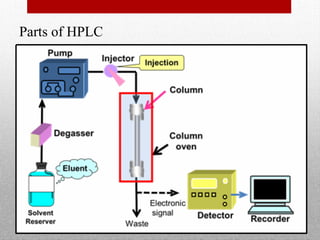
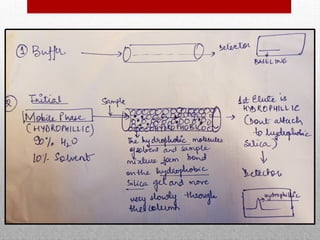
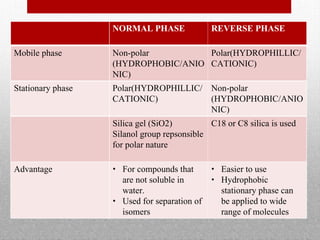
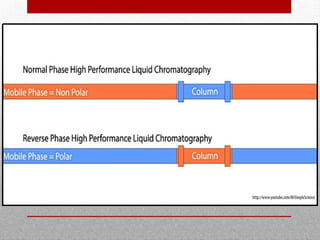
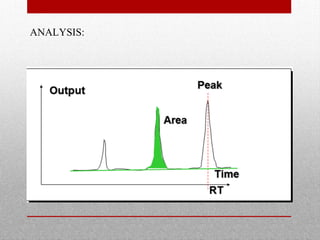
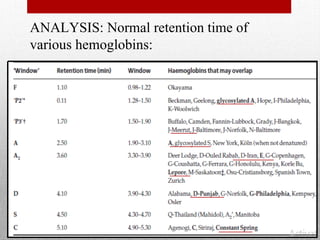
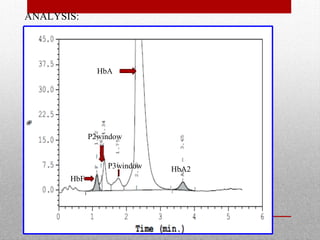
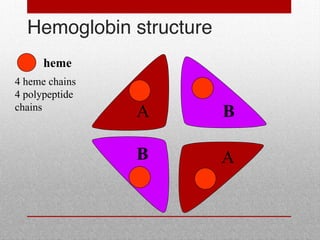
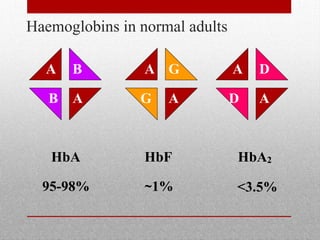
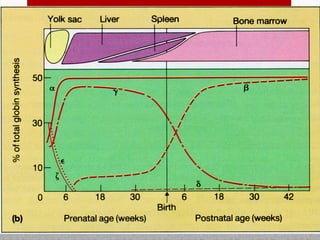
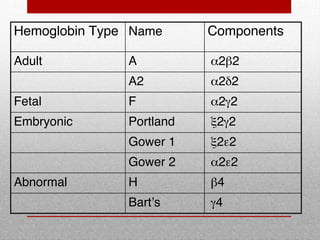
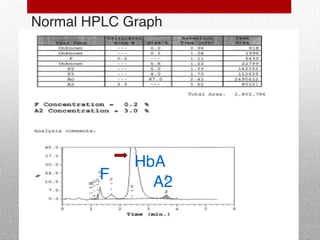
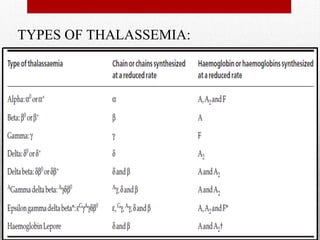
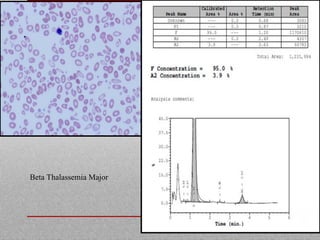
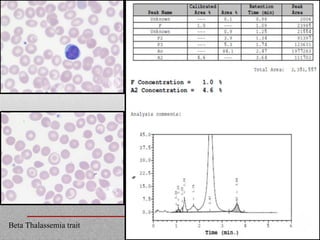
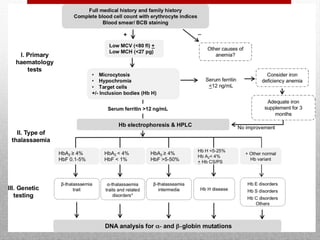
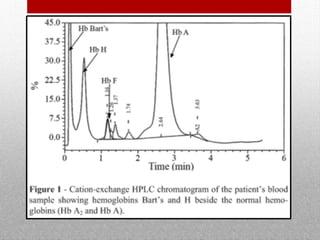
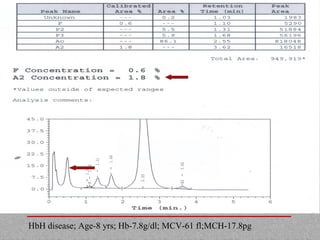
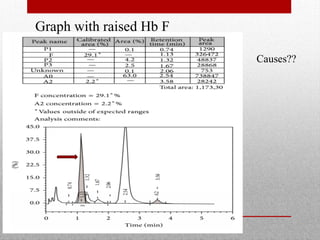
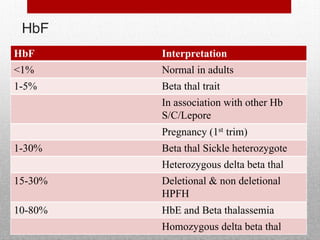
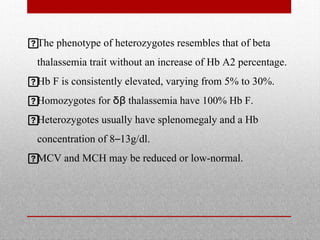
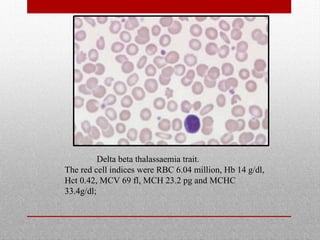
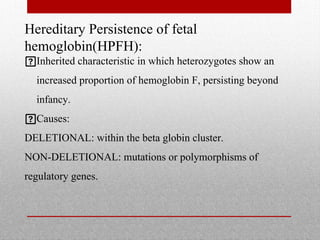
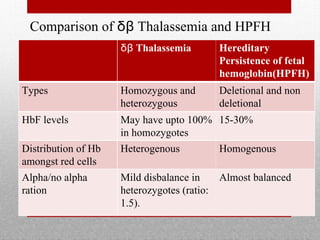
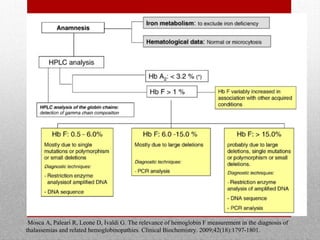
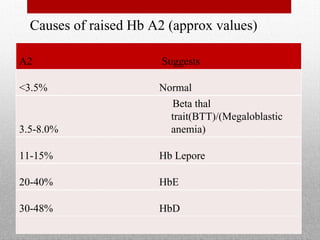
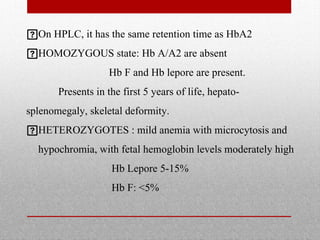
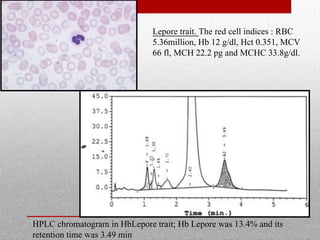
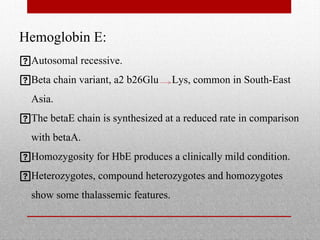
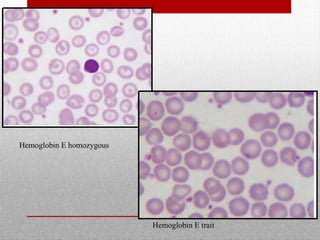
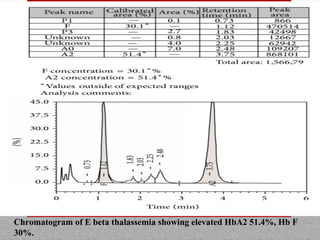
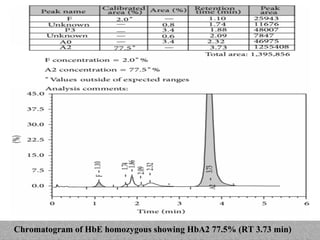
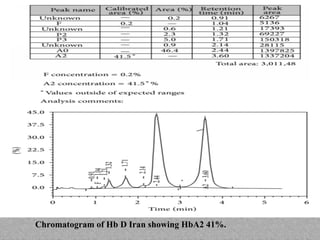
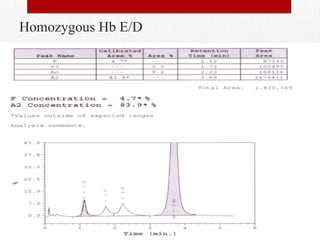
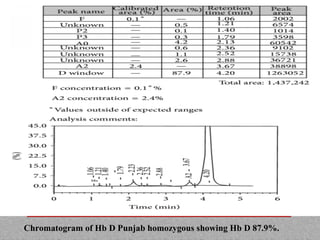
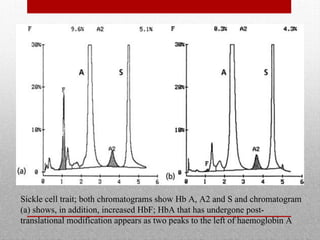
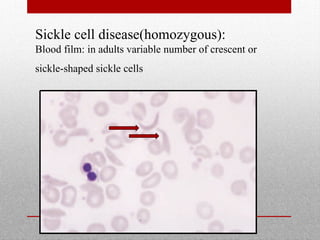
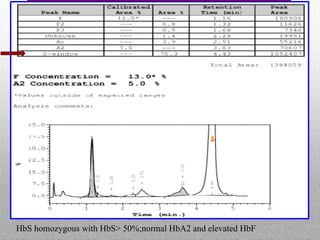
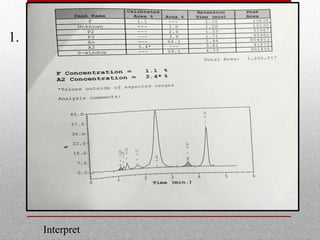
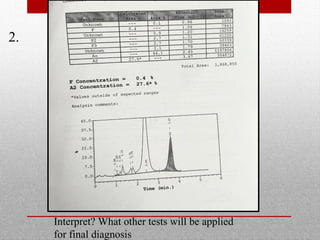
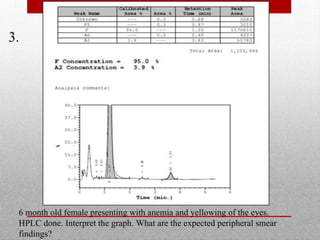
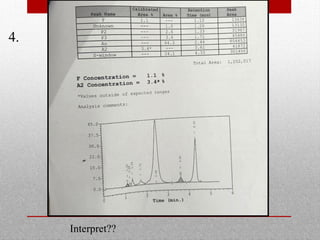
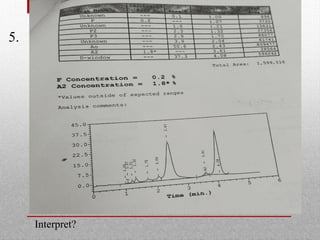
This document provides information on high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and its use in analyzing hemoglobin variants. HPLC is a type of column chromatography that uses small particle sizes and high pressures to efficiently separate molecule mixtures. It is described as being used to separate normal and variant hemoglobins by their adsorption onto a stationary phase within the chromatography column. Specific details are provided on the components and functioning of HPLC systems, along with examples of how HPLC analysis can identify normal hemoglobin levels and detect variants associated with conditions like beta thalassemia trait, delta beta thalassemia, and hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin.