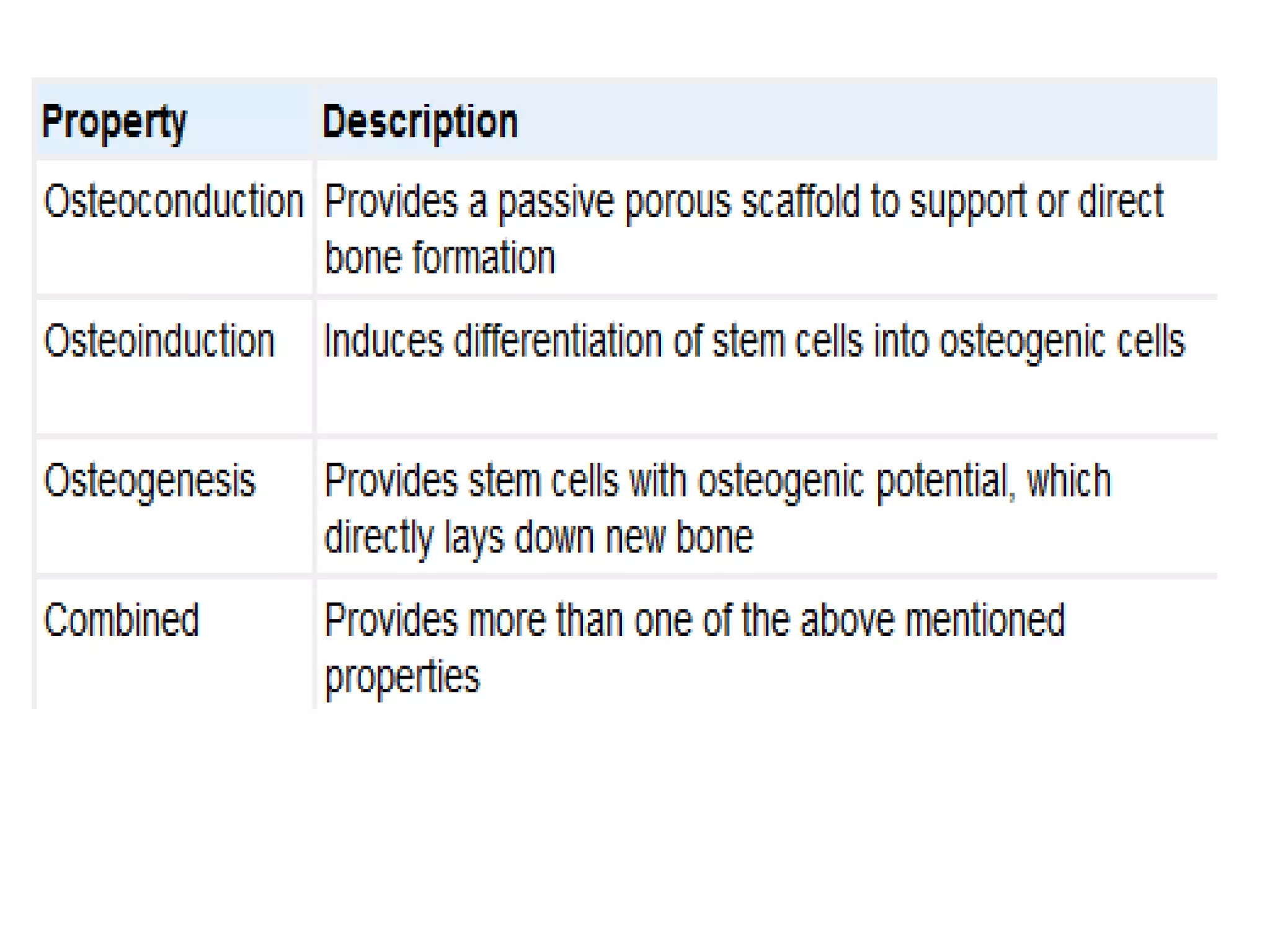
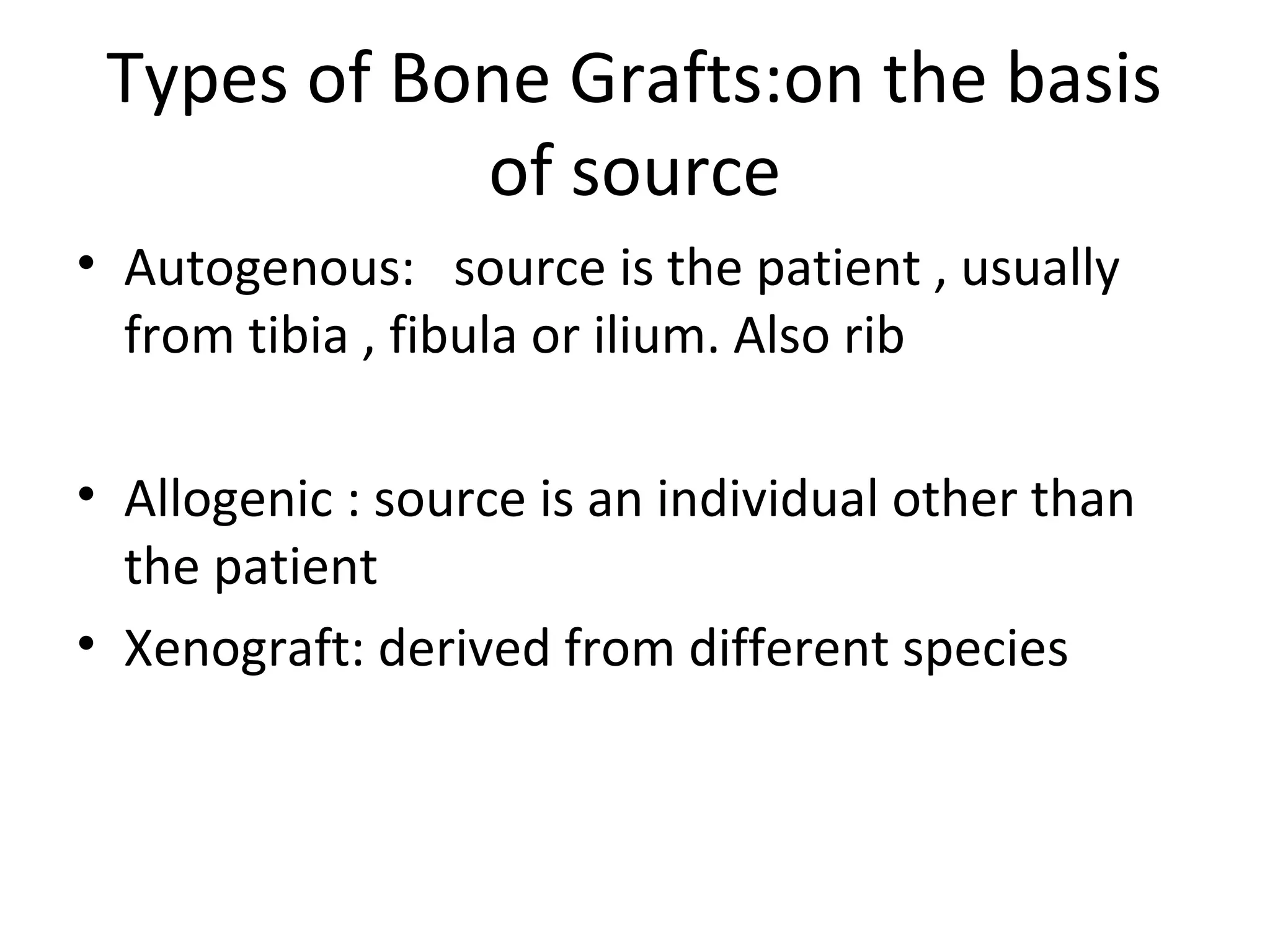
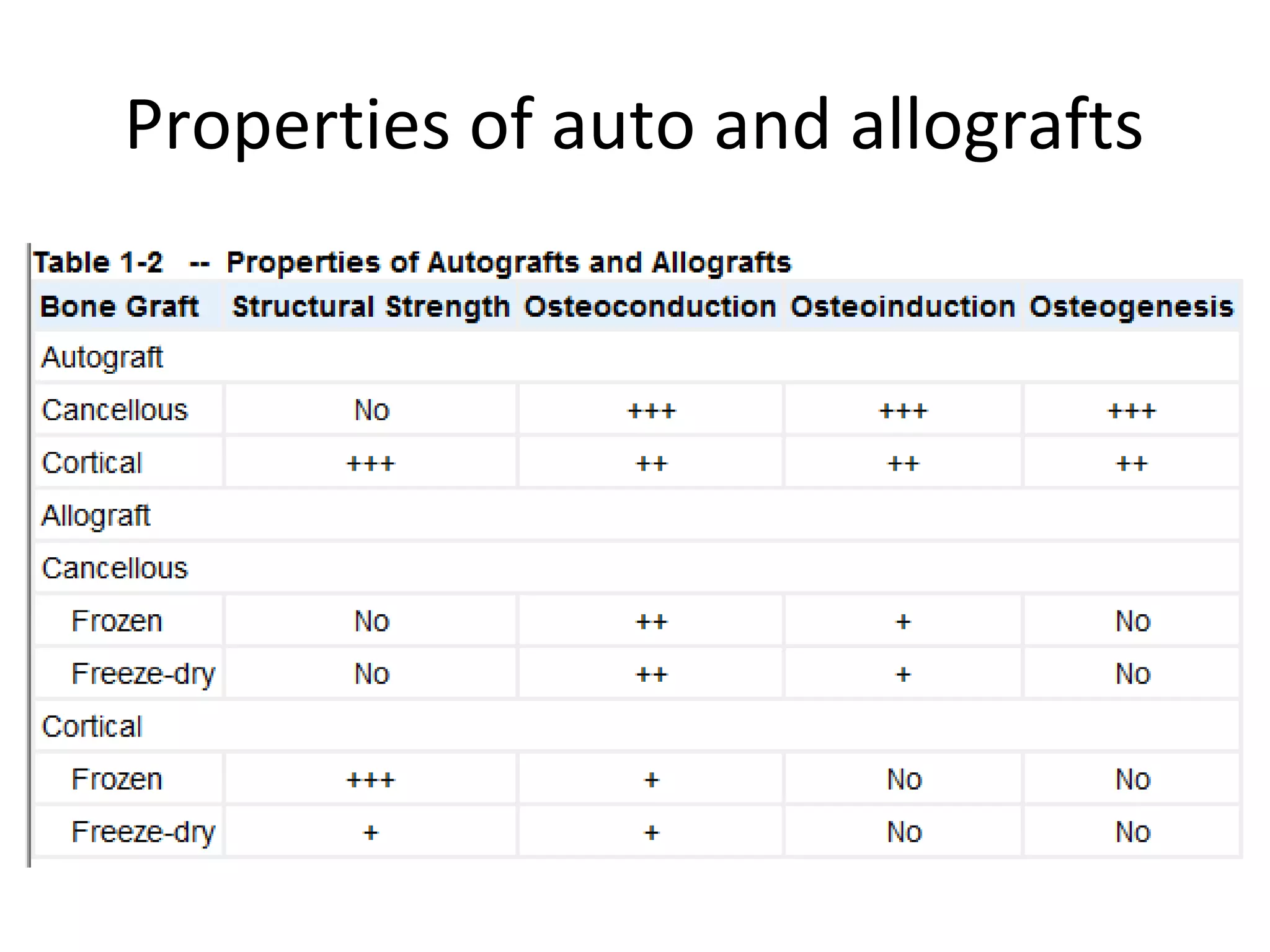
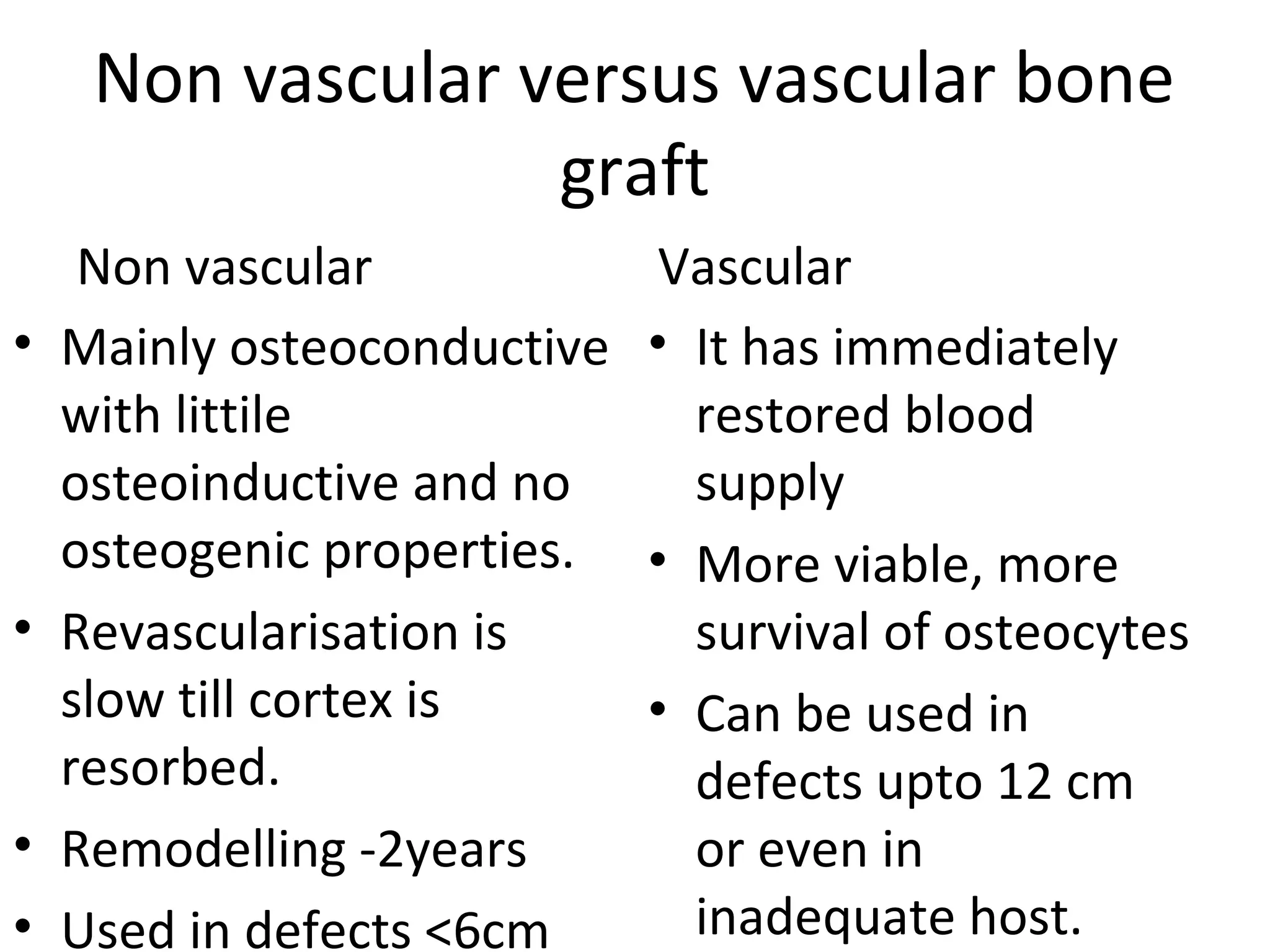
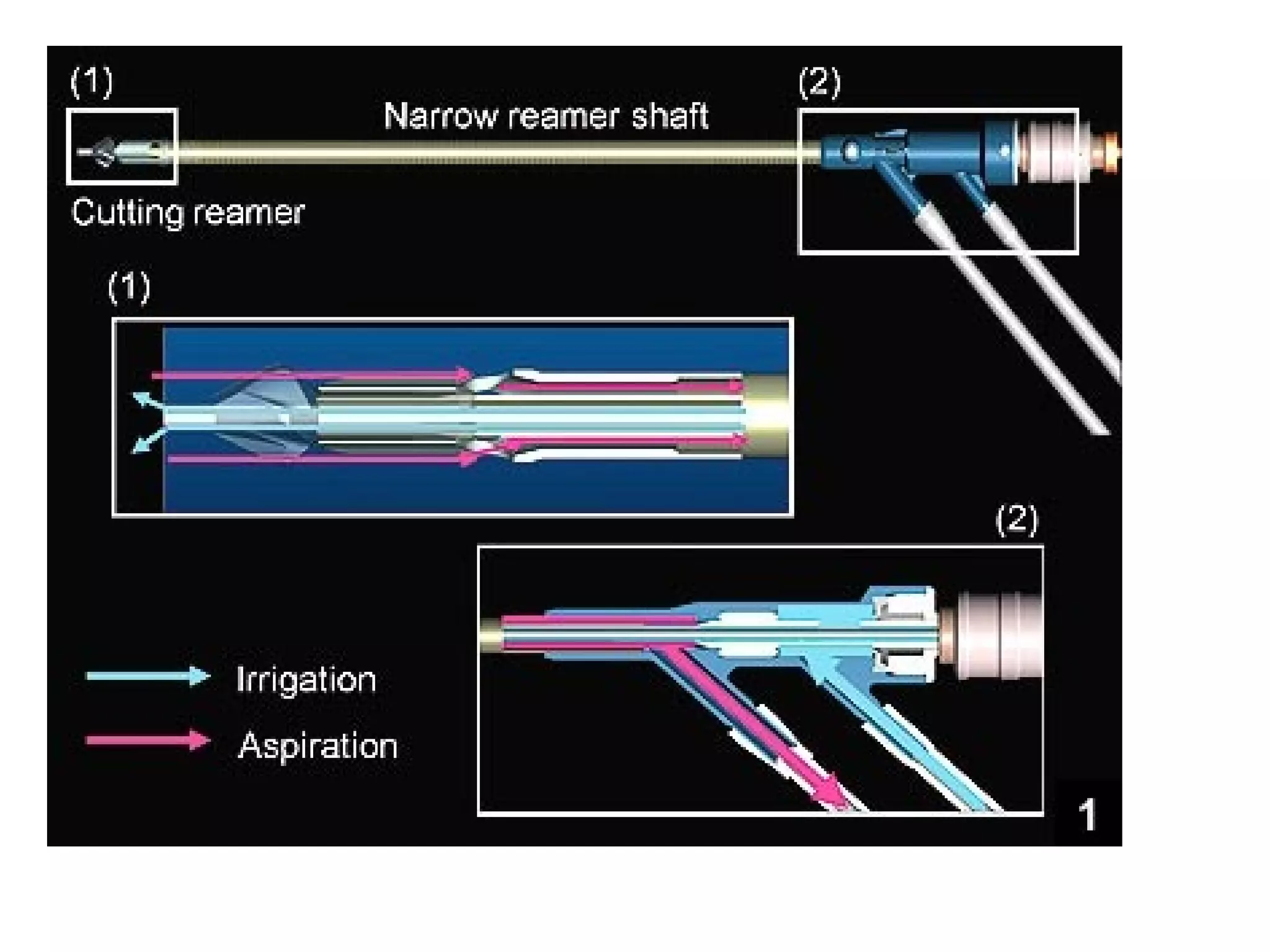
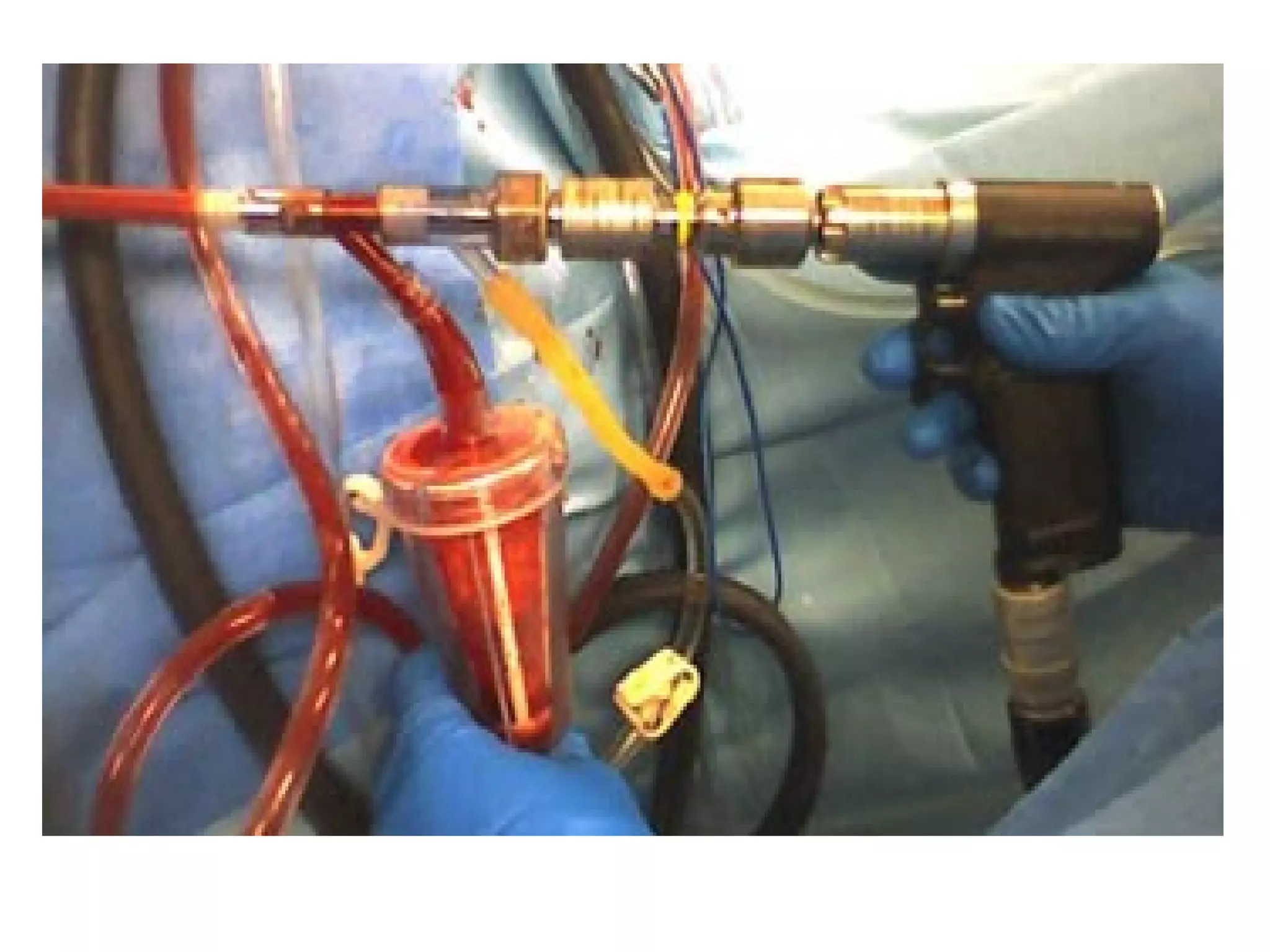
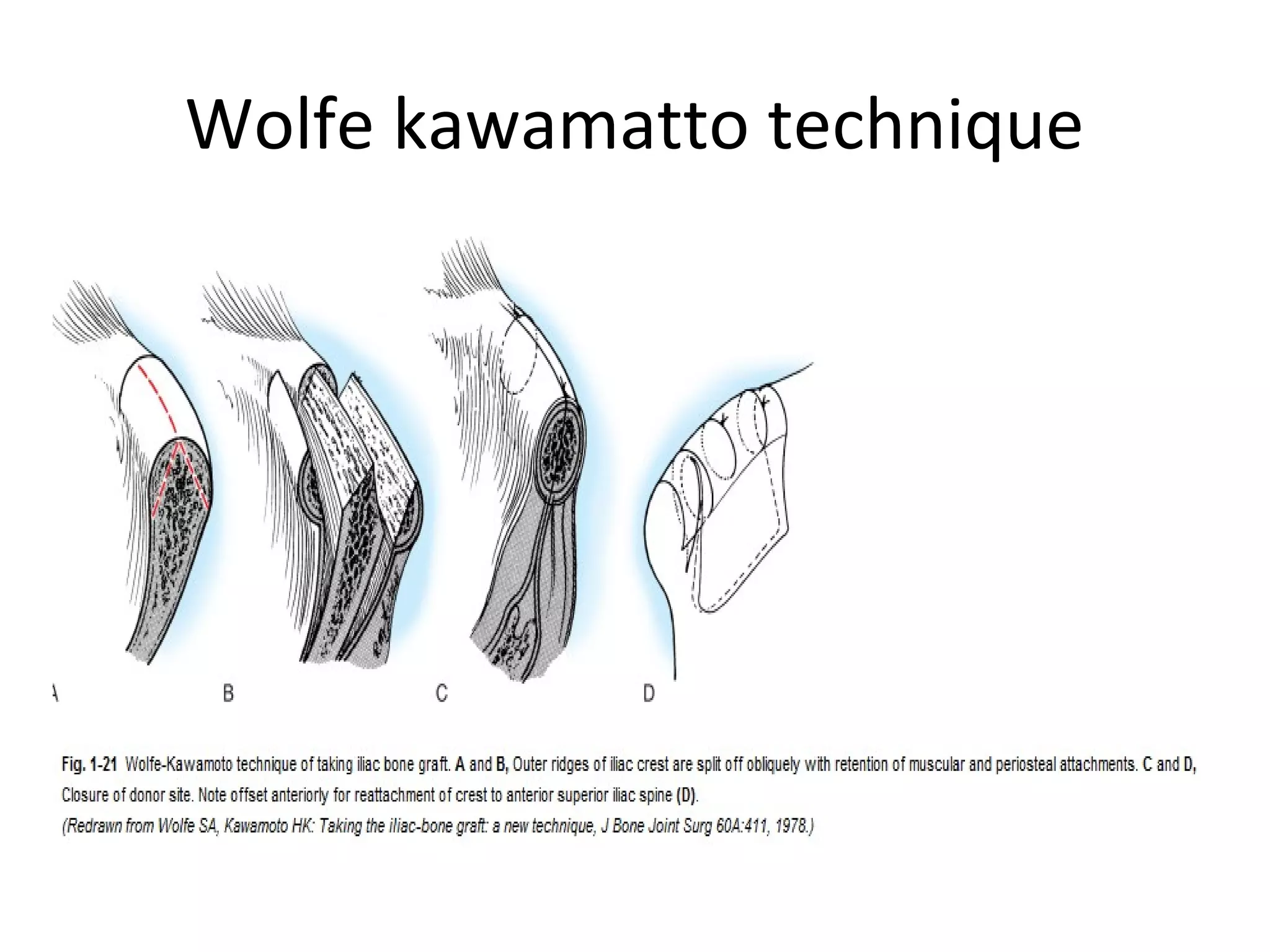
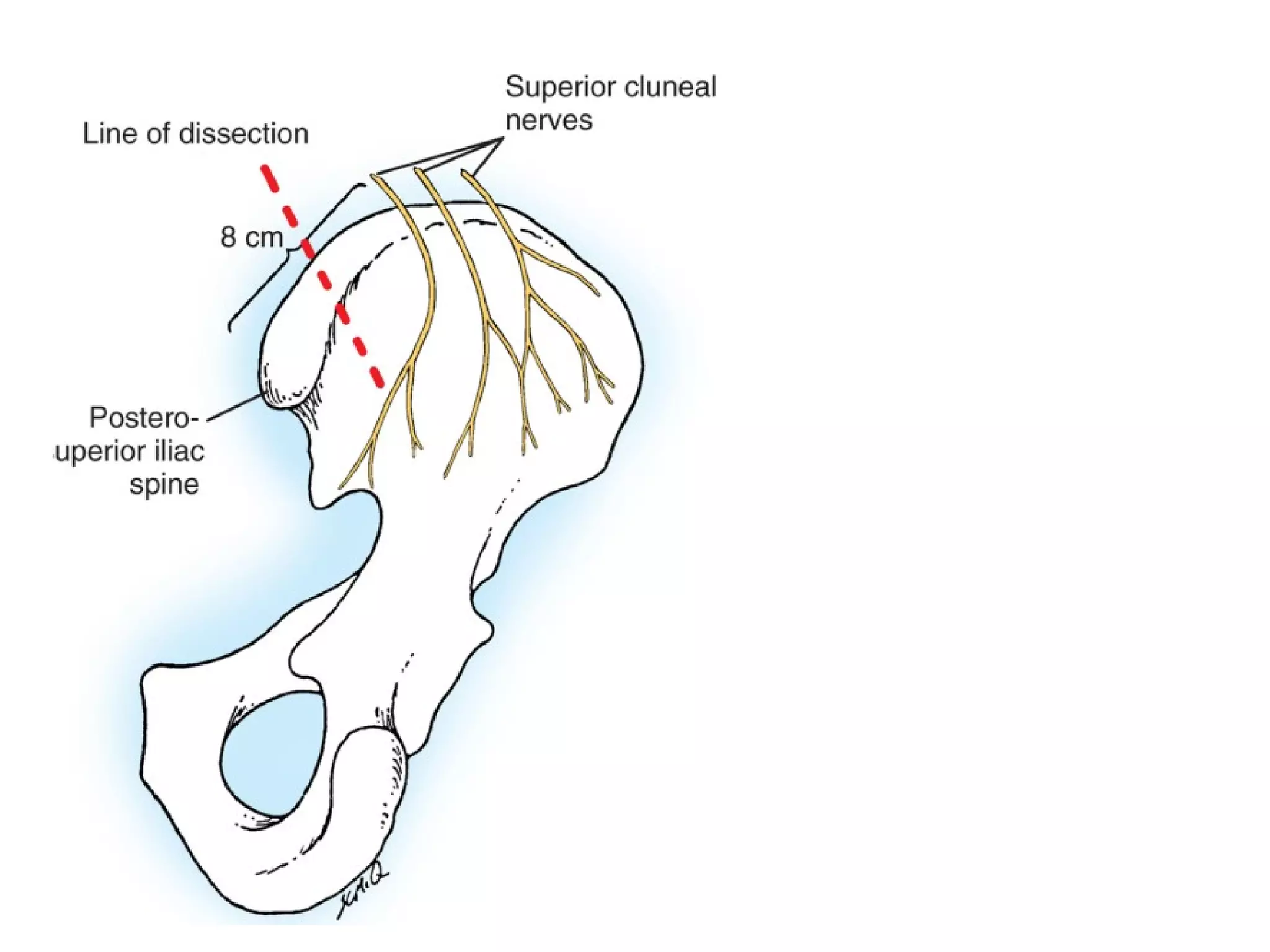
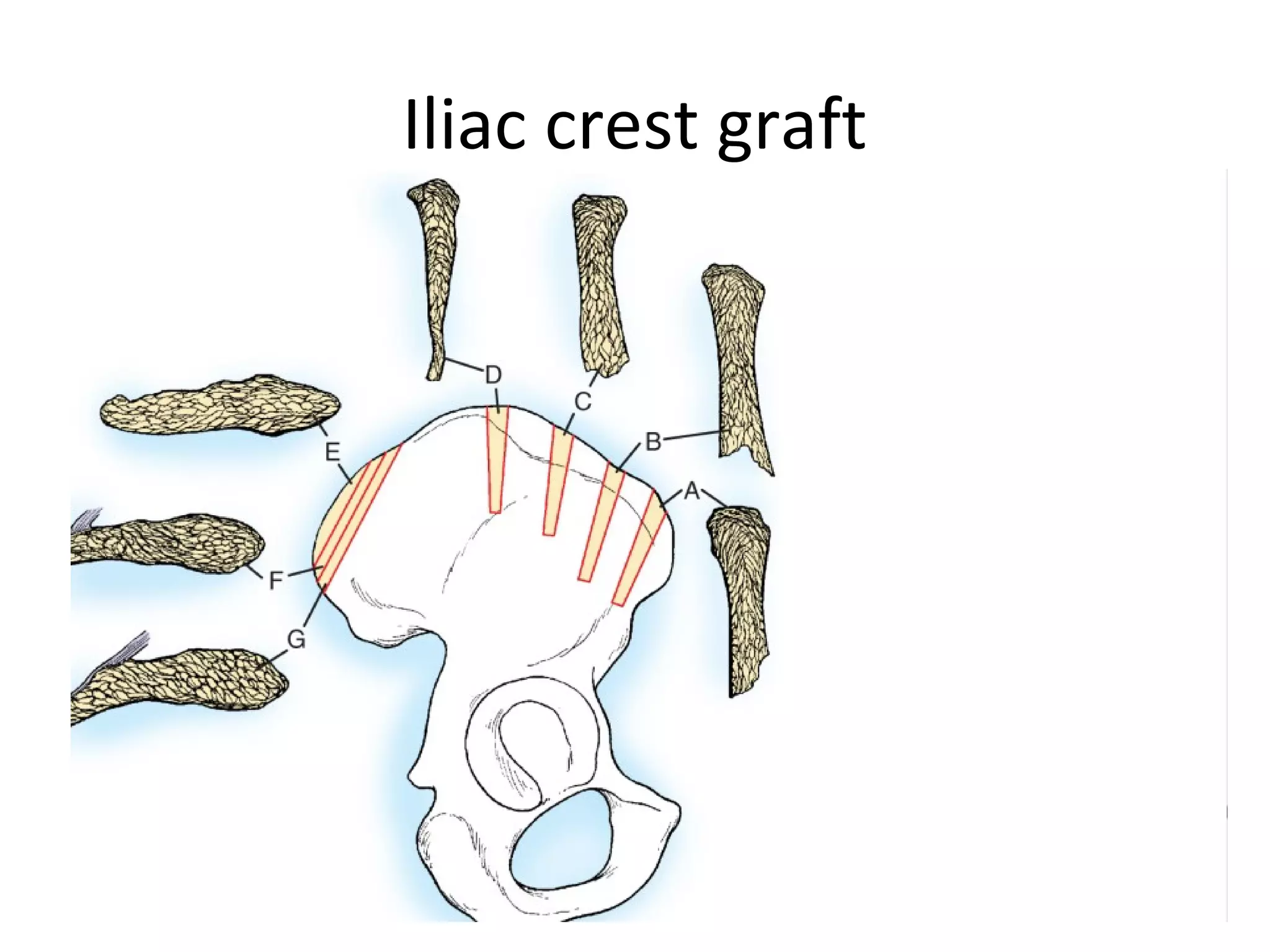
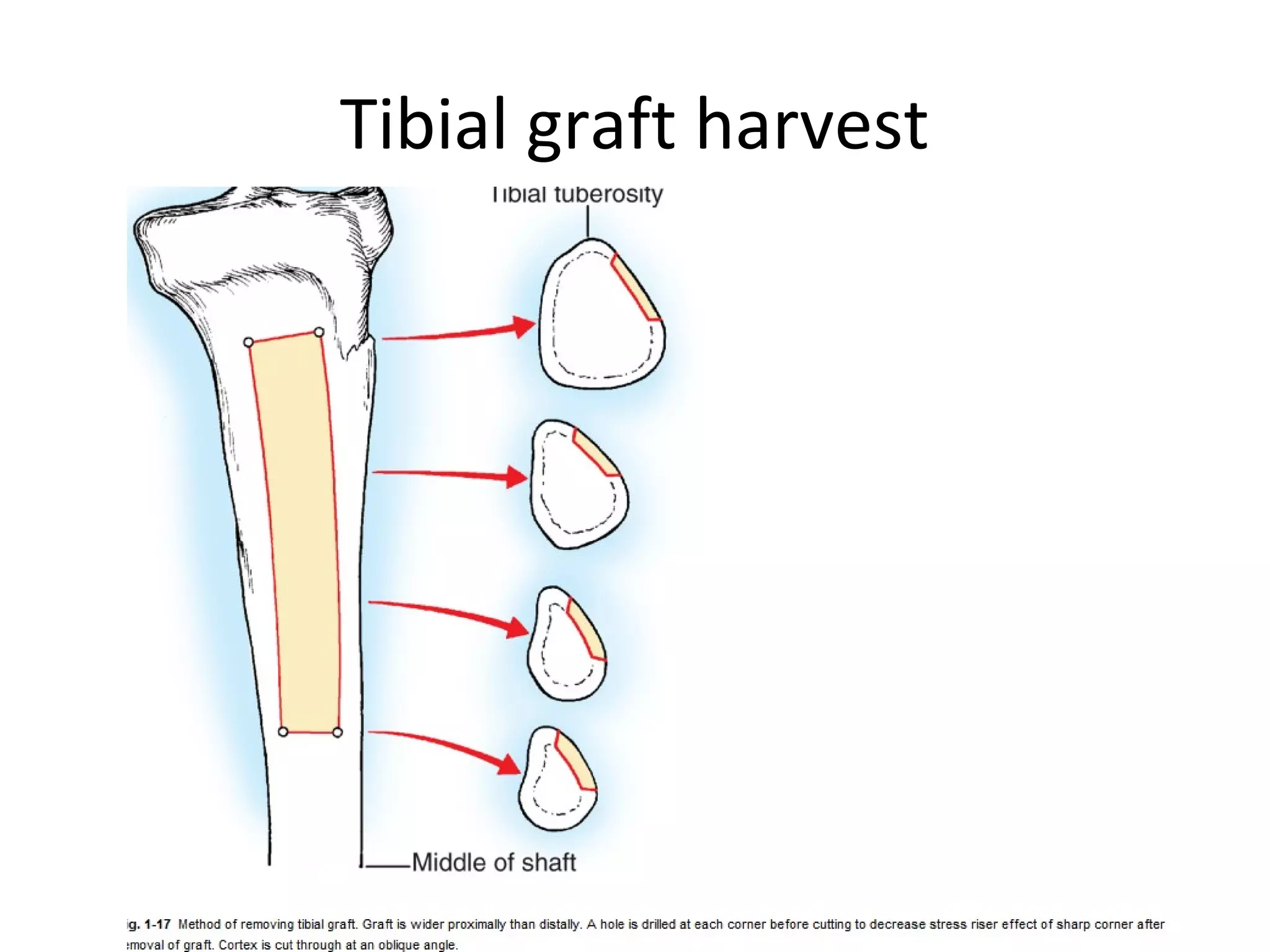
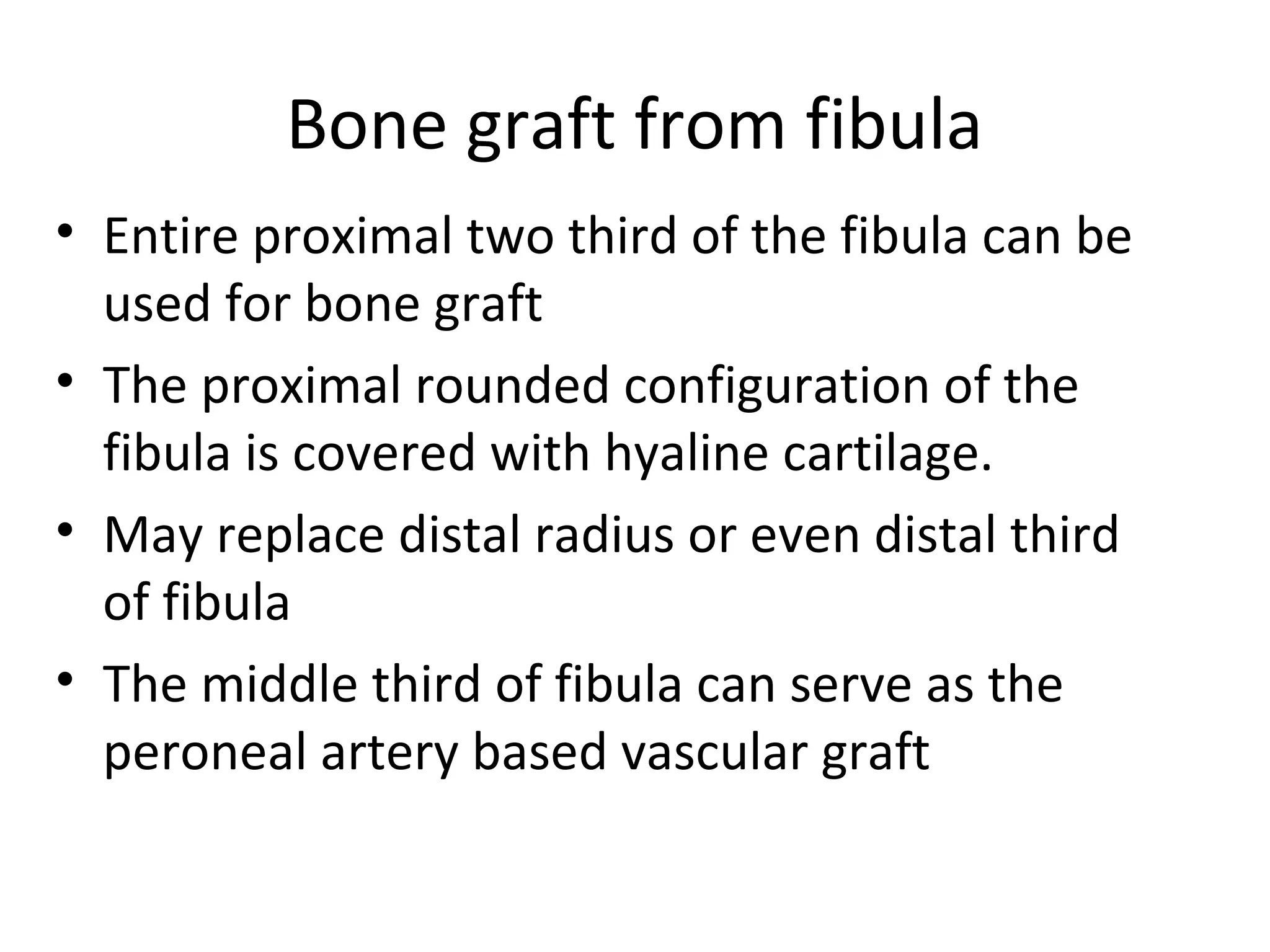
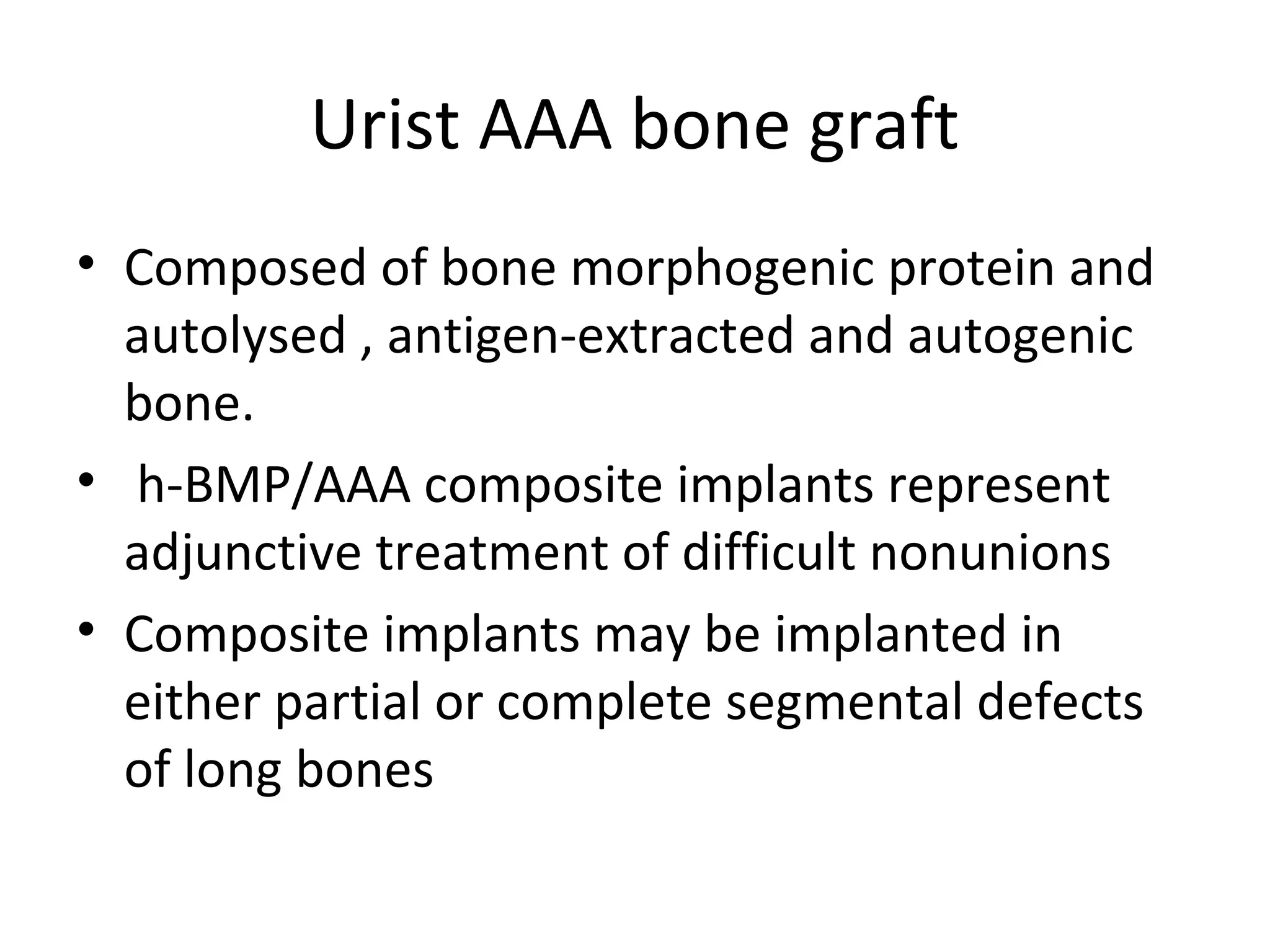
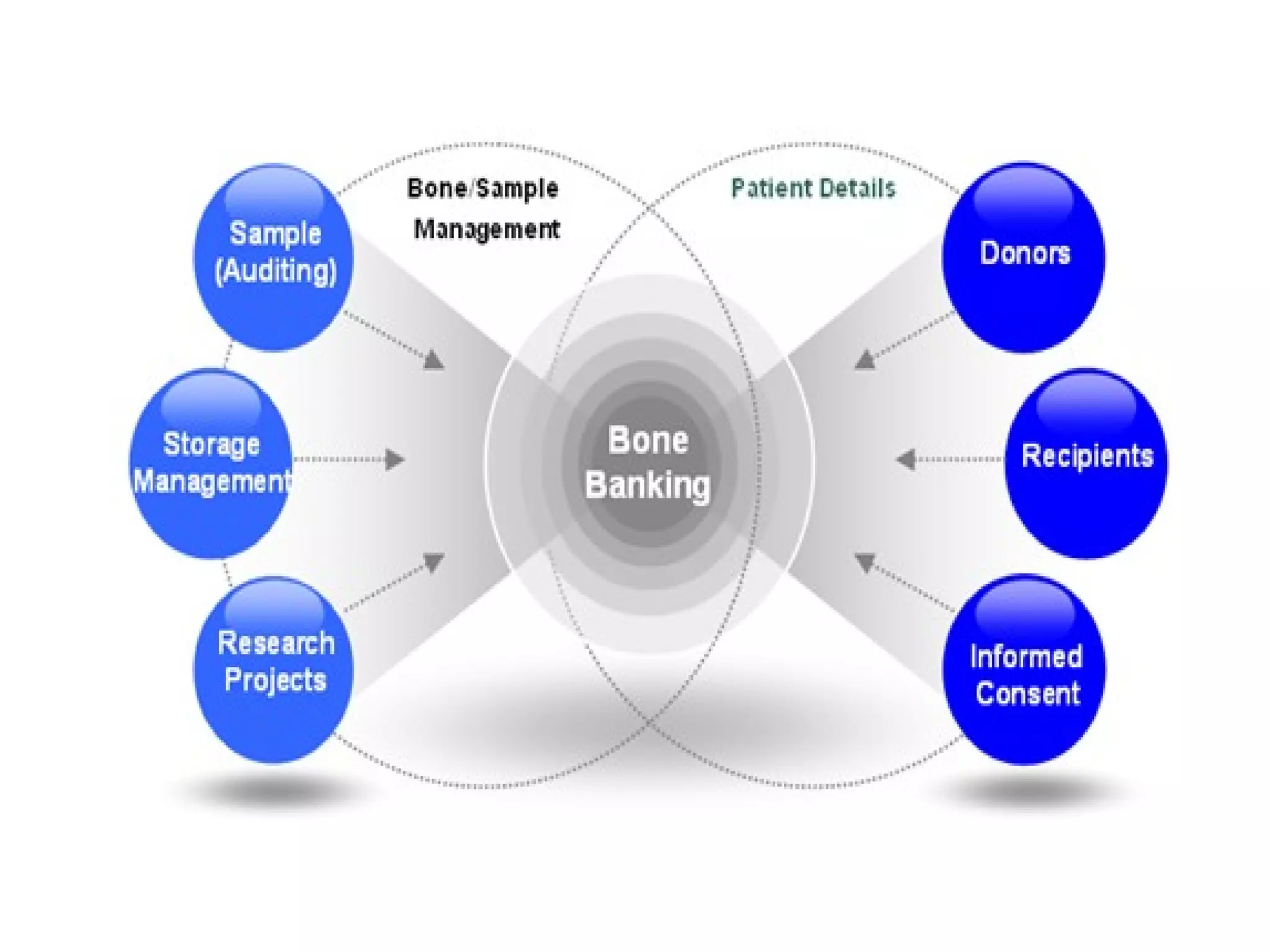
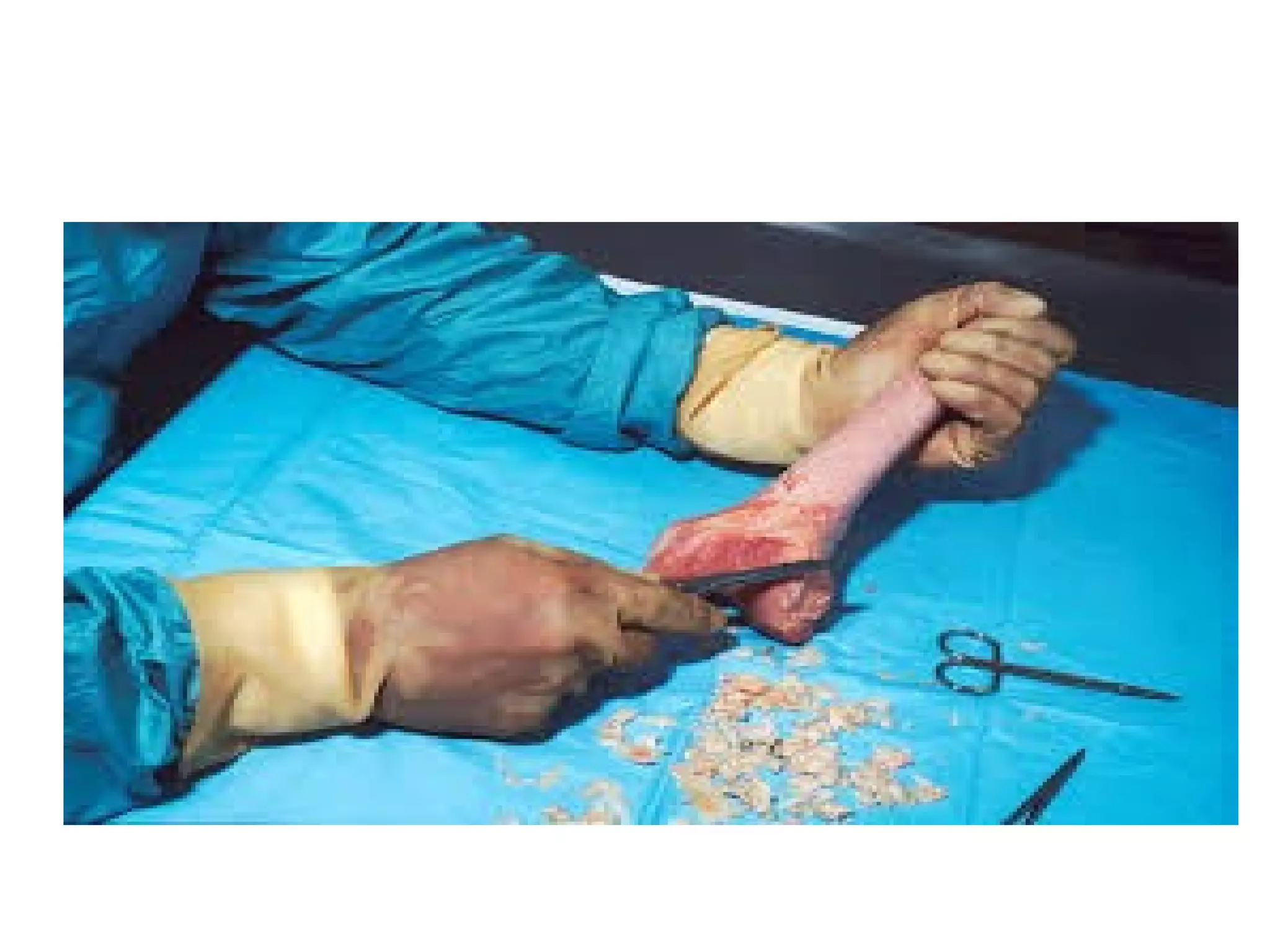
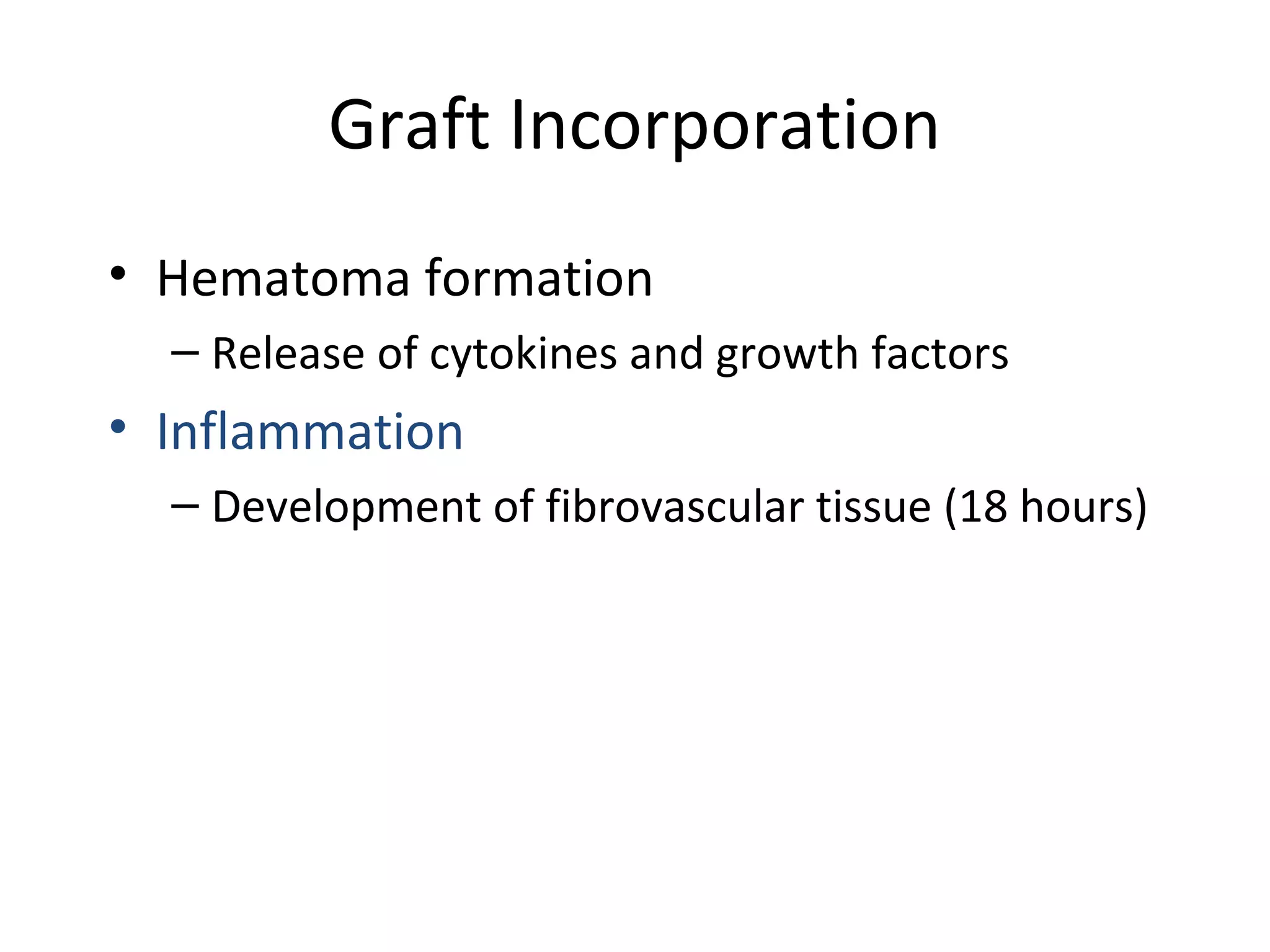
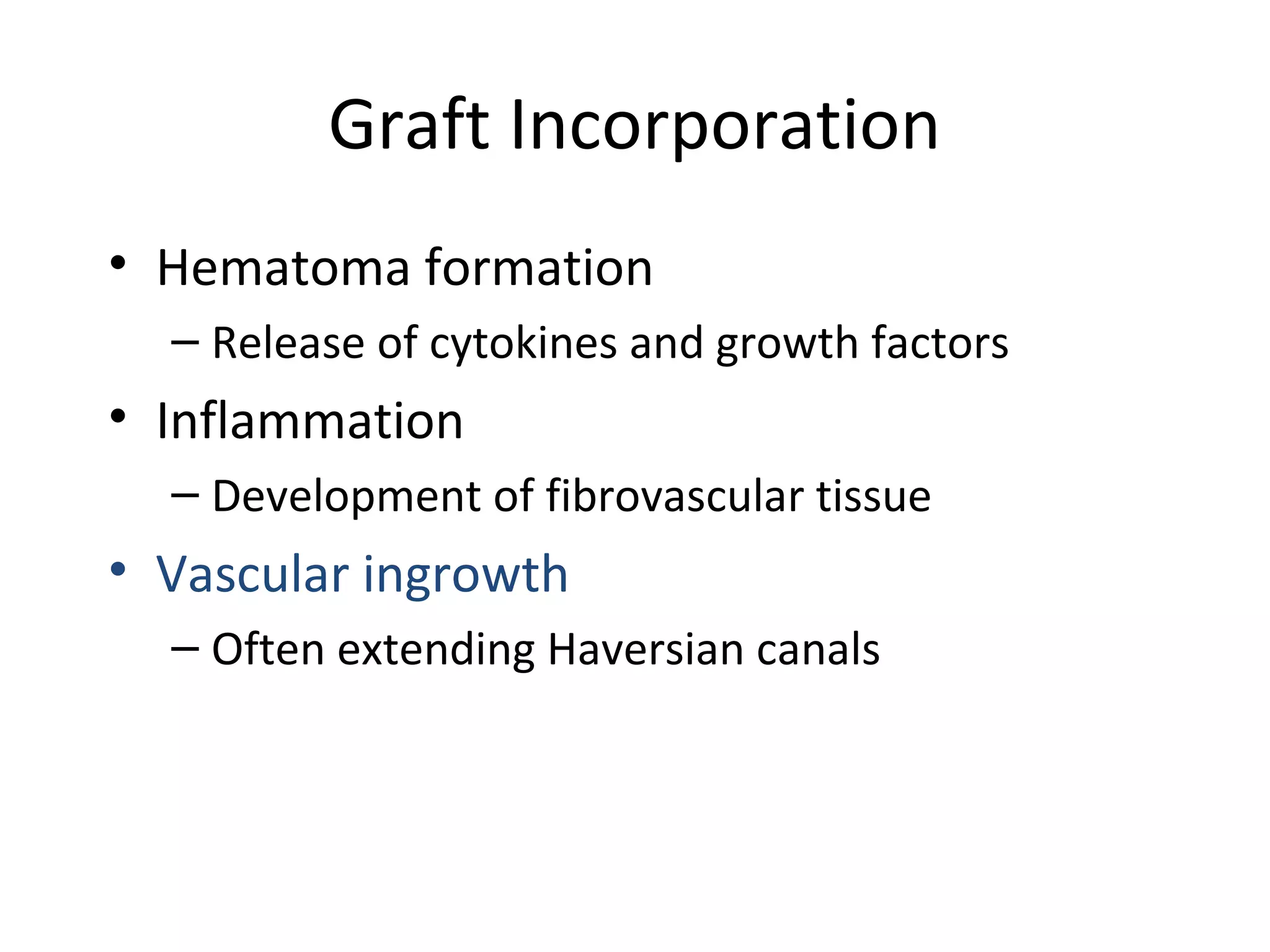
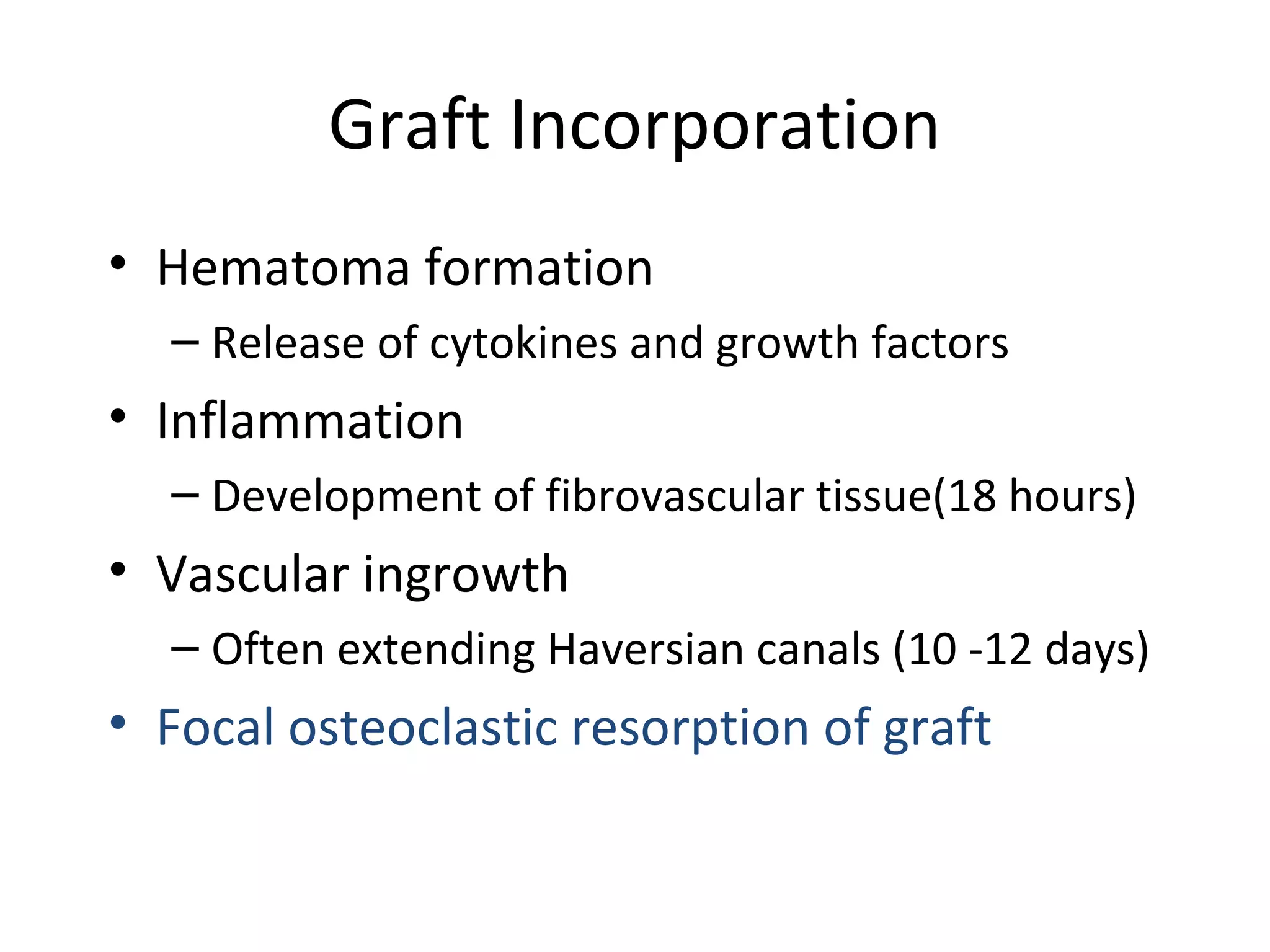
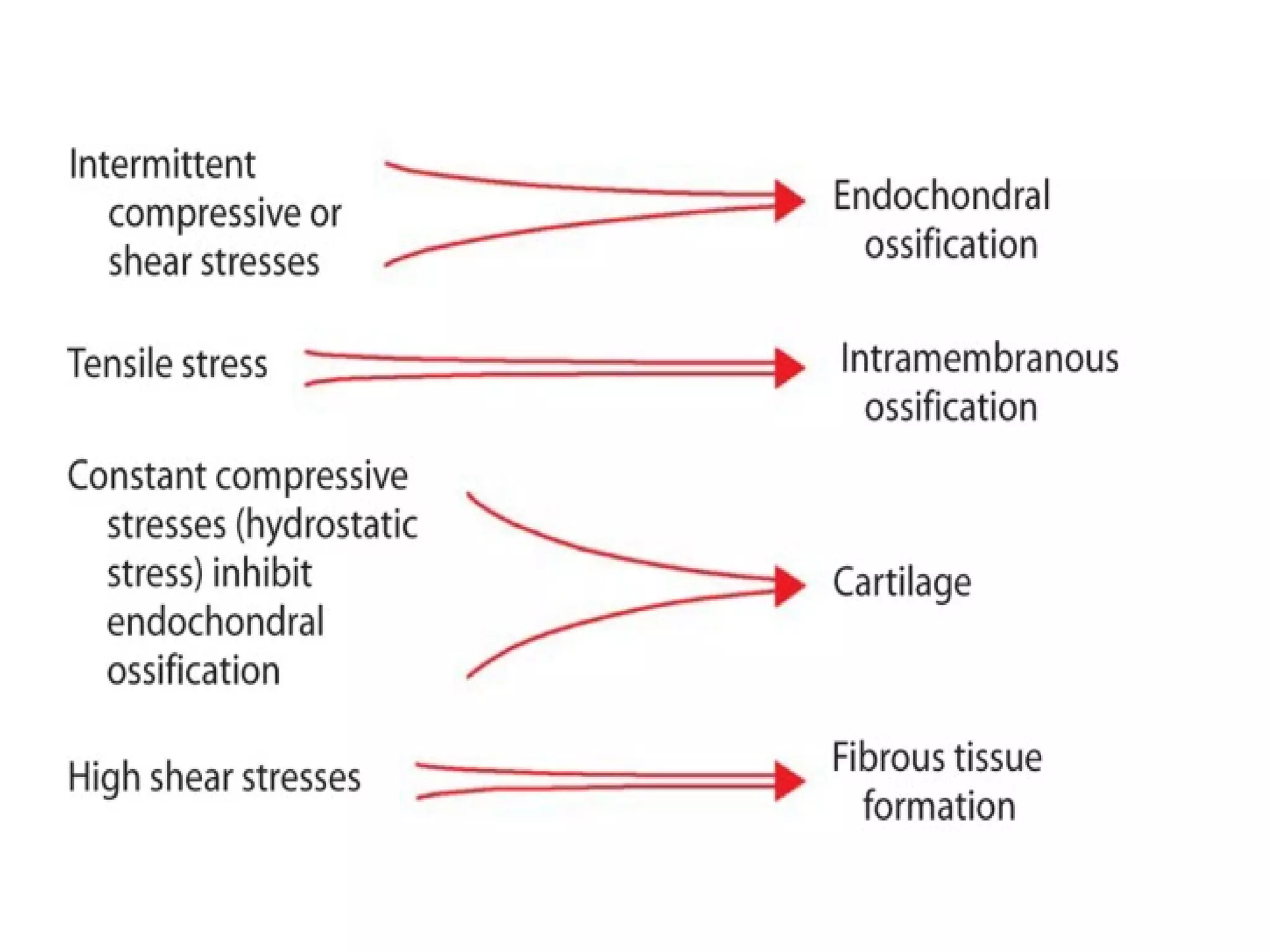
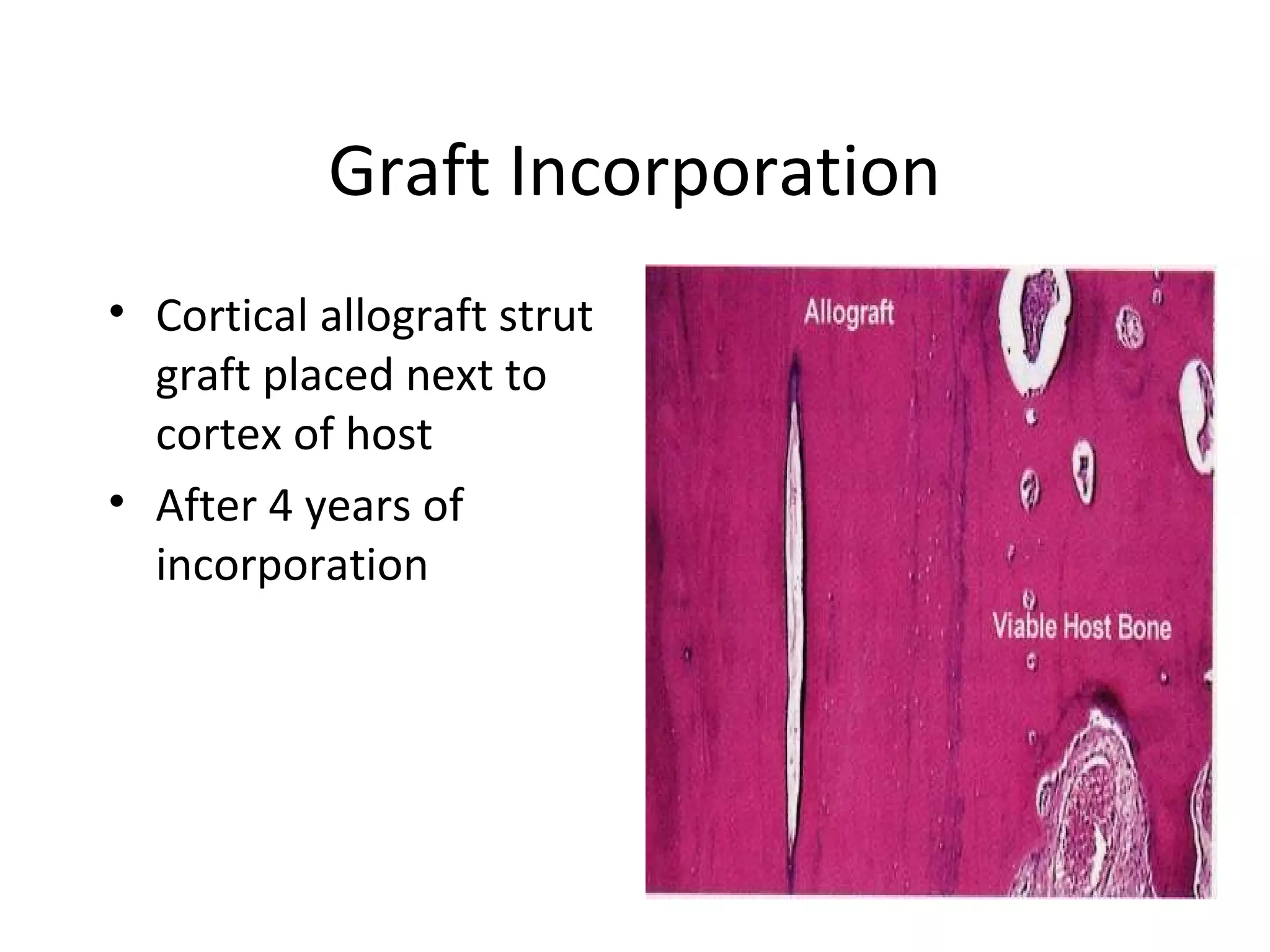
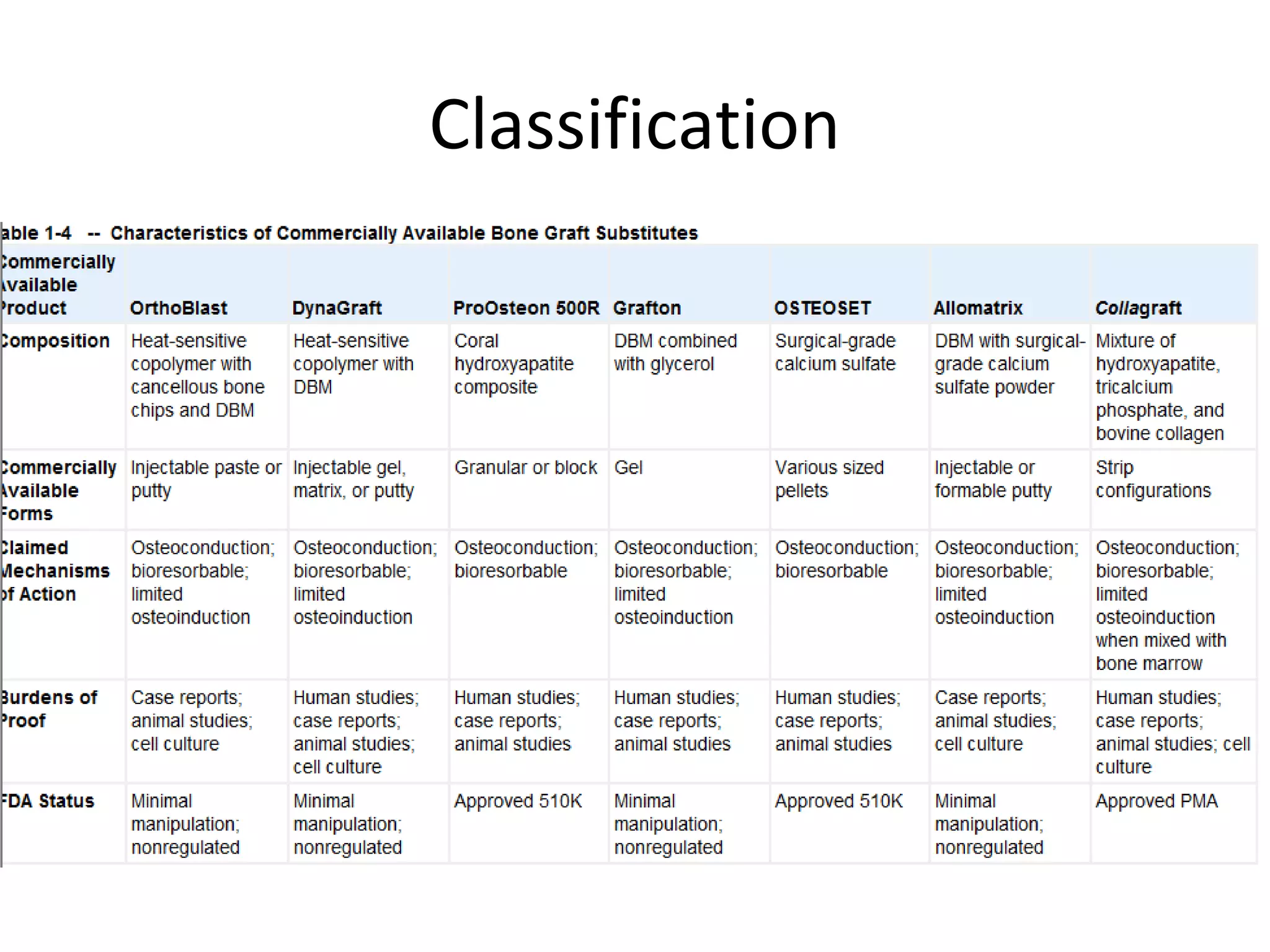
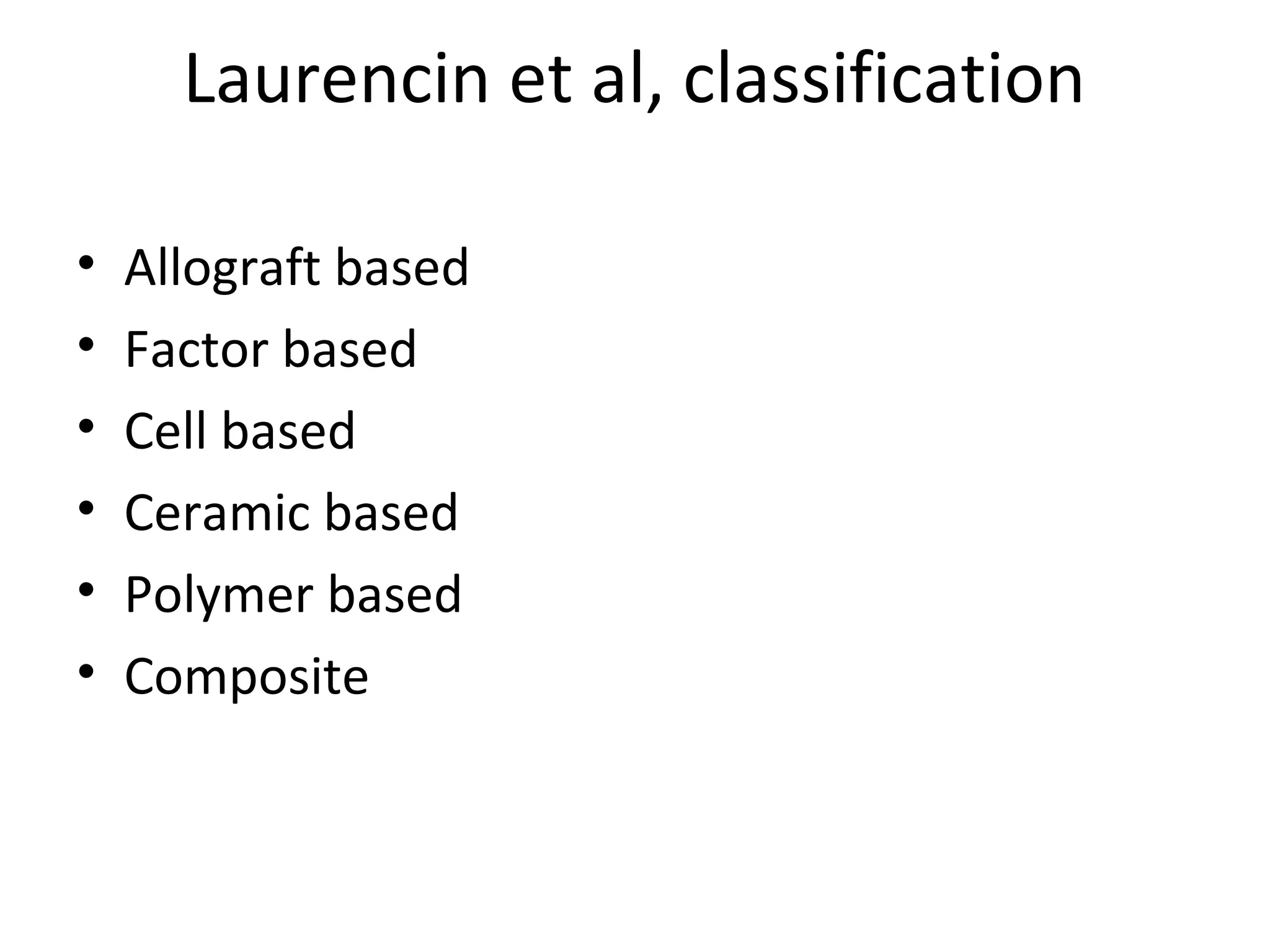
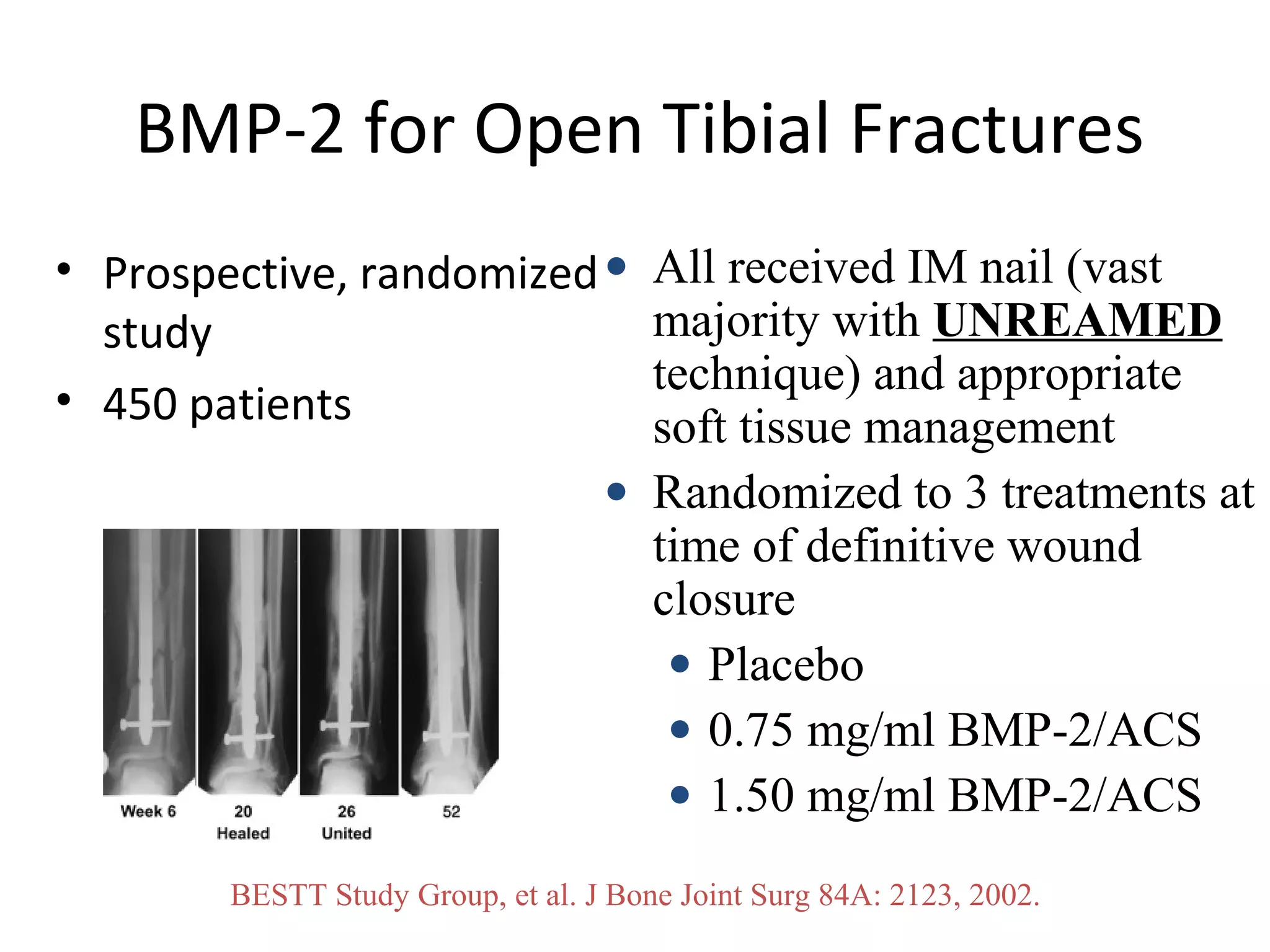
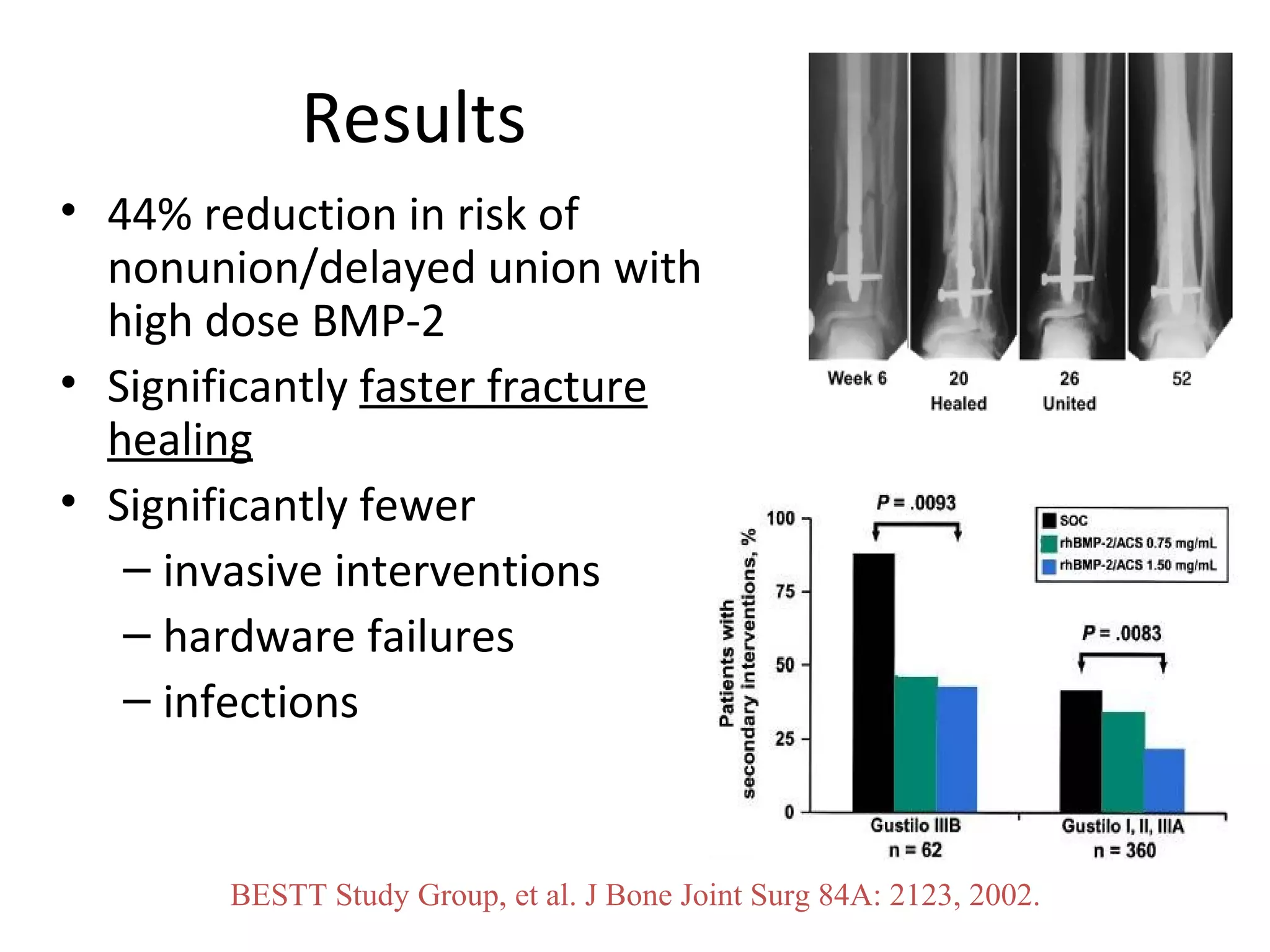
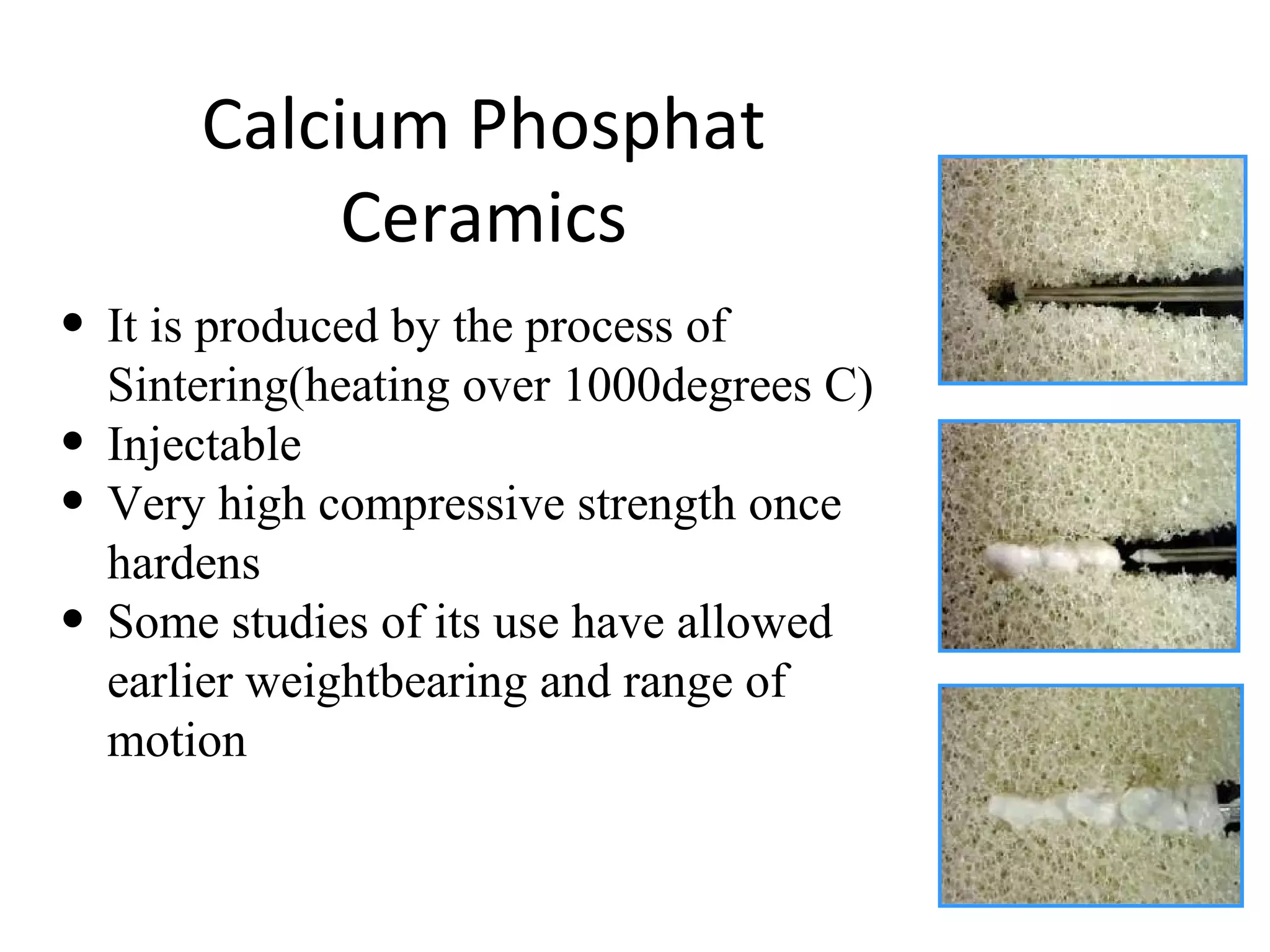
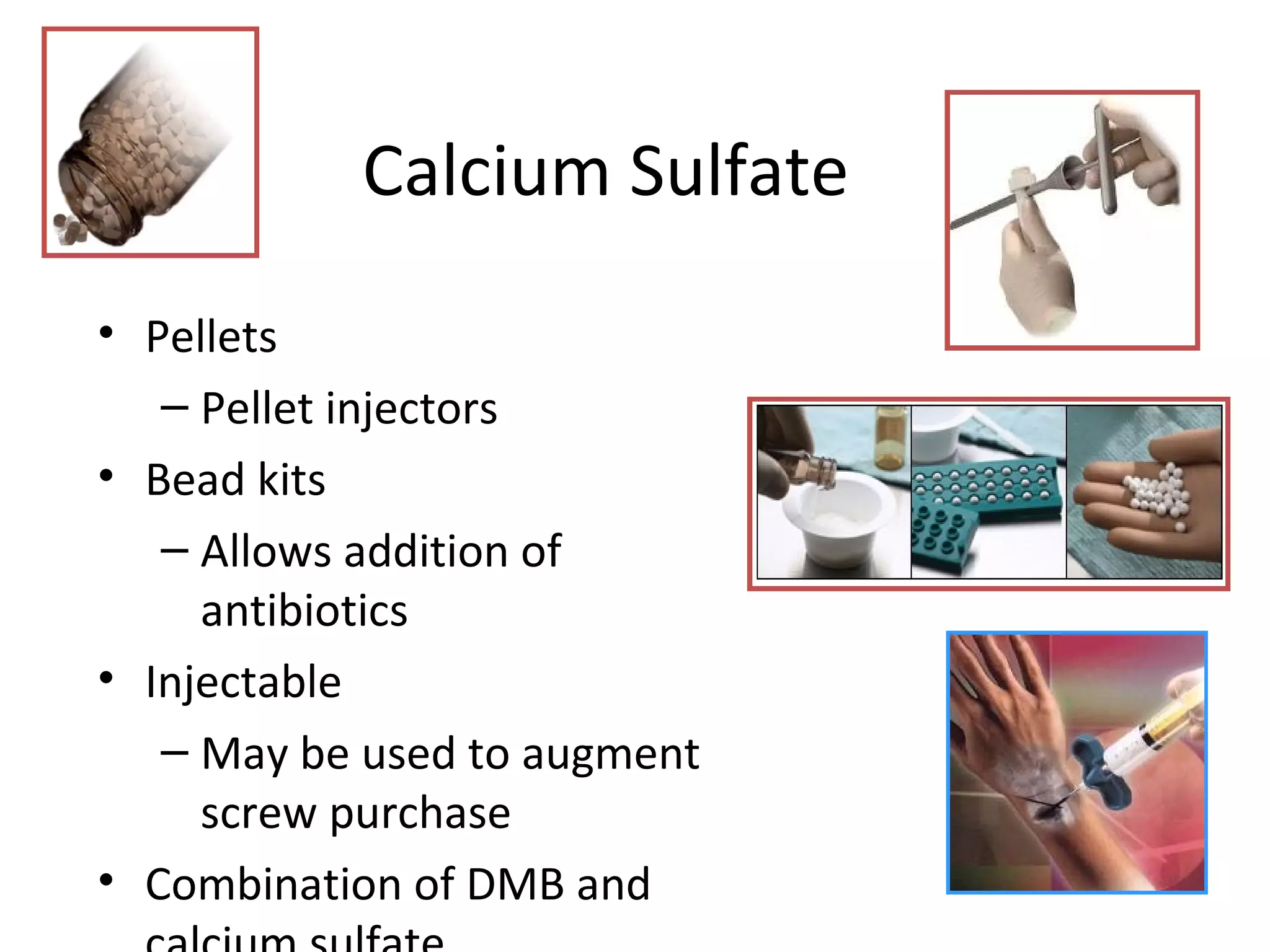
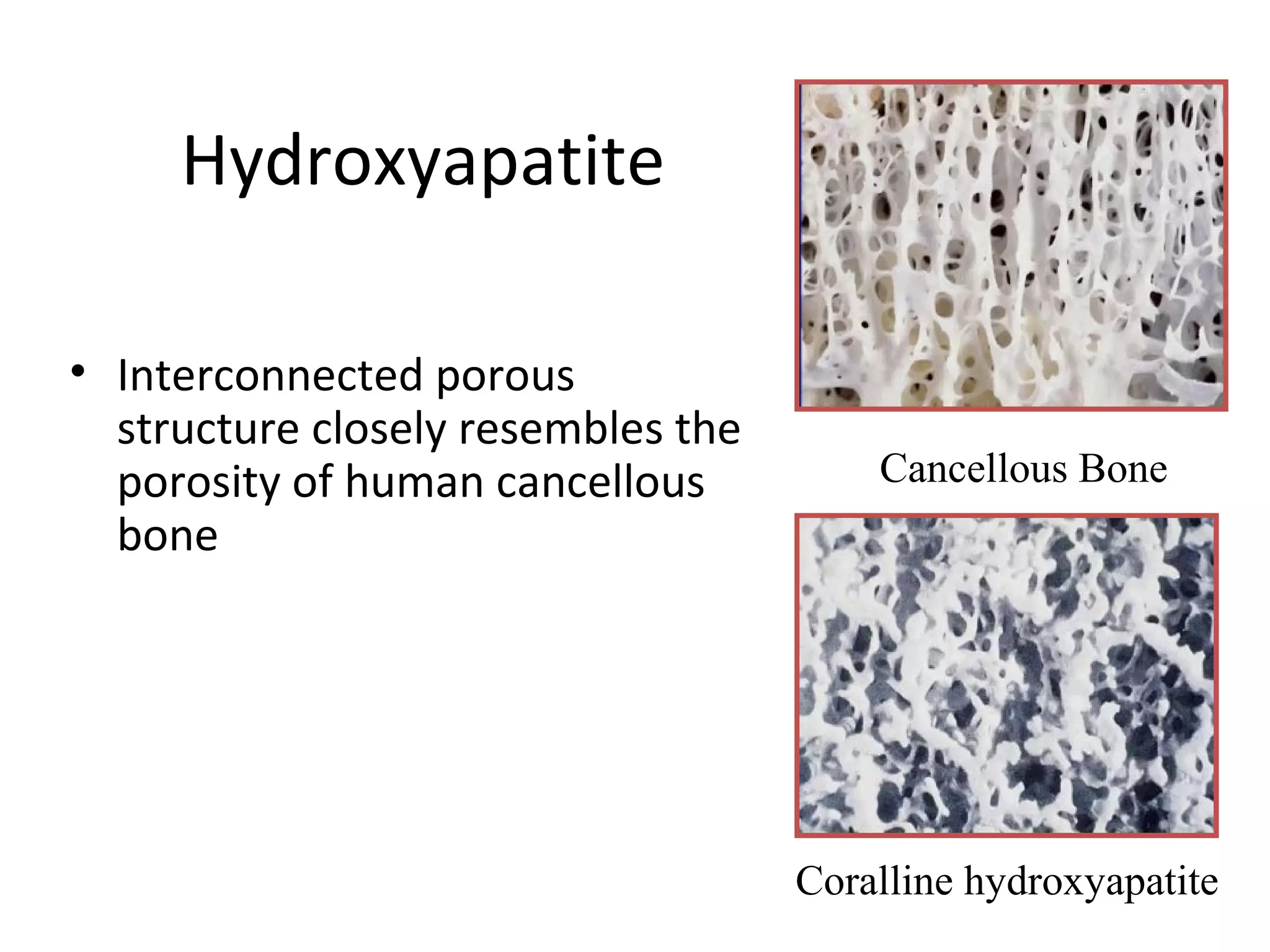
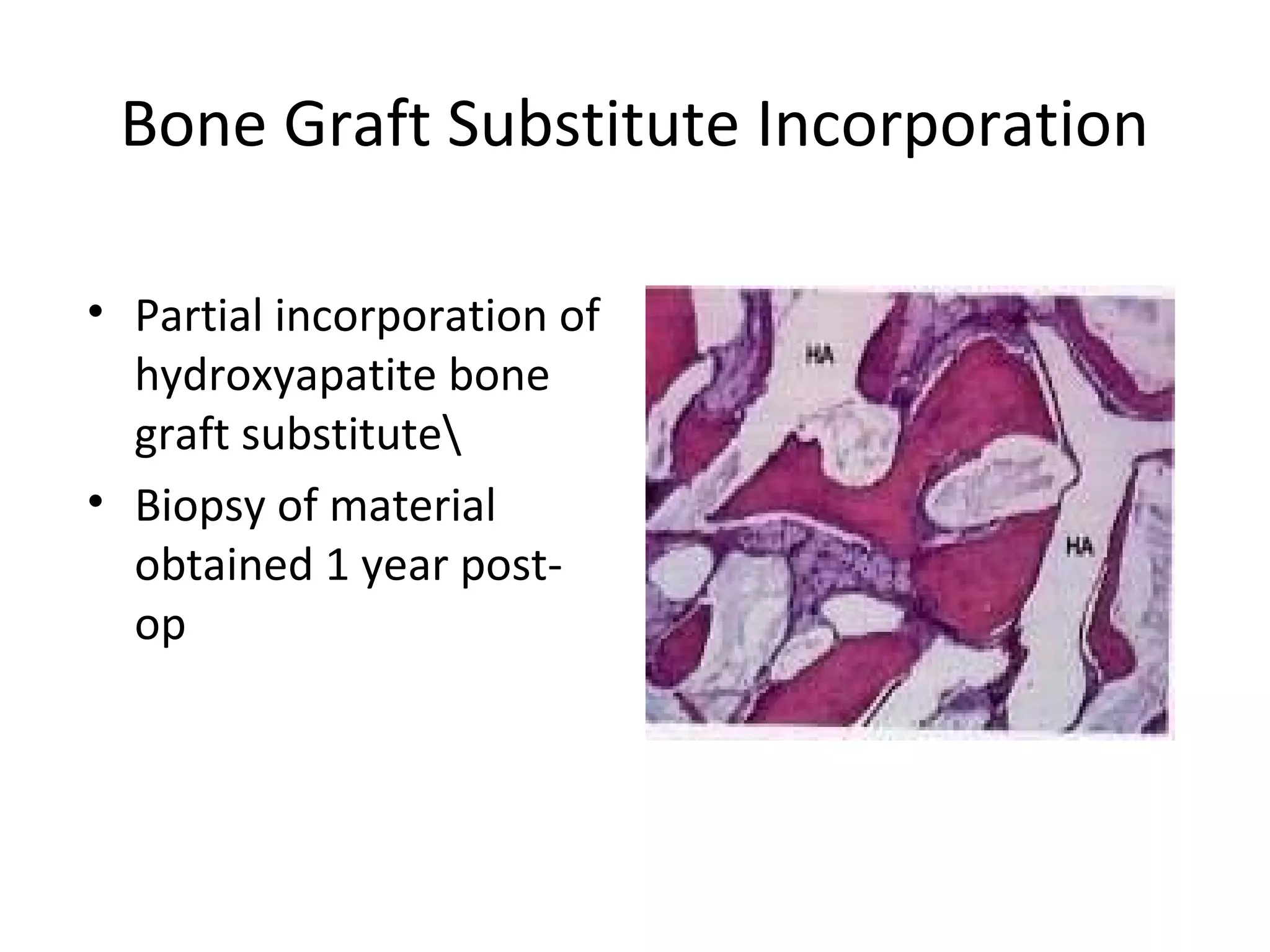
This document summarizes different types of bone grafts and bone graft substitutes. It discusses autogenous bone grafts which are considered the gold standard but have limitations related to donor site morbidity. Allografts from cadaveric donors are also discussed. Bone graft substitutes described include ceramics like calcium sulfate and calcium phosphate, demineralized bone matrix, and growth factors like bone morphogenetic proteins which provide osteoinduction. The properties, advantages, and limitations of each type of graft and substitute are summarized.