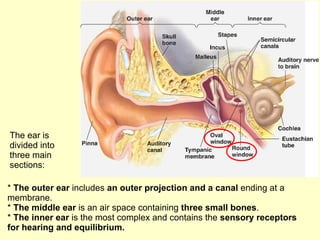
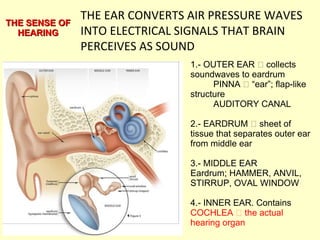
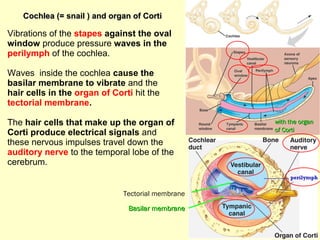
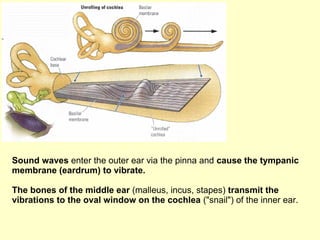
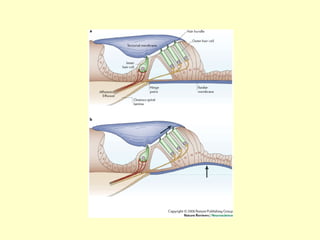
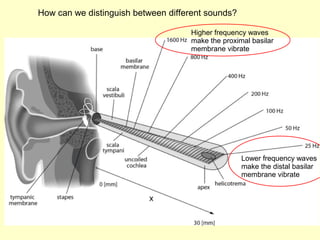
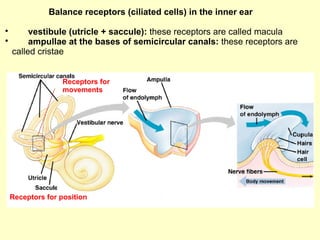
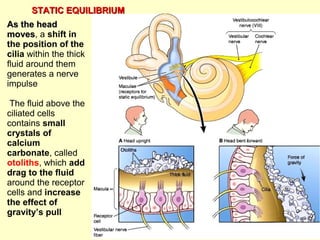
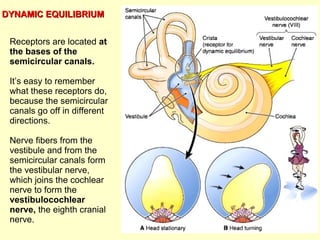
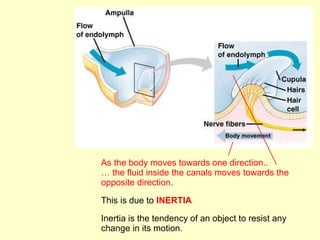
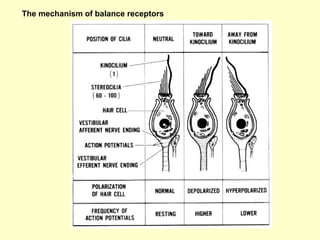
The ear is divided into three main sections - the outer, middle and inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and directs them to the eardrum. The middle ear contains three small bones that transmit vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The inner ear contains the cochlea, which converts sound waves into electrical signals perceived as sound. It also contains organs that sense body movement and position, maintaining equilibrium.