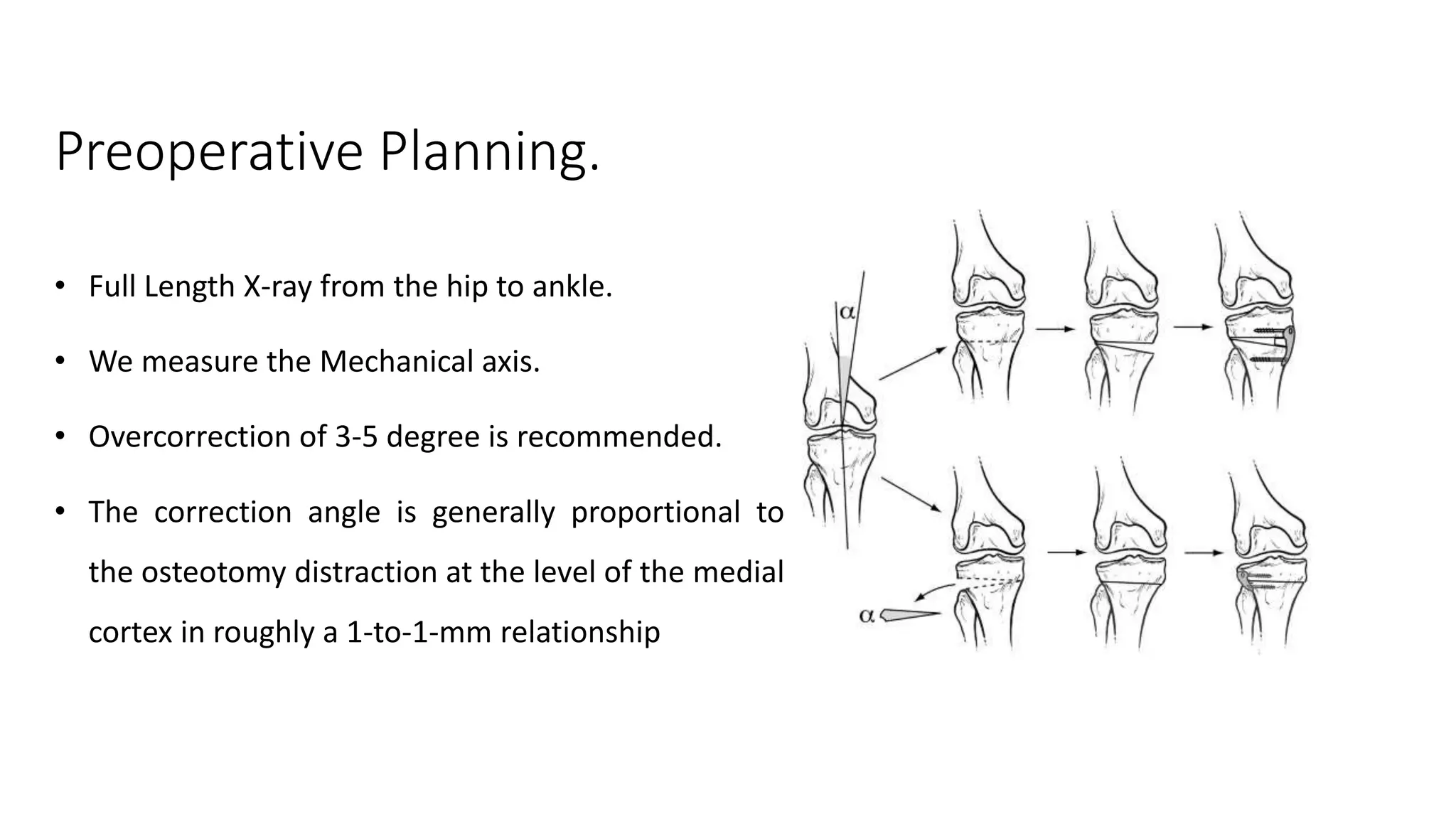
High tibial osteotomies are a surgical procedure used to treat unicompartmental osteoarthritis of the knee caused by malalignment. There are several types of high tibial osteotomies including medial opening wedge, lateral closing wedge, medial opening hemicallotasis, and dome osteotomies. Complications can include recurrence of deformity, irritation or failure of implants, nerve palsy, nonunion, infection, or stiffness. Outcomes of high tibial osteotomies are generally good, though some patients may eventually require total knee arthroplasty. High tibial osteotomies can be combined with cartilage restoration procedures, though long-term outcomes of graft survival are mixed.