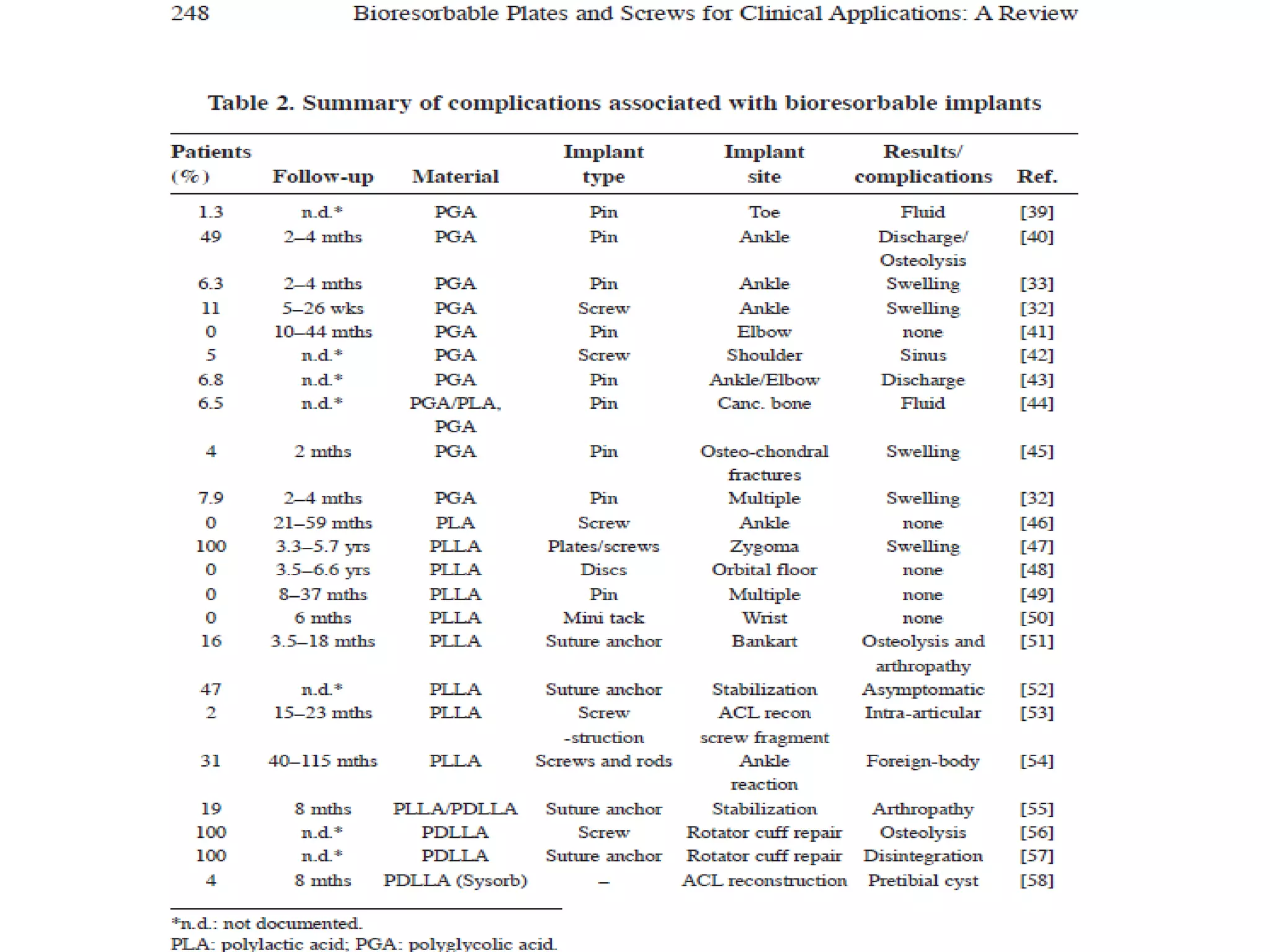
This document discusses bioabsorbable implants used in orthopaedics. It defines bioabsorbable implants as those that gradually degrade through biological processes and are absorbed and excreted by the body. Common materials used include polyglycolic acid and polylactic acid. Bioabsorbable implants offer advantages over metallic implants by eliminating the need for removal surgery and avoiding problems like stress shielding. While offering promise, bioabsorbable implants also have drawbacks like inadequate strength and stiffness. Future areas of development include implants that degrade at medium time periods and ability to deliver drugs locally.