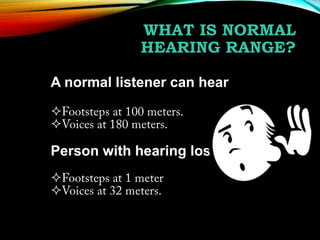
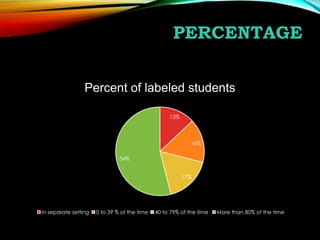
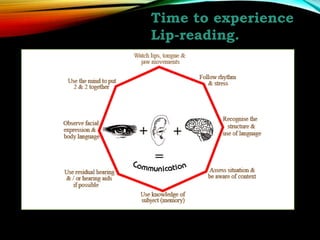
This document compares the characteristics of English language learners and students with hearing loss. It discusses that hearing loss can range from mild to severe and impact a student's ability to process language and perform academically. The document outlines the typical hearing range for normal listeners and those with hearing loss. It describes different types of hearing loss and their causes. Assistive technologies and modified classroom activities are presented to support the inclusion of students with hearing loss. Statistics regarding these students receiving services in separate versus general education settings are also provided.