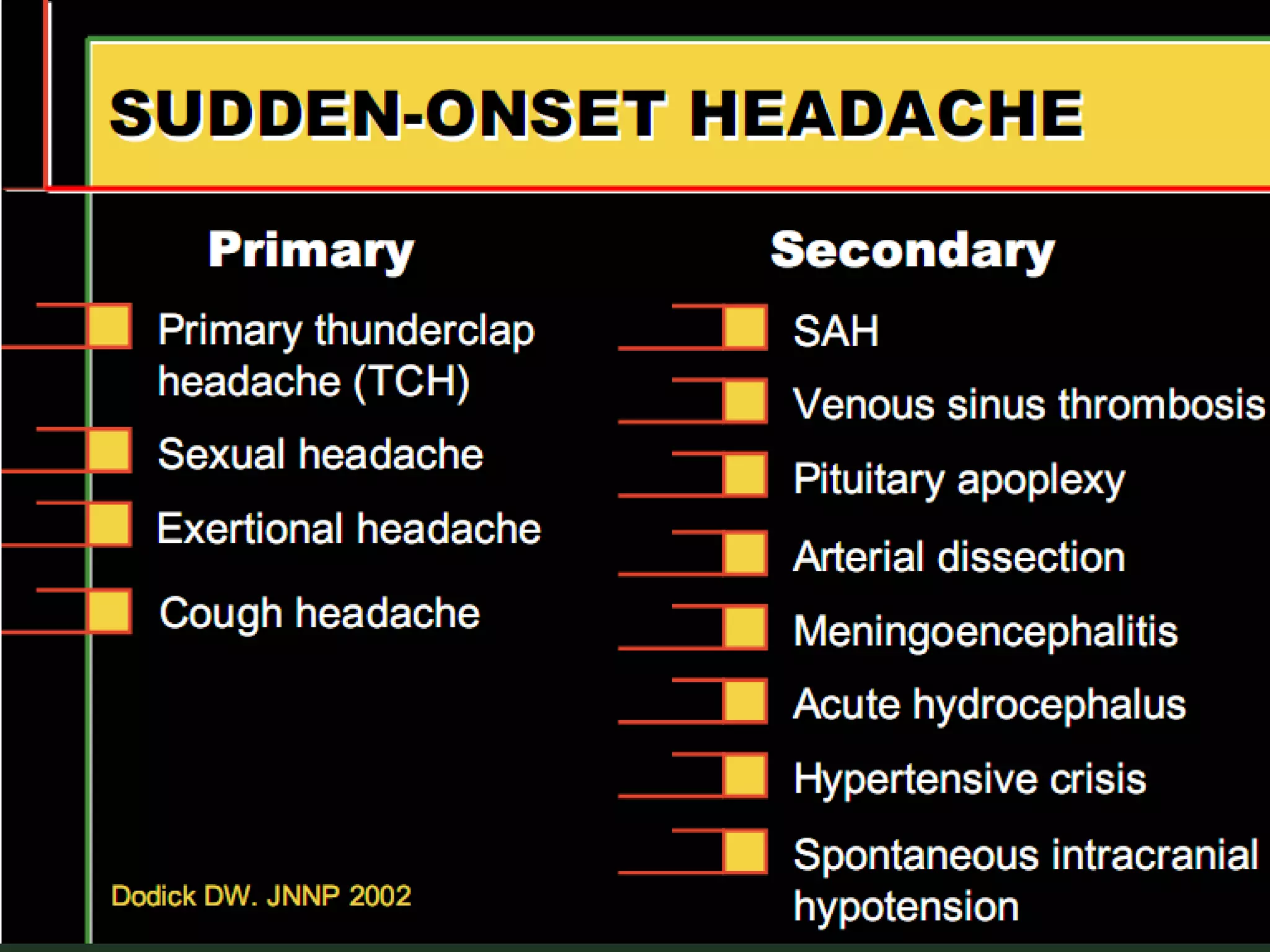
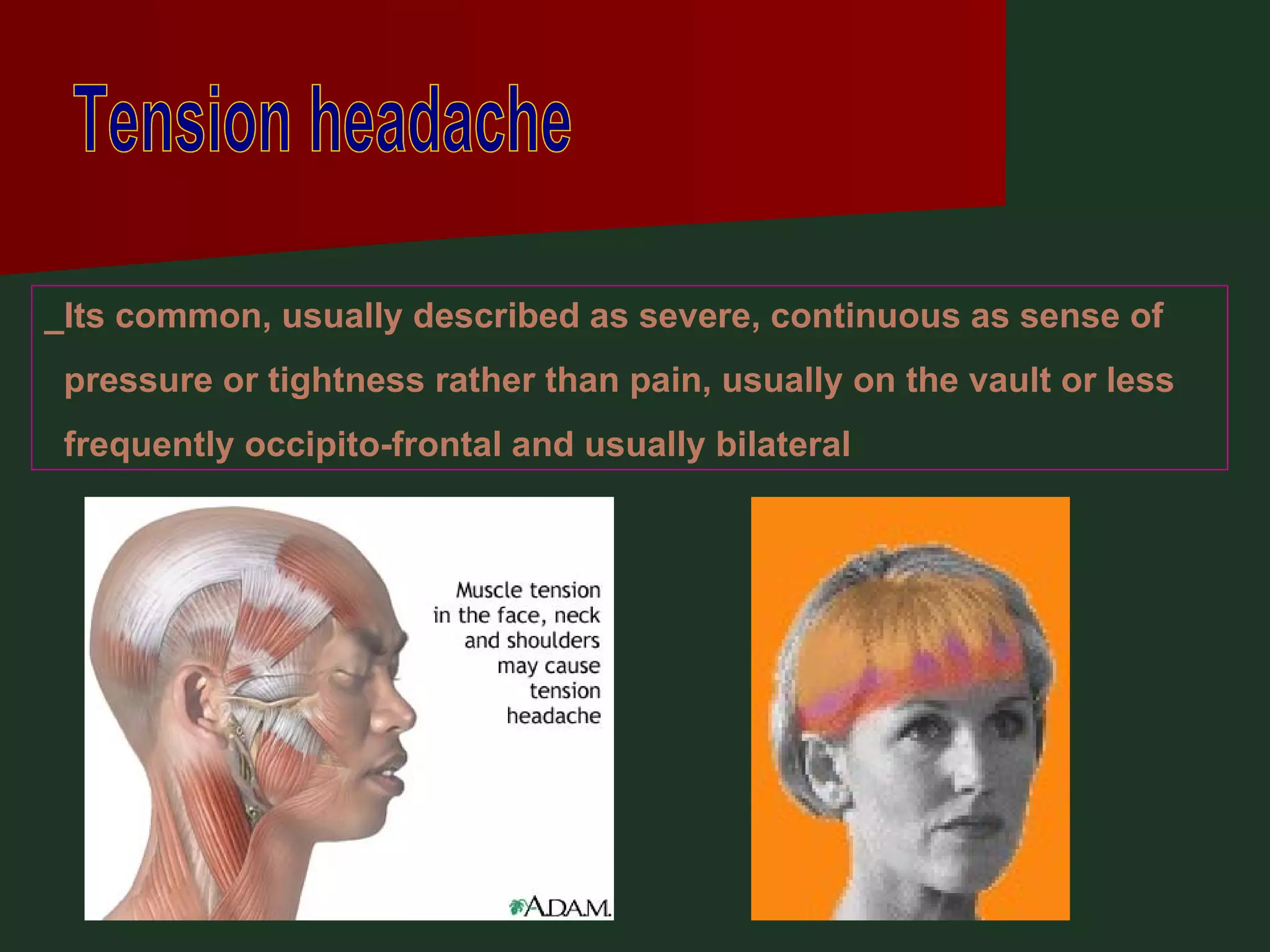
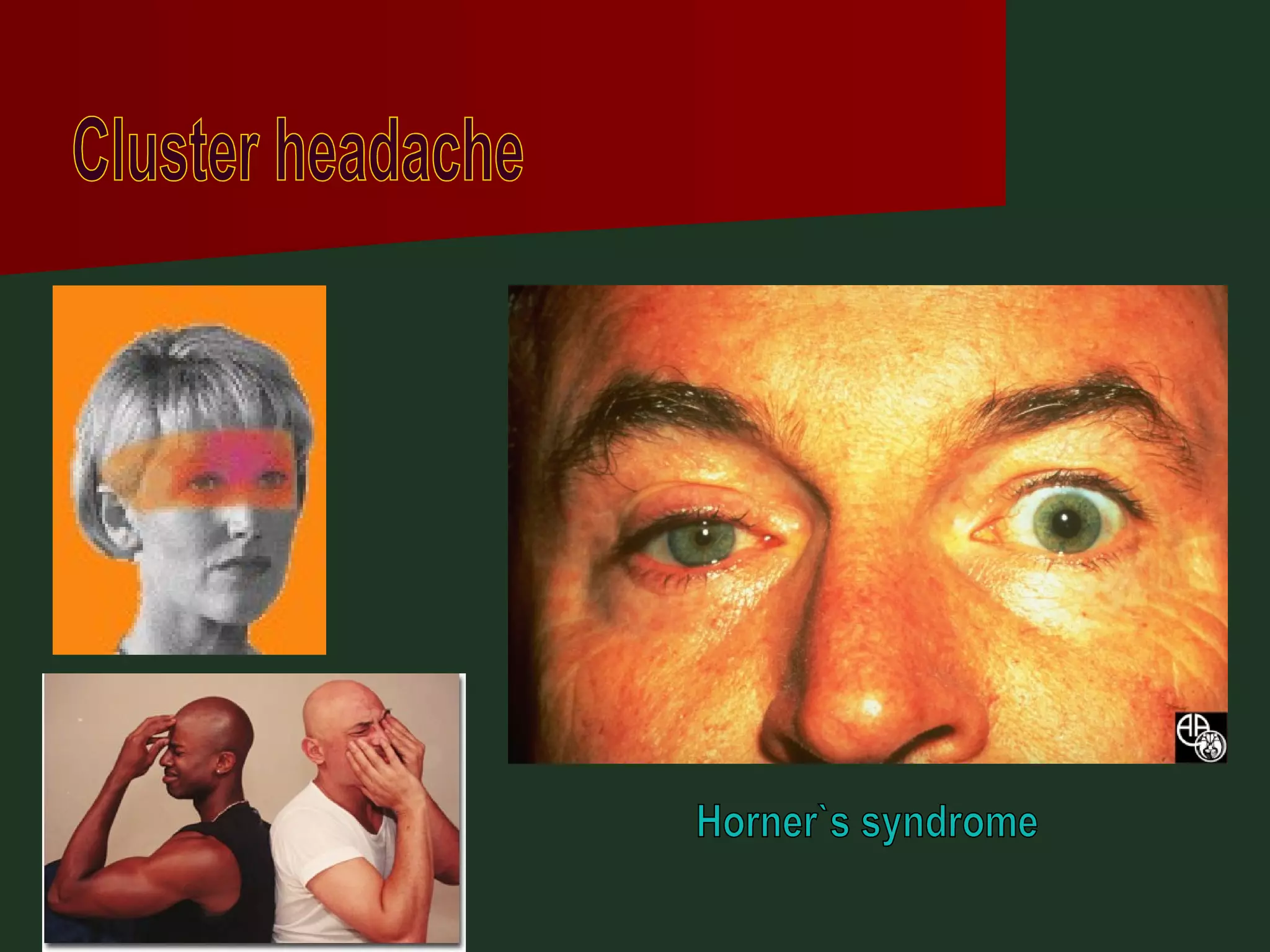
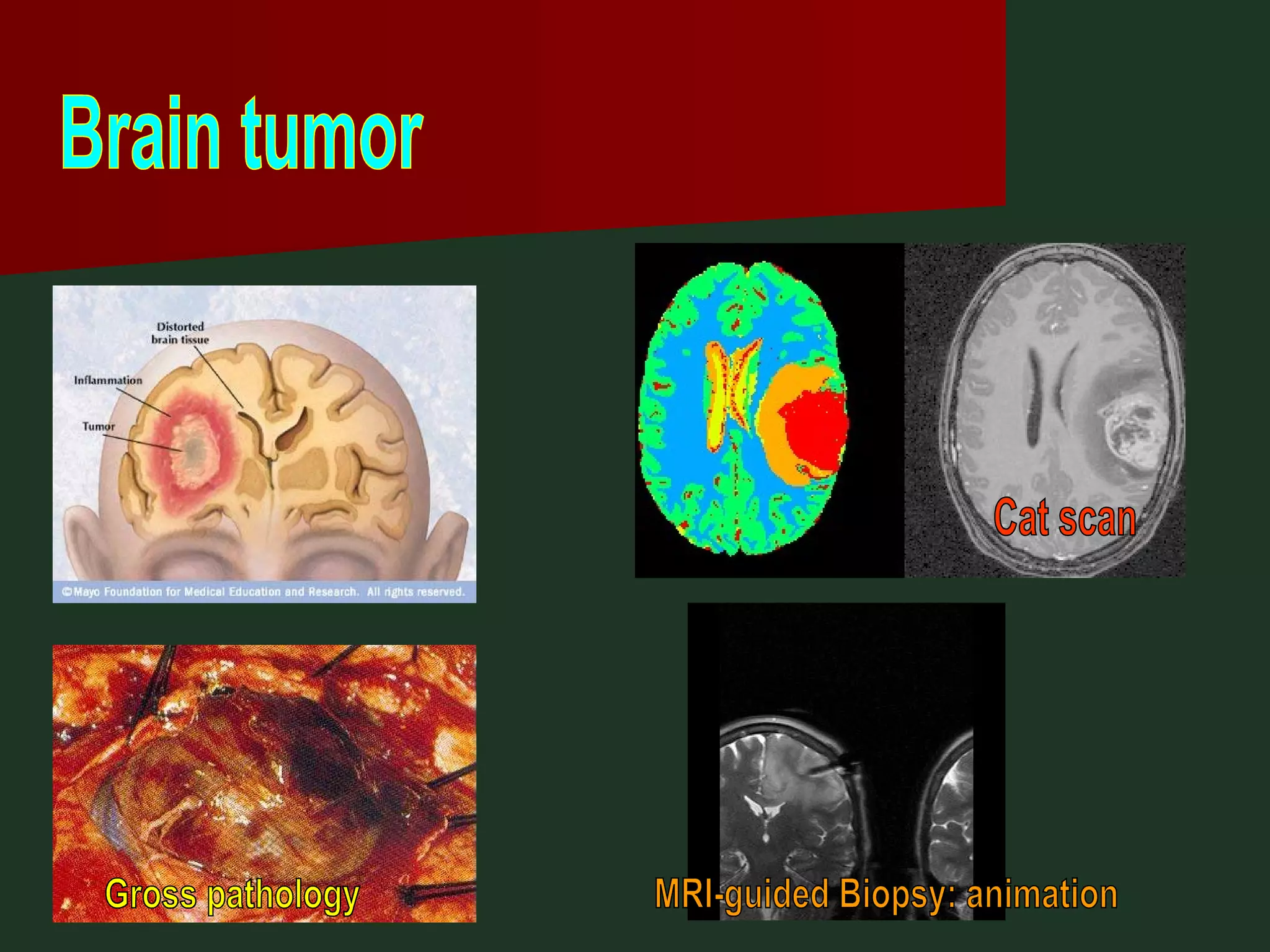
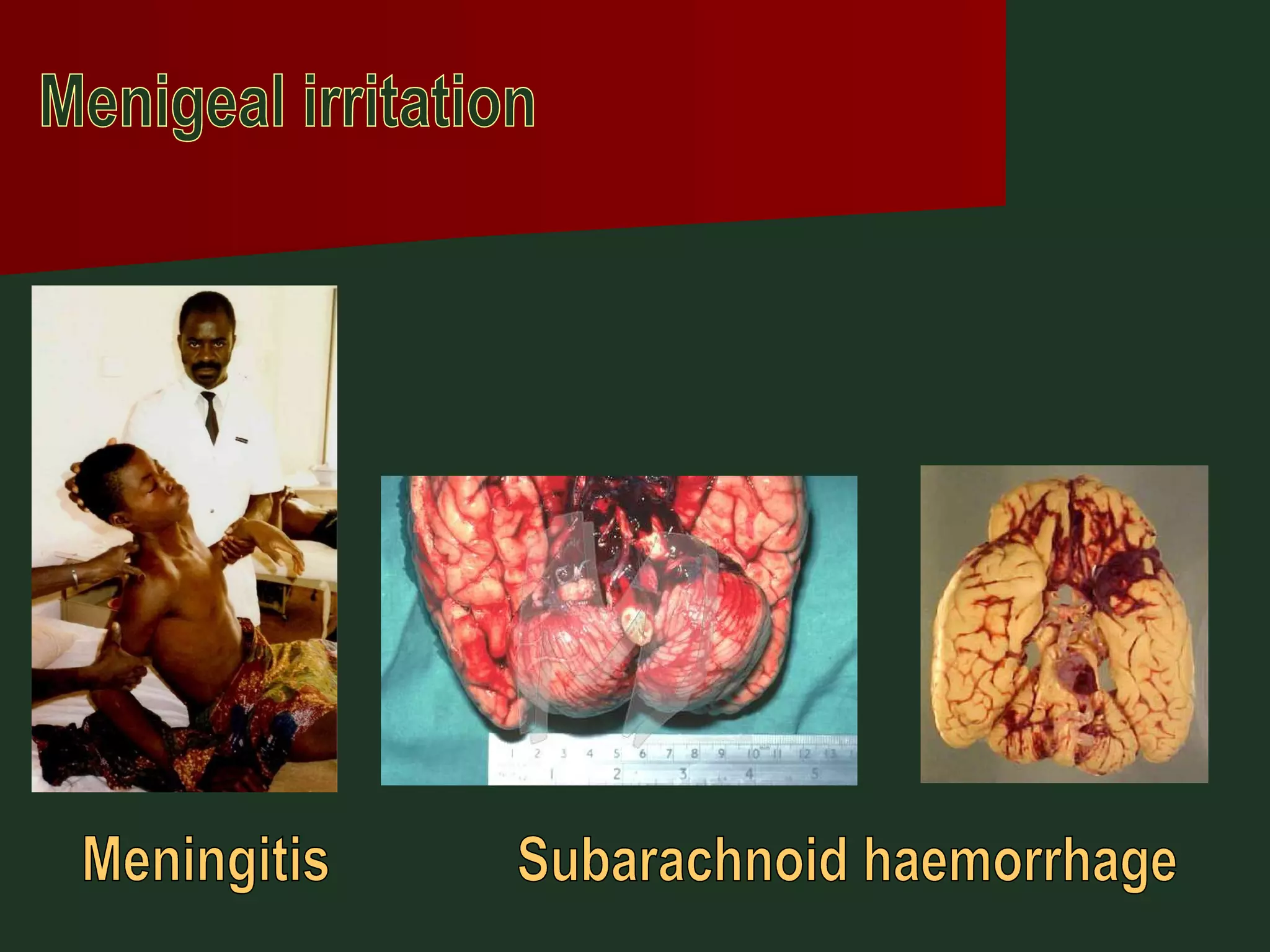
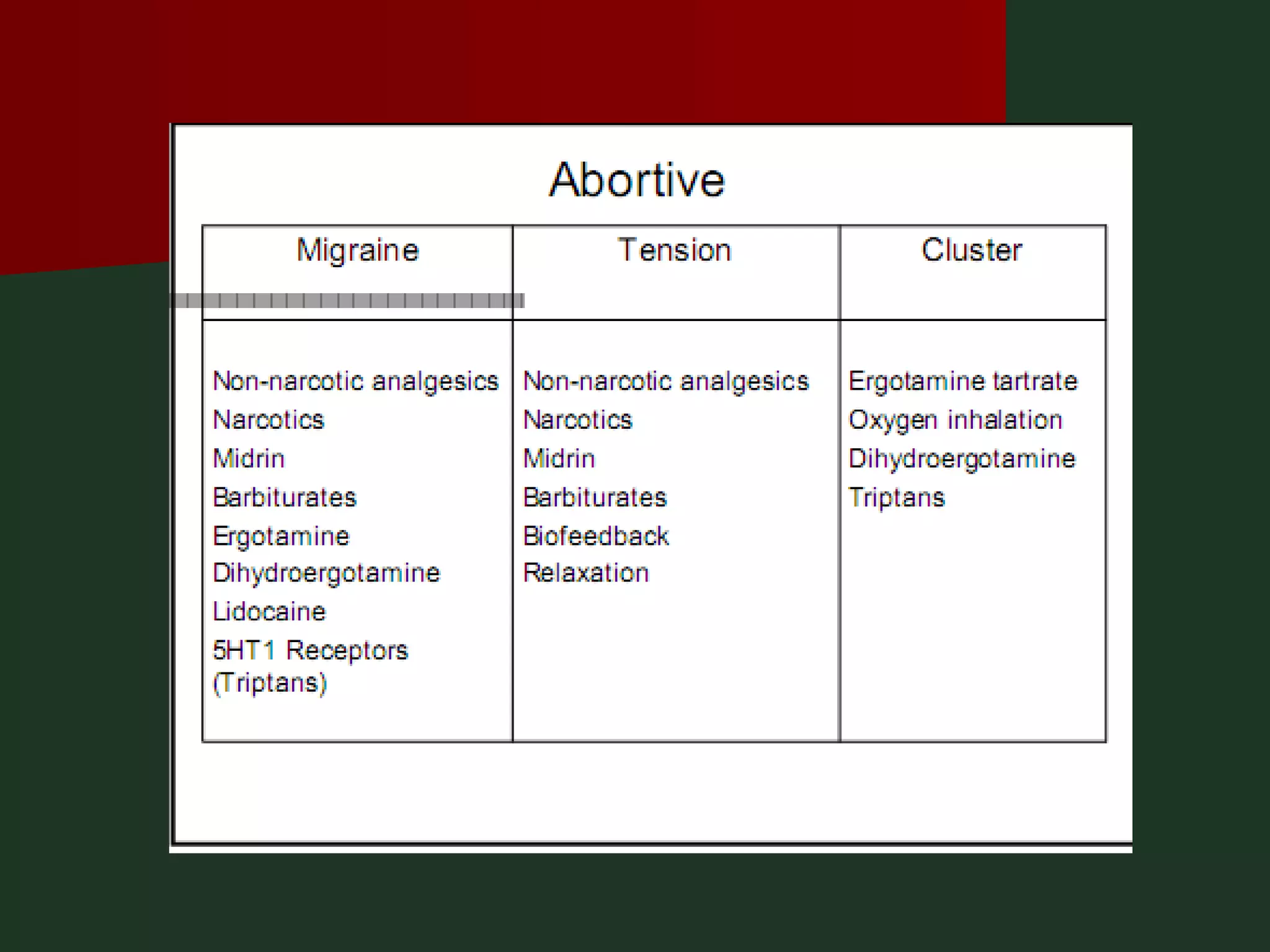
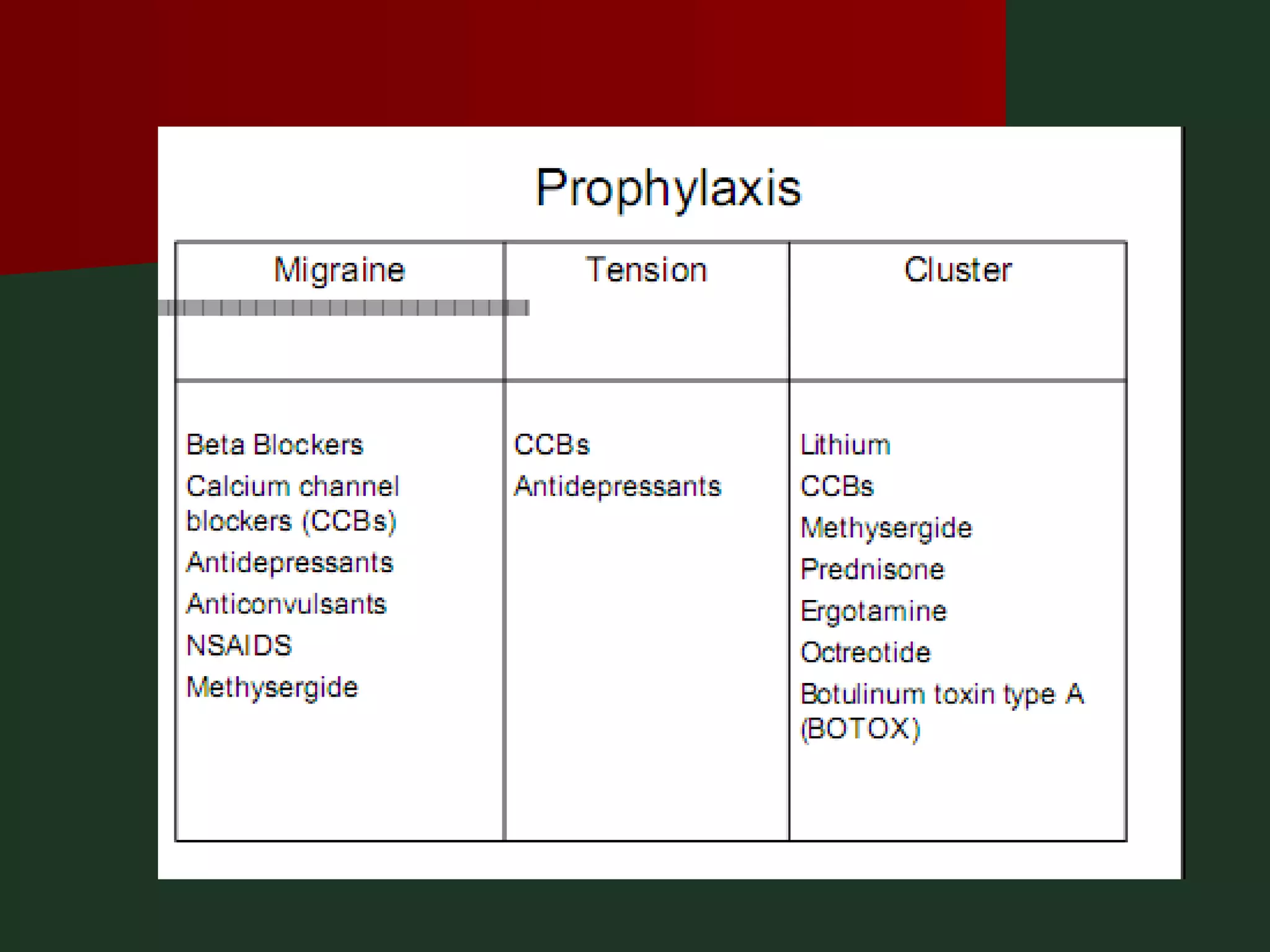
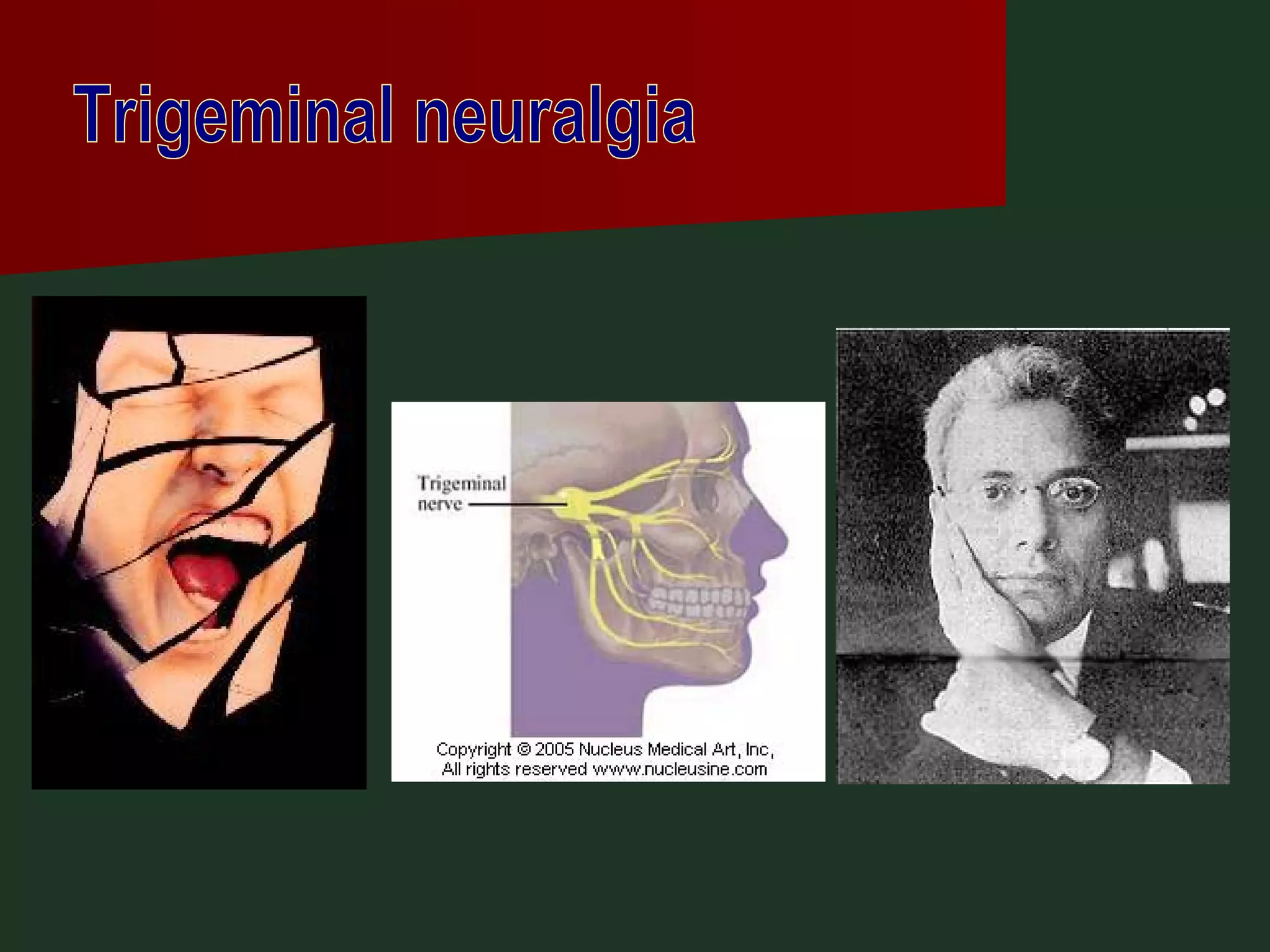
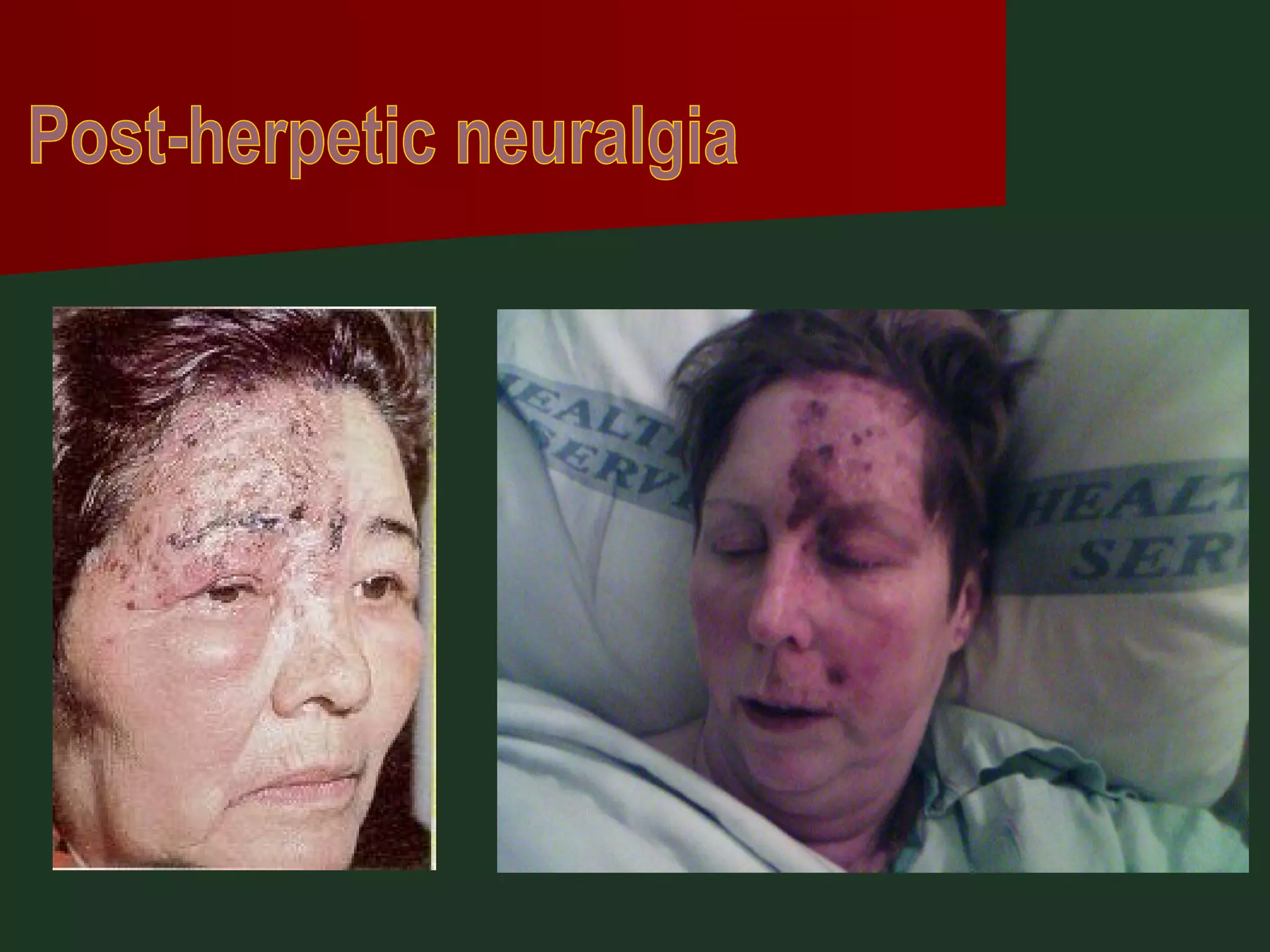
This document provides an overview of common headache types and considerations for their evaluation and diagnosis. It discusses key factors such as duration, location, and aggravating/relieving factors that can help determine the underlying cause. Primary headache types like migraine, tension, and cluster headaches are described. Red flags indicating potential serious conditions are outlined. Secondary headache etiologies like tumors, meningitis, and subarachnoid hemorrhage are also reviewed.