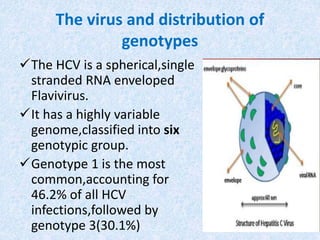
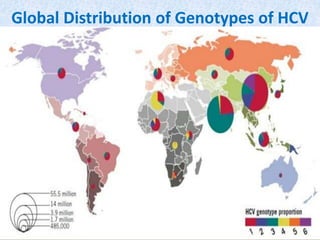
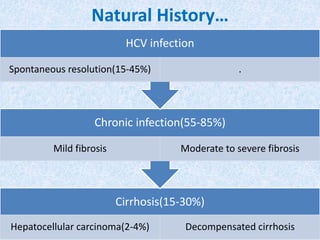
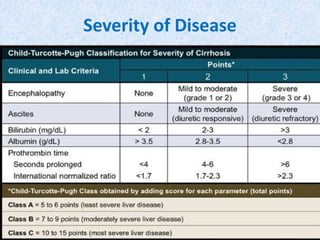
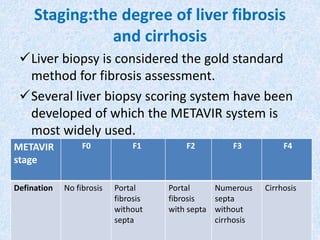
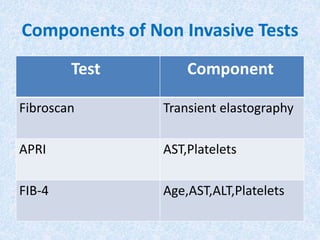
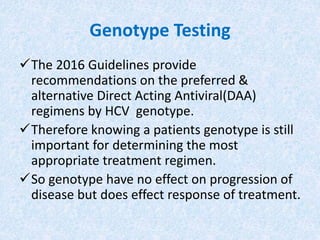
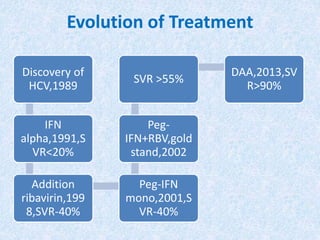
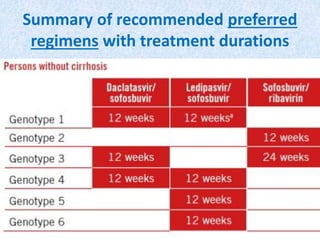
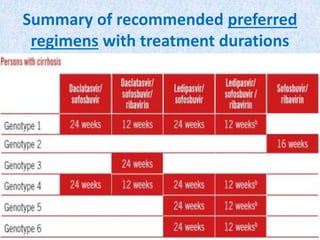
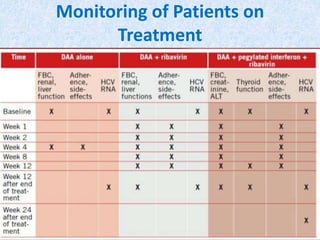
Hepatitis C is a global health problem that causes 700,000 deaths per year. In Bangladesh, 1% of the population has HCV. New guidelines recommend screening high-risk groups and treating with direct-acting antiviral drugs, which have cure rates over 90% and shorter treatment durations compared to previous interferon-based regimens. Proper treatment can prevent cirrhosis, liver cancer and death from HCV. While challenges remain, scientists hope to eliminate HCV globally by 2030 with new pan-genotypic drugs. Prevention through injection safety, screening blood products, and educating healthcare workers is also important to control the disease.