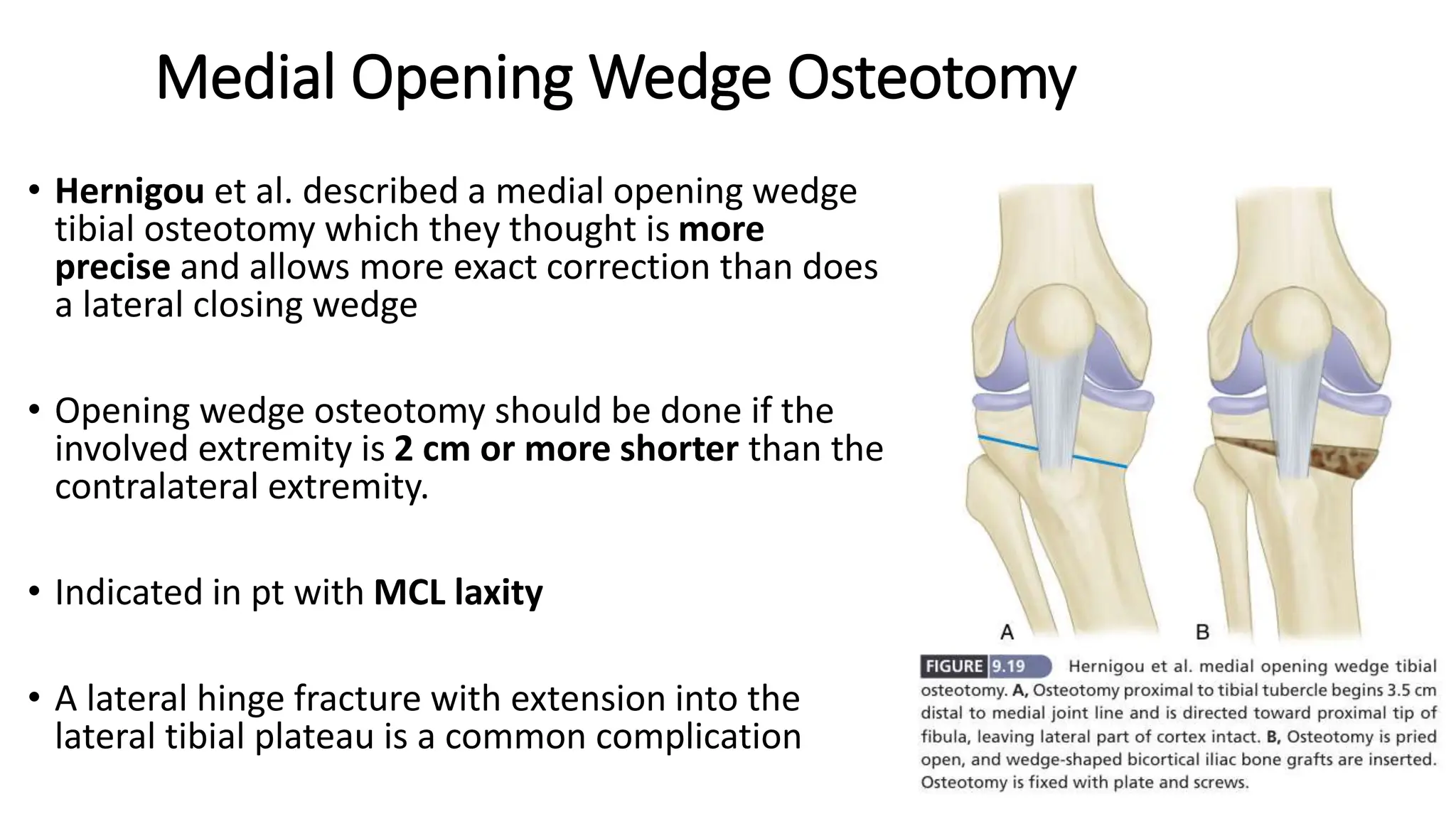
High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a surgical procedure primarily used to treat unicompartmental osteoarthritis of the knee, showing about 80% satisfaction rates at five years. The procedure involves realigning the mechanical and anatomic axes of the tibia through various techniques, including opening and closing wedge osteotomies, to redistribute load and relieve pain. Ideal candidates are usually under 65 years old, have normal range of motion, and possess certain pain tolerance levels, while contraindications include advanced age, inflammatory arthritis, and significant malalignment.