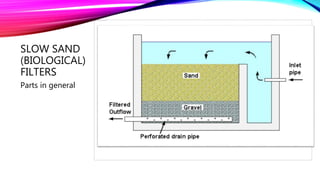
This document discusses methods for large-scale water purification. It describes storage, filtration using slow sand filters and rapid sand filters, and disinfection using chlorination. Slow sand filters rely on biological processes in the schmutzdecke layer and have lower filtration rates than rapid sand filters, which use coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation prior to mechanical filtration. Chlorination is the primary disinfection method and works by producing hypochlorous acid that kills bacteria; a free chlorine residual is important to prevent recontamination. Other disinfection options like ozonation and UV do not provide residual protection. The document reviews these purification methods and discusses related tests and regulations.