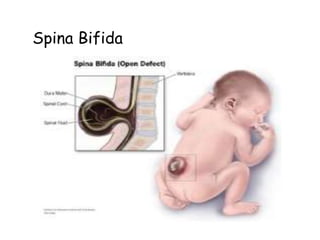
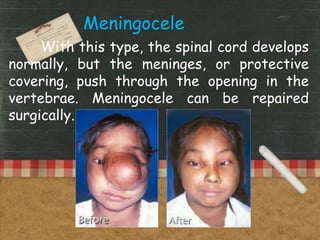
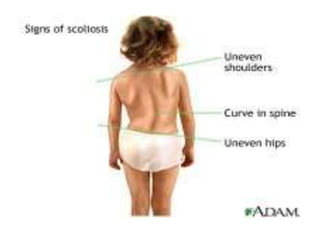
Physical disabilities that affect the body and interfere with educational performance are considered orthopedic impairments. Common causes include genetic abnormalities, diseases, injuries at birth or after. Three main types are neuromotor impairments of the nervous system, musculoskeletal disorders of bones and joints, and degenerative diseases that affect movement like muscular dystrophy. Students may have difficulties with motor skills, mobility, pain, and self-esteem that require accommodations and assistive technology to access education.